Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new agentic framework empowers anomaly detection systems to reason through time series data and diagnose issues with improved accuracy and interpretability.
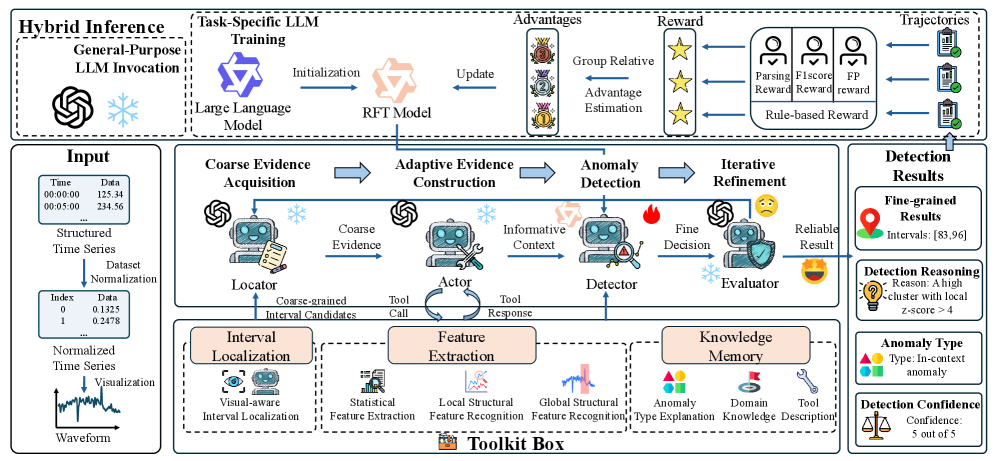
AnomaMind reformulates the problem as sequential decision-making, leveraging tool-augmented reasoning and hybrid inference for enhanced performance.
Existing time series anomaly detection methods often treat anomalies as isolated events rather than diagnostic puzzles, limiting their ability to handle contextual dependencies and diverse patterns. To address this, we introduce AnomaMind: Agentic Time Series Anomaly Detection with Tool-Augmented Reasoning, a novel framework that reformulates anomaly detection as a sequential decision-making process leveraging adaptive feature preparation and self-reflective refinement. By combining reinforcement learning with reusable tool engines, AnomaMind enables context-aware diagnostic analysis and consistently improves detection performance across diverse settings. Could this agentic approach unlock a new paradigm for robust and interpretable time series analysis in complex real-world applications?
The Inevitable Failure of Static Observation
Conventional anomaly detection techniques, designed for simpler datasets, increasingly falter when confronted with the sheer scale and intricacy of modern time series. The proliferation of data streams from sources like IoT devices, financial markets, and climate monitoring systems generates volumes that overwhelm algorithms reliant on static thresholds or predefined patterns. Consequently, these methods frequently generate false positives – flagging normal fluctuations as anomalies – or, more critically, miss genuine critical events hidden within the noise. This inability to discern meaningful deviations stems from a lack of adaptability; traditional systems struggle to account for the inherent non-stationarity and evolving dynamics characteristic of real-world time series, leading to diminished reliability and potentially significant consequences in applications demanding timely and accurate alerts.
Truly effective anomaly detection transcends simple deviation identification; it necessitates a nuanced comprehension of the data’s inherent context and its dynamic evolution over time. Static thresholds and historical averages often fail because time series data isn’t stationary – patterns shift, seasonality changes, and relationships between variables are rarely constant. Consequently, algorithms must incorporate mechanisms to learn these evolving baselines, distinguishing between genuine anomalies and expected fluctuations. This involves analyzing temporal dependencies, recognizing recurring motifs, and potentially leveraging external knowledge to interpret data within its broader operational environment. The ability to model these intricate patterns-rather than merely flagging outliers-is critical for reducing false alarms and ensuring that critical events are accurately identified and addressed, ultimately maximizing the utility of time series analysis.
The Illusion of Control Through Iteration
The anomaly detection process is structured as a series of sequential decisions, rather than a single pass analysis. This iterative approach allows the system to dynamically adjust its analytical focus based on the results of prior evaluations within the time series data. Each decision involves assessing potential anomalies, refining parameters, and prioritizing subsequent investigations. This method is particularly effective with complex time series exhibiting non-stationary behavior or evolving patterns, as the system can adapt to changes and improve accuracy over time by continuously incorporating new information from each iterative step.
