Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research demonstrates how reinforcement learning can optimize trade execution, minimizing market impact and maximizing returns.
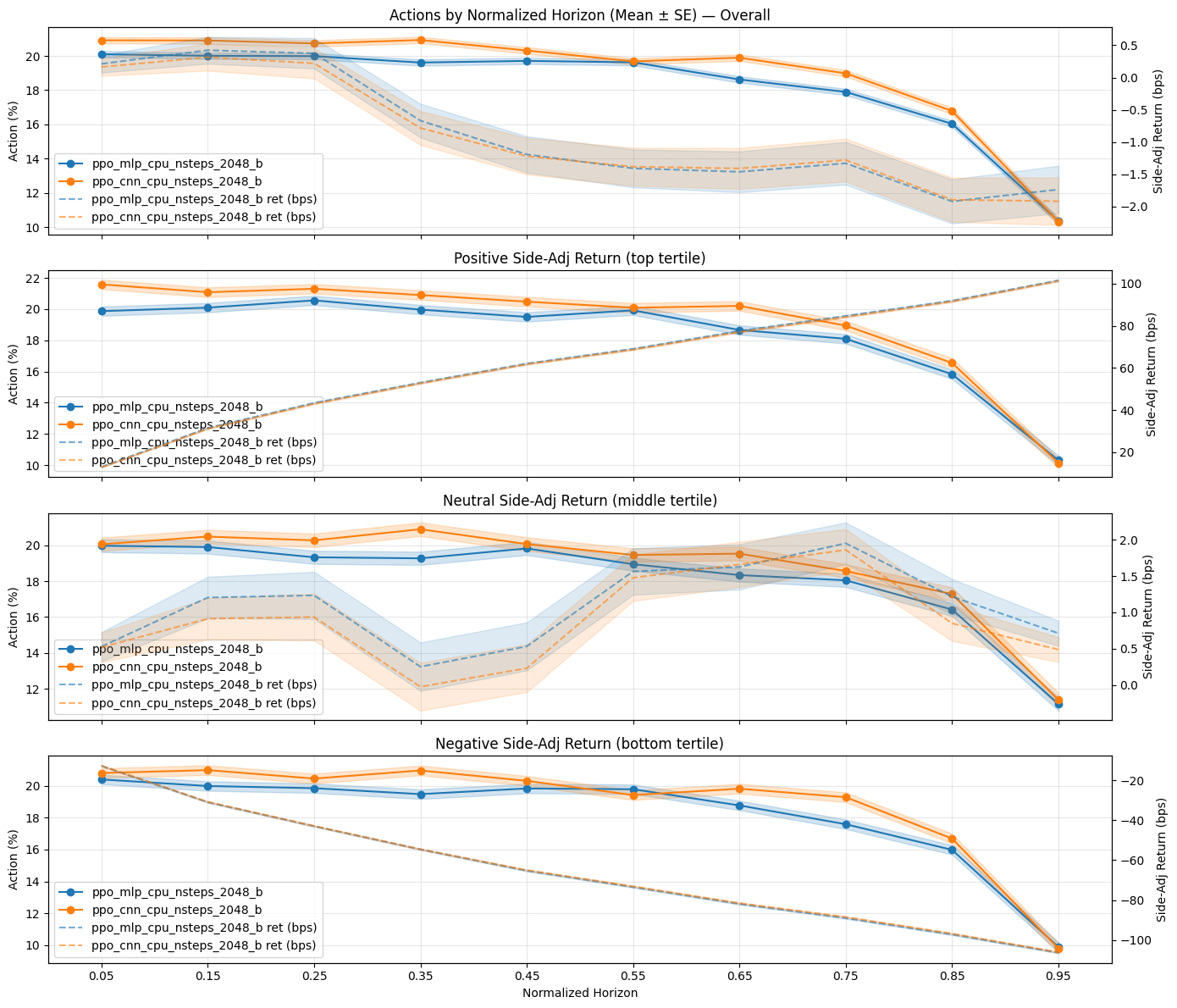
A comparative review of reinforcement learning and quality-diversity approaches to optimal execution schedule generation, leveraging propagator models and the Gymnasium environment.
