Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new framework explores how generative AI and online Q&A forums can move beyond competition and forge a mutually beneficial relationship.
This paper proposes a game-theoretic approach to incentivize AI to contribute challenging questions, mitigating data depletion and restoring utility in declining online forums.
The increasing reliance on generative AI systems creates a paradoxical tension with the online Q&A forums that provide crucial training data. This paper, ‘From Competition to Collaboration: Designing Sustainable Mechanisms Between LLMs and Online Forums’, proposes a game-theoretic framework to model and incentivize a mutually beneficial relationship between these entities. Through data-driven simulations using Stack Exchange and large language models, we demonstrate that strategically incentivizing AI to pose challenging questions can recover approximately half of the utility lost due to declining forum participation. Could this approach pave the way for sustainable knowledge ecosystems that leverage the strengths of both artificial and human intelligence?
The Erosion of Expertise in the Age of AI
A noticeable shift is occurring within online question-and-answer communities like Stack Overflow, as participation from experienced users demonstrably declines with the increasing prevalence of generative AI systems such as ChatGPT. Data indicates a reduction in both the volume of questions posted and, crucially, the number of detailed, expert-driven answers provided. While these platforms historically thrived on the altruism of knowledgeable individuals freely sharing their expertise, the readily available, though sometimes imperfect, responses generated by AI are altering established behavioral patterns. The ease with which AI can provide an answer-even if lacking nuance or thoroughness-appears to be diminishing the motivation for experts to contribute their time and knowledge, potentially jeopardizing the quality and sustainability of these once-vibrant knowledge repositories.
The diminishing engagement on platforms like Stack Overflow signals more than a shift in how information is accessed; it undermines the very basis of their success. These sites were built on the principle of reciprocal knowledge exchange, where experts contribute their time and skills not just to answer questions, but also to refine their own understanding through teaching and peer review. As generative AI increasingly provides direct answers, the incentive for this crucial contribution erodes, potentially creating a feedback loop where expertise is no longer actively cultivated within the community. This poses a significant threat to the long-term health of these platforms, as their value proposition hinges on a vibrant, self-sustaining ecosystem of shared knowledge – an ecosystem now facing potential stagnation and decline without consistent, expert input.
The diminishing engagement within online expertise platforms isn’t solely attributable to artificial intelligence providing solutions; rather, the shift fundamentally alters the motivations driving expert participation. Traditionally, individuals contributed to forums like Stack Overflow driven by a combination of altruism, reputation building, and the intellectual stimulation of tackling challenging problems. However, with AI readily generating answers – even if imperfect – the perceived need to actively engage in question resolution diminishes. This impacts not just the volume of answers, but the proactive posing of complex questions – a crucial element of knowledge refinement and discovery. Consequently, the core engine of these platforms – a community motivated by both sharing and seeking knowledge – is being undermined, threatening the long-term sustainability of crowdsourced expertise.
Designing Collaboration: A Game-Theoretic Framework
The proposed GenAI-Forum collaboration framework is built upon game-theoretic principles, specifically strategic interaction and asymmetric information. This means the interaction isn’t treated as a simple request-response cycle, but as a deliberate exchange where both the GenAI and the forum participants make choices to optimize outcomes. Crucially, this framework recognizes that the GenAI and the forum possess differing levels of knowledge; the GenAI may have superior capabilities in processing and answering questions, while the forum members possess a better understanding of question relevance, context, and potential utility. This informational imbalance-asymmetric information-is central to the design, requiring a collaborative strategy beyond a non-strategic, ‘first-come, first-served’ methodology.
The differential access to information regarding question utility is central to the proposed collaboration framework. GenAI models, while capable of processing and responding to questions, lack inherent understanding of the question’s value to the forum’s user base – factors such as existing discussion, user expertise, or potential for community engagement. Conversely, forums and their moderators possess contextual knowledge regarding user needs and the existing information landscape. This asymmetric information distribution necessitates a collaborative strategy where question selection isn’t random, but informed by the forum’s assessment of utility, maximizing the benefit of GenAI’s response capabilities and ensuring relevance to the community.
The GenAI-Forum collaboration is conceptualized as a strategic game where both parties actively select questions to optimize outcomes, departing from a sequential, non-selective method. This game-theoretic model recognizes that forums possess information regarding question relevance to their user base-specifically, the likely utility and engagement a question will generate-while GenAI possesses capabilities for answering questions. By strategically selecting questions, the forum can prioritize those likely to benefit its community and maximize user engagement, while the GenAI can focus on questions where its capabilities will be most valuable, improving answer quality and reducing computational cost. This selective approach aims to create a mutually beneficial exchange, increasing the overall utility derived from the collaboration compared to a random or ‘first-come, first-served’ assignment of questions.