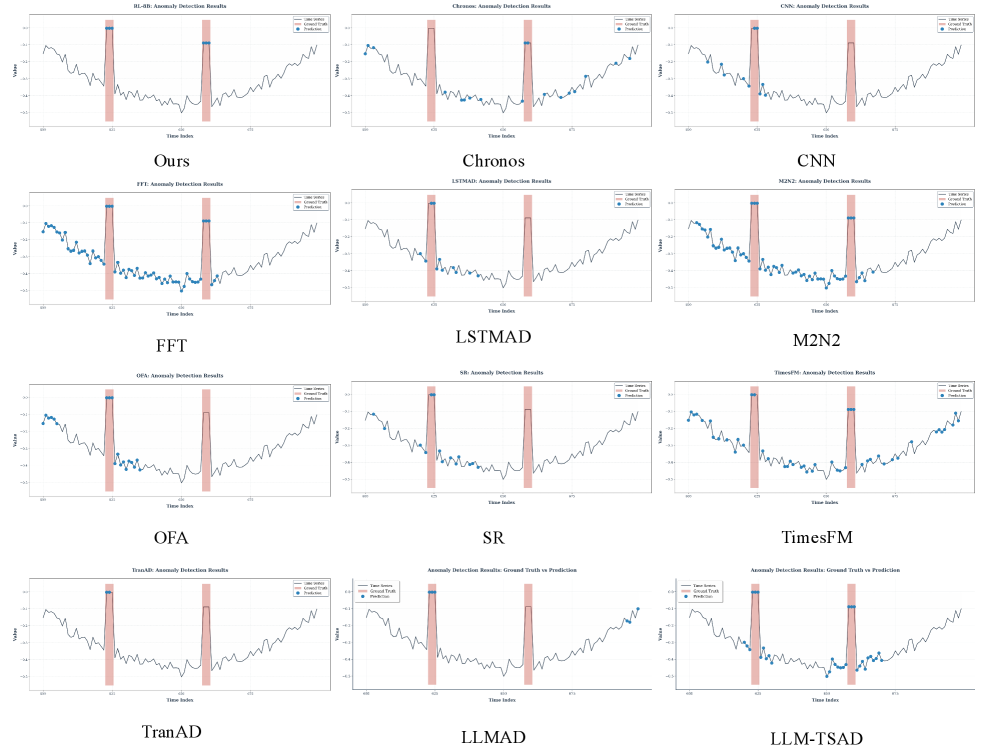
The agentic workflow utilizes tool-augmented reasoning to improve anomaly detection performance. This approach integrates external tools – such as statistical analysis packages and time series decomposition algorithms – into the reasoning process, allowing the system to perform more complex data evaluation than traditional methods. Empirical results demonstrate consistent improvements in F1-score across multiple datasets when compared to baseline anomaly detection techniques. Specifically, the integration of these tools enables more accurate identification of subtle anomalies and reduces false positive rates, leading to enhanced analytical capabilities and improved overall accuracy in time series analysis.
The system implements a coarse-to-fine workflow by initially identifying potential anomalies through broad data scans, then subjecting these anomaly candidates to focused analytical steps. This refinement process involves utilizing specialized tools and reasoning techniques to validate or reject initial findings. Subsequent analyses concentrate on the characteristics of the remaining candidates, increasing precision and reducing false positives. This staged approach allows for efficient resource allocation, prioritizing detailed investigation only for the most likely anomalies and improving overall analytical throughput.
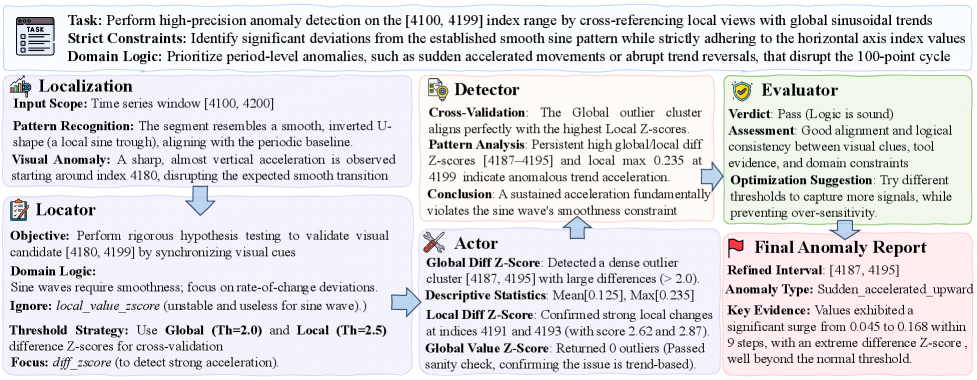
The Mirage of Precision: Localization and Feature Extraction
Interval localization utilizes visual-language models to identify specific segments within a time series data stream that exhibit anomalous behavior. These models are trained to correlate visual representations of time series data with linguistic descriptions of potential anomalies. Rather than pinpointing single data points, the technique focuses on defining intervals-contiguous periods of time-where deviations from expected patterns are observed. This interval-based approach allows for the detection of anomalies that manifest as trends or sustained deviations, which might be missed by point-based detection methods. The visual-language model outputs a confidence score for each potential interval, indicating the likelihood that the segment contains an anomaly, thereby enabling prioritization and further analysis.