Achieving consistently optimal trade execution remains challenging amidst dynamic market conditions and the complexities of transient market impact. This is addressed in ‘Diverse Approaches to Optimal Execution Schedule Generation’, which investigates the application of quality-diversity algorithms-and high-performing reinforcement learning agents-to learn regime-specialist execution strategies. Results demonstrate that a CNN-based Proximal Policy Optimization agent substantially reduces arrival slippage-achieving 2.13 bps versus 5.23 bps for VWAP-while quality-diversity methods offer a promising, though computationally intensive, path toward adaptive execution. Will these combined approaches ultimately unlock more robust and nuanced strategies for navigating the inherent uncertainties of financial markets?
The Illusion of Optimal Execution
The pursuit of Optimal Execution – minimizing the costs associated with trading financial instruments – represents a persistent challenge within modern markets. While seemingly straightforward, achieving this goal is complicated by the inherent dynamics of supply and demand, regulatory constraints, and the fragmented nature of trading venues. Transaction costs extend beyond simple brokerage fees to encompass market impact – the price distortion caused by the trade itself – as well as opportunity costs stemming from the time taken to complete the order. Consequently, traders constantly seek strategies to navigate these complexities, balancing speed, price, and the overall cost of executing large orders. This necessitates sophisticated algorithms and a deep understanding of market microstructure, as even fractional improvements in execution quality can translate into substantial gains over time, particularly for institutional investors managing large portfolios.
Established order execution strategies, such as Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) and Time Weighted Average Price (TWAP), frequently underperform in rapidly evolving markets because they rely on static instructions. These techniques assume consistent participation rates and predictable liquidity throughout the trading period, a condition rarely met in practice. When faced with sudden shifts in order flow, increased volatility, or unexpected news events, VWAP and TWAP fail to dynamically adjust, leading to suboptimal pricing and increased transaction costs. Consequently, traders are increasingly seeking more sophisticated algorithms capable of real-time adaptation to market microstructure and order book dynamics, recognizing that a rigid approach to execution can significantly diminish profitability in modern financial landscapes.
Accurately predicting transient market impact – the immediate, often fleeting, change in asset price caused by a trade itself – presents a significant hurdle in optimal order execution. Unlike predictable, long-term trends, this impact is a function of numerous variables, including order size relative to prevailing liquidity, the speed of execution, and the hidden intentions of other market participants. Models attempting to capture this phenomenon must account for the order book’s dynamics, recognizing that a large order can temporarily deplete available liquidity, driving up prices as it’s filled. Sophisticated approaches now utilize machine learning techniques to infer these hidden effects and forecast how a trade will influence the price before it occurs, moving beyond simple linear models to better represent the non-linear relationship between trade size and price movement. The inherent complexity, however, means that even the most advanced models are often approximations, introducing uncertainty into execution strategies and demanding continuous refinement.
