As a seasoned researcher with over two decades of experience in financial markets under my belt, I’ve seen firsthand the pivotal role that the VIX plays in understanding market dynamics and investor sentiment. It’s not just another fancy acronym for us; it’s a crucial tool that helps us navigate the tumultuous seas of Wall Street.
The Volatility Index (VIX), created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), is a crucial financial measurement that gauges investors’ anticipated short-term market volatility, specifically within the next 30 days, using data from S&P 500 index options. Known as the “Fear Index” or “Fear Gauge,” the VIX plays a significant role in interpreting investor sentiment and assessing market stability by reflecting their level of worry or fear.
The VIX gauges the predicted volatility of the market based on the examination of both put and call options related to the S&P 500 index. These options symbolize wagers made by investors about whether the index will increase or decrease, with their prices mirroring the perceived level of uncertainty or risk in the market. In essence, the VIX quantifies the overall expectation among traders regarding the potential short-term volatility of the S&P 500.
The index is determined using a sophisticated equation that takes into account the prices of various S&P 500 options, each with different strike prices and expiration dates. This calculation results in a figure expressed as a percentage, which indicates the predicted annualized fluctuation of the S&P 500 index over the next month. For instance, a VIX value of 20 points to an estimated annual volatility of 20%, equivalent to roughly 5.77% volatility per month.
The VIX, also known as the “Fear Index” or “Fear Gauge,” increases when there’s market instability or uncertainty. This happens when investors become worried about potential market drops due to economic volatility, geopolitical conflicts, or unforeseen financial events. In such scenarios, investors tend to purchase more options for protection or speculation, which raises option prices and, by extension, the VIX. On the flip side, when the market is steady and investor trust is high, option prices usually drop, resulting in a lower VIX value.
Here is why VIX is so important for investors and traders:
- Market Sentiment Indicator. The VIX provides a real-time snapshot of market sentiment. A rising VIX indicates increasing fear and uncertainty, suggesting that investors are anticipating greater market volatility. This information is invaluable for traders and investors as it helps them gauge the overall mood of the market and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Risk Management. Investors use the VIX to manage risk in their portfolios. For instance, during periods of high VIX, indicating high volatility, investors might reduce their exposure to equities or increase their use of hedging strategies such as buying put options or investing in volatility-related products. Conversely, a low VIX might encourage investors to take on more risk, as it suggests a stable market environment.
- Hedging and Speculation. The VIX is also a popular tool for hedging and speculation. Financial instruments such as VIX futures and options allow investors to hedge against potential market downturns or to speculate on future volatility. By taking positions in these instruments, investors can profit from increases in market volatility or protect their portfolios from significant losses during turbulent times.
- Economic Indicator. Beyond the financial markets, the VIX serves as an economic indicator. High VIX values can signal broader economic concerns, such as looming recessions or financial crises. Policymakers and economists monitor the VIX to understand the underlying health of the financial system and to make informed decisions about monetary and fiscal policies.
Investors closely monitor the VIX to predict future market trends. A sharp increase in the VIX could signal an upcoming market correction, causing investors to prepare for defensive strategies. Conversely, a decreasing VIX might imply that the market is stabilizing, leading investors to consider higher-risk investment opportunities.
Additionally, the Volatility Index (VIX) is frequently combined with other technical and fundamental analysis tools to create well-rounded trading plans. For instance, traders might search for discrepancies between the VIX and the S&P 500 index. When the S&P 500 rises while the VIX simultaneously increases, it could indicate that the market’s upward trend is not sustainable, suggesting a possible reversal may be imminent.
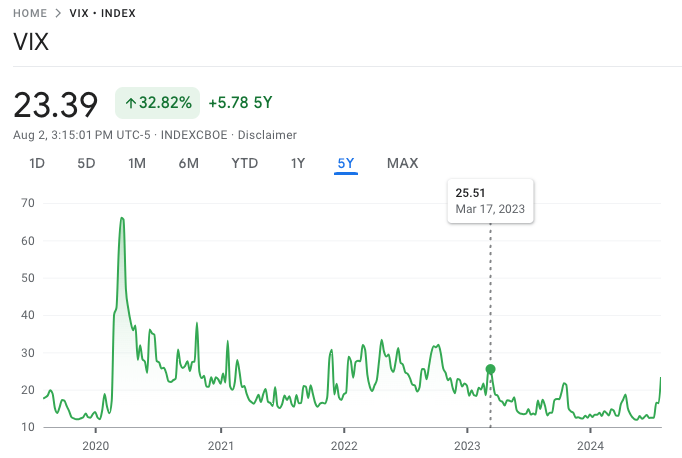
As someone who has witnessed several market fluctuations throughout my investment journey, I find myself growing increasingly concerned about the recent surge in the VIX index this week. After a prolonged period of relative calm, the sudden spike in volatility is reminiscent of past market selloffs that have often preceded economic downturns. The VIX jumped significantly on Friday following Thursday’s gains, fueled by a dismal labor market report that hinted at potential signs of an impending recession in the U.S. economy. In fact, it skyrocketed over 25%, reaching its highest level since March 2023 – a stark reminder of the unpredictable nature of financial markets and the importance of staying vigilant during such turbulent times. I’m keeping a close eye on developments and will be adjusting my investment strategy accordingly, as I believe it is essential to adapt to market conditions in order to protect and grow my hard-earned savings.
Read More
- Apothecary Diaries Ch.81: Maomao vs Shenmei!
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Batman and Deadpool Unite: Epic DC/Marvel Crossover One-Shots Coming Soon!
- Who was Peter Kwong? Learn as Big Trouble in Little China and The Golden Child Actor Dies at 73
- Mobile MOBA Games Ranked 2025 – Options After the MLBB Ban
- Hunter Schafer Rumored to Play Princess Zelda in Live-Action Zelda Movie
- 30 Best Couple/Wife Swap Movies You Need to See
- Netflix’s ‘You’ Season 5 Release Update Has Fans Worried
- Gachiakuta Chapter 139: Rudo And Enjin Team Up Against Mymo—Recap, Release Date, Where To Read And More
- Summer Game Fest 2025 schedule and streams: all event start times
2024-08-03 19:53