Following interval localization, feature extraction employs statistical analysis to convert identified time series segments into quantifiable characteristics used for anomaly scoring. These characteristics include measures of central tendency, such as mean and median, as well as dispersion, represented by standard deviation and interquartile range. Further statistical features calculated include skewness, kurtosis, and autocorrelation to capture the shape and temporal dependencies within the localized segments. These extracted features are then assembled into a feature vector for each segment, providing a numerical representation of its characteristics that enables quantitative comparison and anomaly scoring using algorithms like z-score normalization or Principal Component Analysis (PCA).
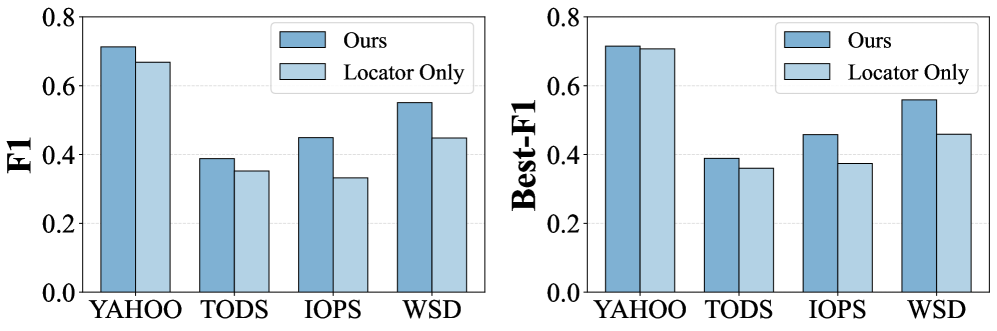
The combination of interval localization – a qualitative method using visual-language models to identify anomalous segments – with subsequent feature extraction via statistical analysis significantly improves anomaly detection reliability. This dual approach yields higher Best-F1 values when benchmarked against standard anomaly detection methods. Best-F1, a harmonic mean of precision and recall, provides a balanced measure of the system’s accuracy in identifying anomalies. The qualitative localization step reduces false positives by narrowing the scope of analysis, while quantitative feature extraction provides objective metrics for anomaly scoring, ultimately leading to a more robust and accurate detection process.
The Inevitable Shift: Hybrid Inference and its Limitations
Hybrid inference represents a significant advancement in predictive modeling by strategically combining the capabilities of broadly trained, general-purpose models with the focused precision of task-specific learning. This approach allows systems to leverage existing knowledge – understanding contextual nuances and complex relationships – while simultaneously honing their predictive accuracy on particular challenges. Rather than relying solely on extensive retraining for each new task, hybrid inference fine-tunes a foundational model, inheriting its robust understanding of underlying patterns. The result is a system capable of both broad comprehension and highly accurate prediction, offering improved performance and adaptability compared to either approach used in isolation. This synergy is particularly valuable in complex domains where data is limited or constantly evolving, enabling more reliable and efficient decision-making.