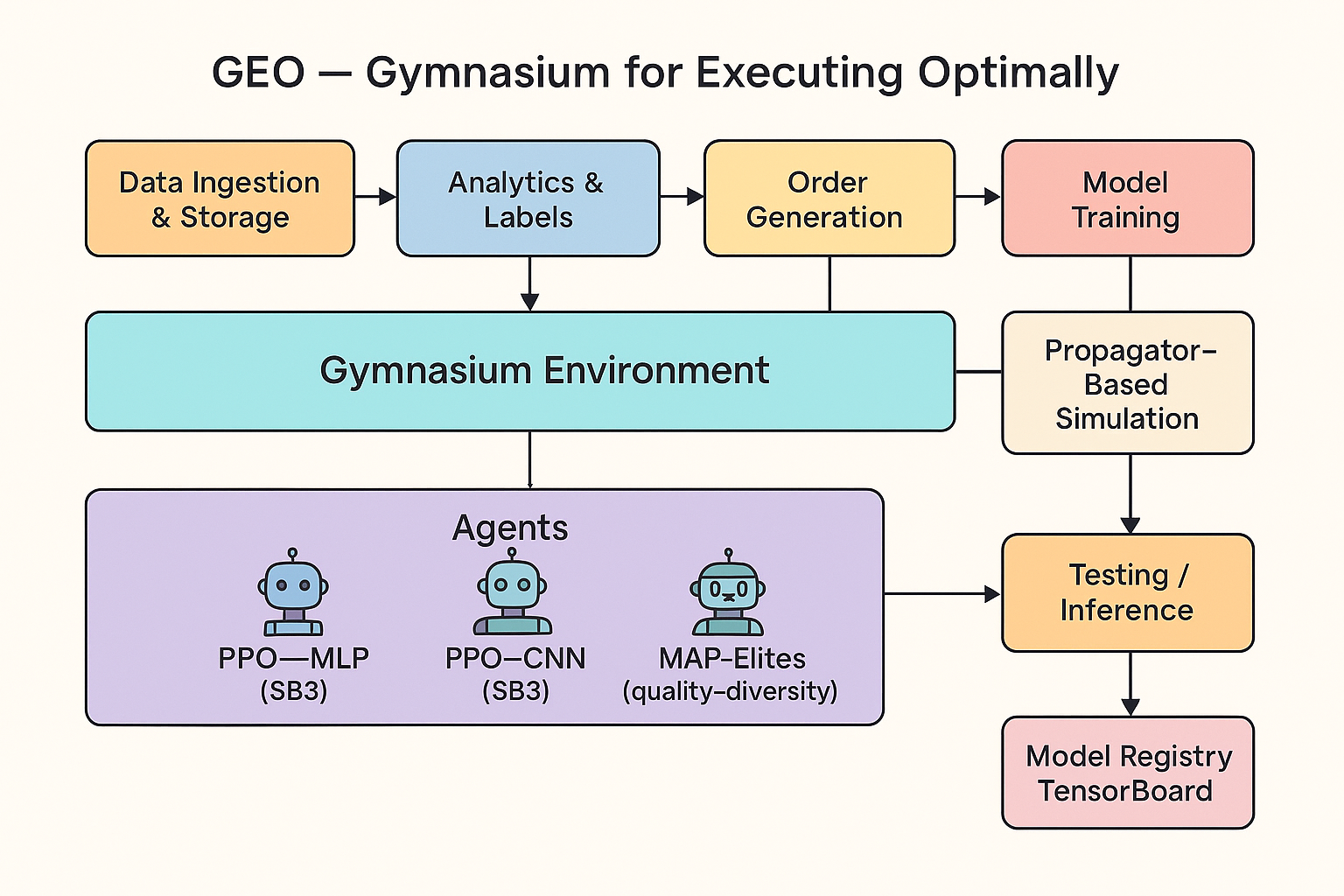
Forging Adaptability: Reinforcement Learning for Execution
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is employed to develop an automated agent capable of optimizing order execution strategies. This agent learns through trial and error within a simulated market environment, receiving rewards for profitable trades and penalties for unfavorable outcomes. The RL framework allows the agent to adapt its actions – such as order size, timing, and placement – based on observed market conditions, with the objective of minimizing transaction costs and maximizing realized prices. This approach contrasts with traditional rule-based systems by enabling the agent to discover optimal strategies without explicit programming for every possible market scenario, facilitating a data-driven approach to algorithmic trading.
The order execution agent utilizes a deep convolutional neural network (PPO-CNN) as its policy network. This architecture enables the agent to process high-dimensional input data representing order flow – including volume, price, and time – and extract relevant features for predicting market impact. Convolutional layers are employed to identify patterns in the order book and time series data, while the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm refines the network’s parameters to maximize cumulative reward. The PPO-CNN effectively models the non-linear relationship between order placement and resulting price movements, allowing for adaptive execution strategies that minimize transaction costs and maximize fill rates.
The simulation environment is constructed utilizing the Gymnasium framework, a widely adopted toolkit for developing and comparing reinforcement learning algorithms. This choice facilitates robust experimentation by providing a standardized interface and a suite of tools for creating diverse market scenarios, including varying order types, liquidity conditions, and volatility levels. Furthermore, Gymnasium’s design emphasizes reproducibility; experiments are easily versioned and rerun with defined seeds, ensuring consistent results and enabling reliable validation of the trained agent’s performance across different market simulations. The framework also supports parallelization, accelerating the training process and allowing for efficient exploration of the parameter space.
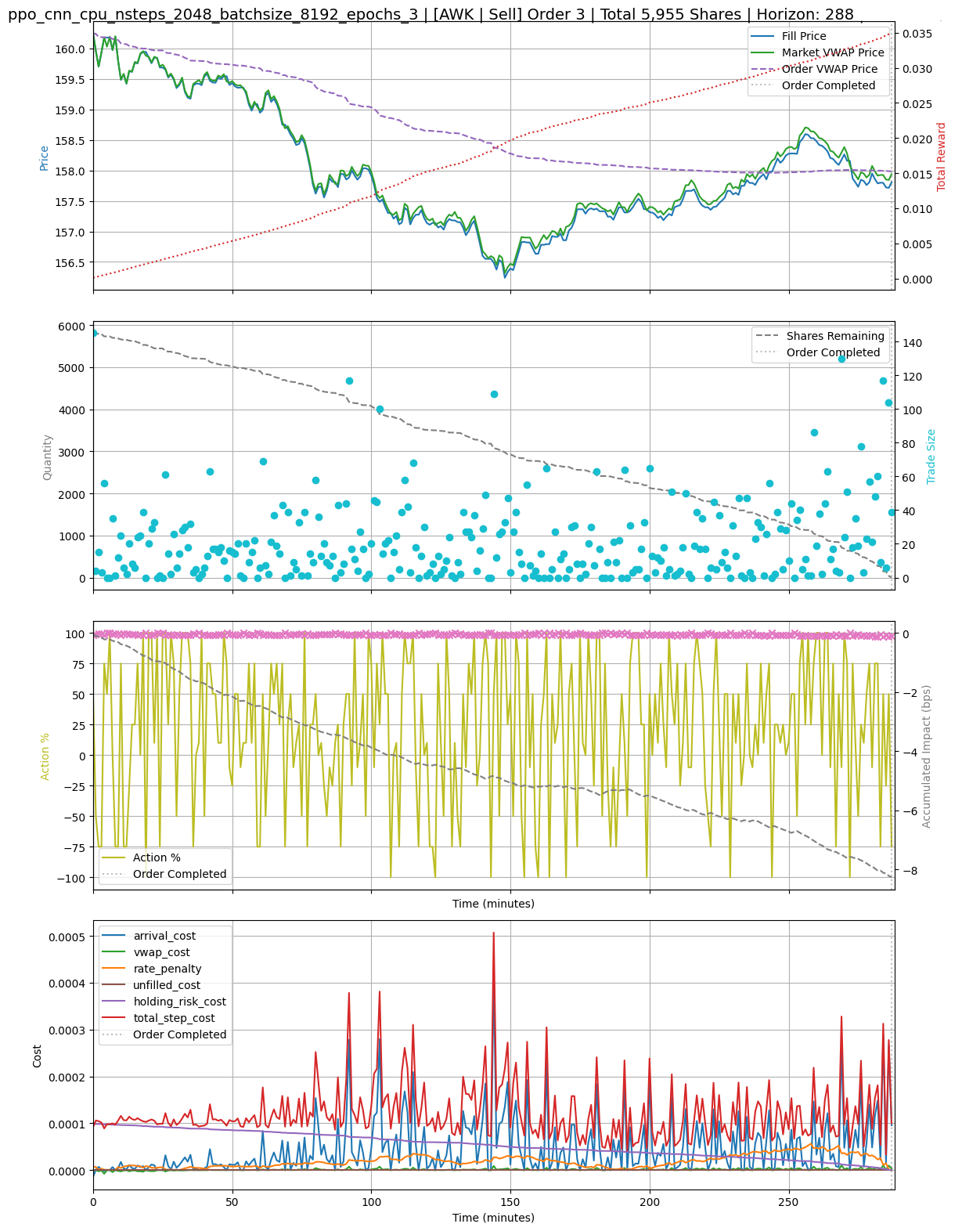
Sculpting a Portfolio of Strategies with Quality and Diversity
The execution strategy generation process utilizes MAP-Elites, a Quality-Diversity (QD) algorithm, to cultivate a population of diverse policies. Unlike traditional optimization methods that seek a single optimal solution, MAP-Elites aims to maintain a broad range of high-performing policies, each adapted to distinct market conditions. This is achieved by mapping policies onto a feature space defined by characterizing market regimes, and subsequently maintaining a collection of policies that maximize both performance and diversity within that space. The algorithm encourages specialization by rewarding policies that excel in underrepresented areas of the feature space, effectively creating a portfolio of strategies designed to perform well across a variety of market dynamics.
Implementation Shortfall serves as the primary metric for evaluating the performance of each execution policy generated by the algorithm. It quantifies the total cost incurred when executing an order, encompassing both explicit costs – such as brokerage fees – and implicit costs arising from the price impact of the trade itself. Specifically, Implementation Shortfall is calculated as the difference between the price realized after execution and the optimal benchmark price available at the time the order was initiated, expressed as a percentage of the notional trade value. Minimizing Implementation Shortfall is crucial for maximizing trading performance, and therefore directly informs the selection and refinement of execution strategies within the Quality-Diversity framework.