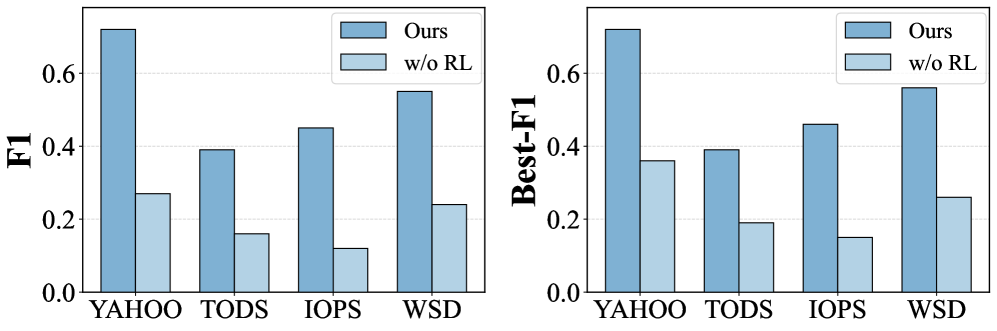
The system employs reinforcement learning to dynamically refine its anomaly scoring, moving beyond static thresholds to achieve a continuously improving level of accuracy. This process treats anomaly detection as a sequential decision problem, where the system learns from the consequences of its scoring choices. By receiving feedback – whether a flagged anomaly proves genuine or is a false positive – the learning algorithm adjusts its scoring strategy to maximize rewards, effectively prioritizing the identification of true anomalies while minimizing unnecessary alerts. This iterative refinement allows the system to adapt to evolving data patterns and maintain optimal performance even as the characteristics of anomalies shift over time, resulting in a robust and self-optimizing anomaly detection capability.
Investigations into the system’s architecture revealed a critical dependency on global structural feature recognition; its removal led to a substantial decrease in the F1-score for both Input/Output Operations Per Second (IOPS) and Write Speed Detection (WSD) metrics. This finding underscores the component’s importance in accurately characterizing system behavior and facilitating effective anomaly detection. Complementing this architectural sensitivity analysis, rigorous temperature sensitivity testing demonstrated consistent and stable performance across a wide operational range. These results suggest the system maintains reliable functionality even under varying environmental conditions, highlighting its robustness and suitability for deployment in diverse and potentially challenging settings.
The pursuit of automated anomaly detection, as demonstrated by AnomaMind, feels less like engineering and more like tending a garden. One cultivates conditions – a framework for sequential decision-making, tool-augmented reasoning – and observes what flourishes, and what inevitably withers. As Andrey Kolmogorov observed, “The most important discoveries are often the result of a search for the simplest explanation.” AnomaMind’s hybrid inference mechanism, striving for both performance and interpretability, echoes this sentiment. It acknowledges the inherent complexity of time series data, yet seeks a parsimonious understanding, knowing full well that any ‘solution’ is merely a temporary truce with chaos. Technologies change, dependencies remain; the anomalies will always find a way.
What Lies Ahead?
AnomaMind attempts to sculpt order from the chaos of time series data, framing anomaly detection not as a static problem, but as a dialogue. Yet, this very framing reveals the core tension. The pursuit of ‘agentic’ systems is, at its heart, a search for predictable unpredictability. Each tool added, each layer of reasoning, is a commitment to a particular future – a prophecy of the failures that will inevitably arise when the data deviates from the expected. Scalability is merely the word used to justify ever-increasing complexity, a complexity that erodes the very flexibility it promises.
The hybrid inference mechanism, while offering a path toward interpretability, simply postpones the inevitable. Explanations are brittle things, easily fractured by novel anomalies. The real challenge isn’t diagnosing what has happened, but building systems that gracefully degrade – that acknowledge their inherent limitations. The perfect architecture is a myth, a comforting fiction constructed to stave off despair.
Future work will undoubtedly focus on expanding the repertoire of tools available to these agents, refining the reward functions, and pushing the boundaries of sequential decision-making. But perhaps a more fruitful avenue lies in embracing the inherent messiness of real-world data. Instead of striving for perfect detection, the field might benefit from shifting its focus towards robust resilience – towards systems that can learn to coexist with uncertainty, and even to benefit from it.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.13807.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Building 3D Worlds from Words: Is Reinforcement Learning the Key?
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Securing the Agent Ecosystem: Detecting Malicious Workflow Patterns
- 2025 Crypto Wallets: Secure, Smart, and Surprisingly Simple!
- Mel Gibson, 69, and Rosalind Ross, 35, Call It Quits After Nearly a Decade: “It’s Sad To End This Chapter in our Lives”
- TV Shows Where Asian Representation Felt Like Stereotype Checklists
- The Best Directors of 2025
- Games That Faced Bans in Countries Over Political Themes
- 📢 New Prestige Skin – Hedonist Liberta
- Most Famous Richards in the World
2026-02-17 11:16