The algorithm categorizes market conditions using two primary features: volatility and liquidity. Volatility, measured as the standard deviation of asset returns, indicates the degree of price fluctuation. Liquidity is quantified by the ratio of traded volume to the total order book size, representing the ease with which assets can be bought or sold without significantly impacting price. By defining market regimes based on these two parameters, the system facilitates the discovery of specialized execution strategies optimized for specific conditions – for example, strategies suited for high volatility and moderate liquidity versus those performing optimally in low-volatility, high-liquidity environments. This approach aims to improve overall portfolio performance by adapting to changing market dynamics rather than relying on a single, universally-applied execution policy.
The relationship between order flow and resulting transient market impact was modeled and calibrated, yielding an R-squared value ranging from 0.02 to 0.10. This indicates a limited, but statistically present, explanatory power of the model in predicting market impact based solely on observed order flow. While the low R-squared value suggests other factors significantly contribute to transient market impact, the calibrated model provides a baseline for assessing the cost of execution and is utilized within the broader Quality-Diversity framework to evaluate and differentiate execution policies.
Utilizing the MAP-Elites quality-diversity algorithm, a specialized execution policy was identified that demonstrated a 10.3% performance improvement specifically within market conditions characterized by high volatility and medium liquidity. This improvement was quantified using Implementation Shortfall as the primary performance metric, indicating a reduction in the cost of executing orders under these specific market dynamics. The algorithm’s ability to discover this specialist policy highlights its effectiveness in adapting to and optimizing for distinct market regimes, offering a potential advantage in dynamic trading environments.
A Glimpse into the Future: Intelligent Execution and Beyond
The Propagator Model offers a robust mechanism for representing how trades themselves influence market prices, a crucial element when training artificial intelligence for automated execution. Unlike traditional models that treat prices as exogenous, this approach integrates the anticipated price movements caused by an agent’s own orders directly into the reinforcement learning environment. By predicting how a trade will propagate through the order book, the agent learns to strategically place orders to minimize adverse price impact and maximize execution quality. This internal representation of market dynamics allows the AI to move beyond simply reacting to existing prices and instead proactively shape them, leading to more sophisticated and effective trading strategies. The model’s ability to forecast price responses, even under varying market conditions, establishes a strong foundation for building adaptable and resilient algorithmic trading systems.
A key benefit of employing reinforcement learning in trade execution lies in its capacity to cultivate a repertoire of strategies, rather than relying on a single, static approach. This diversity proves particularly valuable when navigating turbulent market conditions, as different strategies will naturally perform better under varying circumstances. The system can dynamically allocate capital to the most promising strategy at any given moment, effectively hedging against unforeseen volatility and minimizing the potential for adverse selection. This adaptive capability fosters resilience, as the portfolio isn’t overly exposed to the weaknesses of any single tactic, and ultimately contributes to a more stable and predictable reduction in execution costs, even amidst significant market stress.
Rigorous testing reveals the PPO-CNN model significantly minimizes arrival slippage, a critical metric for evaluating execution performance. Specifically, the model achieved a 59% reduction in arrival slippage – registering 2.13 basis points (bps) – when contrasted with a widely used Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) strategy, which yielded 5.23 bps. This substantial improvement indicates the model’s capacity to intelligently navigate order book dynamics and execute trades at more favorable prices, directly translating to cost savings and enhanced profitability. The observed performance suggests that the PPO-CNN model effectively learns optimal trading behaviors, surpassing the performance of traditional, static strategies in minimizing the immediate impact of trades on market prices.
A significant outcome of this research demonstrates a substantial reduction in total execution costs. Utilizing the proposed reinforcement learning framework, the model achieved a total cost of 178 basis points, representing nearly half the expense incurred by a traditional Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) strategy, which registered 303 basis points. This improvement highlights the potential for intelligent algorithms to optimize trade execution, minimizing market impact and maximizing efficiency for investors. The observed cost reduction suggests a pathway towards more economical trading practices and increased profitability in financial markets.
Continued development centers on integrating live, streaming market data and granular transaction costs directly into the model’s learning process. This refinement aims to move beyond backtesting with historical data and create a system capable of dynamically adapting to current market conditions. Incorporating real-time information, such as order book dynamics and varying exchange fees, will allow for more precise predictions of market impact and optimization of execution strategies. Such enhancements are expected to yield further reductions in slippage and overall transaction costs, ultimately improving the robustness and practical applicability of the reinforcement learning framework for automated trading.
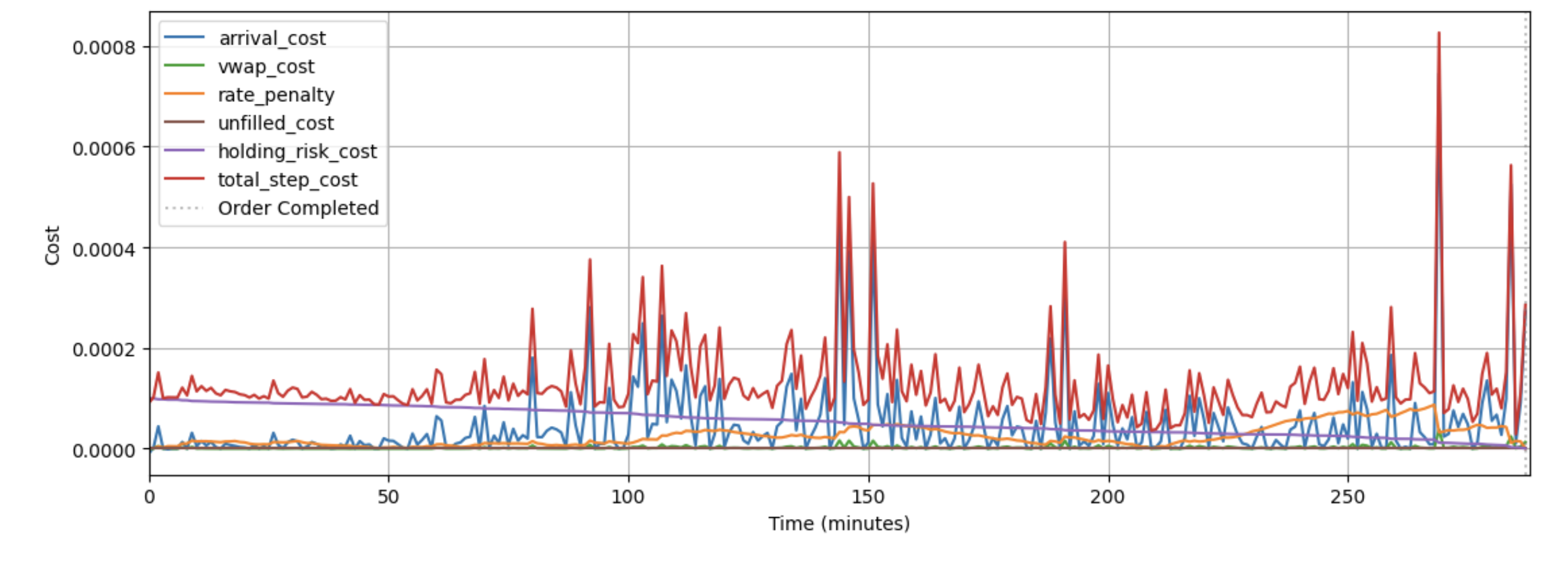
The pursuit of optimal execution, as detailed in the study, isn’t about finding a single, perfect solution, but rather about navigating a landscape of probabilities. It’s a dance with transient impact, a subtle coaxing of the market rather than brute force control. This echoes Søren Kierkegaard’s sentiment: “Life can only be understood backwards; but it must be lived forwards.” The reinforcement learning agent doesn’t predict the market; it reacts to it, learning from each interaction-a continuous, forward-moving process of adaptation. Each model is a spell, temporarily effective until the unpredictable currents of production inevitably shift, demanding a new incantation. The agent doesn’t seek certainty, only the most persuasive path through the chaos.
What Lies Ahead?
The pursuit of optimal execution, predictably, reveals itself not as a problem solved, but a surface meticulously polished to better reflect the chaos beneath. This work, while demonstrating the aptitude of convolutional neural networks for divining short-term market currents, merely refines the art of profitable illusion. The agent learns to appear to minimize transaction costs, but the market, being a fundamentally forgetful entity, will undoubtedly conjure new inefficiencies to exploit. It’s a perpetual game of chasing shadows, and each ‘improvement’ is simply a temporary truce.
Quality-diversity approaches offer a faint glimmer of hope-a suggestion that specialization, rather than monolithic optimization, might be a more resilient strategy. Yet, achieving robust specialization remains elusive. The challenge isn’t merely generating diverse strategies, but ensuring those strategies persist when confronted with the inevitable distortions of real-world data. Metrics, of course, offer a comforting narrative of progress, a form of self-soothing in the face of irreducible uncertainty.
Future work will likely focus on hybrid systems – agents that dynamically blend learned behaviors with analytically derived models. But it’s crucial to remember that all learning is, at its core, an act of faith. Data never lies; it just forgets selectively. The true frontier isn’t building better predictors, but accepting the inherent limitations of prediction itself, and designing systems that gracefully degrade when the future inevitably refuses to cooperate.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.22113.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- 2025 Crypto Wallets: Secure, Smart, and Surprisingly Simple!
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Brown Dust 2 Mirror Wars (PvP) Tier List – July 2025
- Banks & Shadows: A 2026 Outlook
- Gemini’s Execs Vanish Like Ghosts-Crypto’s Latest Drama!
- ETH PREDICTION. ETH cryptocurrency
- The Weight of Choice: Chipotle and Dutch Bros
- Uncovering Hidden Groups: A New Approach to Social Network Analysis
- Gay Actors Who Are Notoriously Private About Their Lives
- The 10 Most Beautiful Women in the World for 2026, According to the Golden Ratio
2026-02-01 18:20