Quantifying Collaborative Potential Through Game Theory
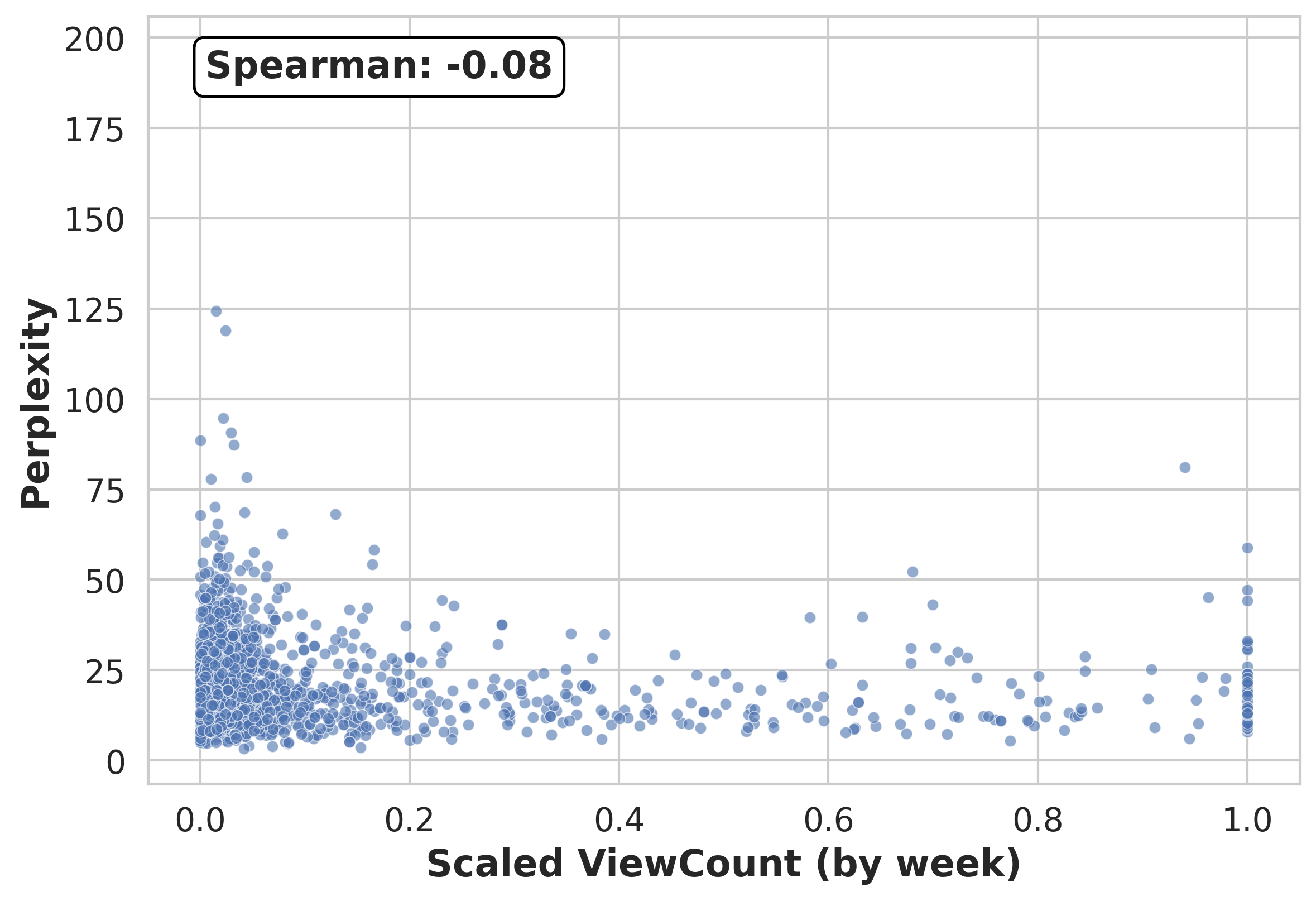
A game-theoretic model was constructed to analyze the interaction between Generative AI (GenAI) and online forums, treating question utility as the central element of this interaction. To quantify this utility, the model employs perplexity as a proxy for GenAI’s assessment of a question’s informational content – lower perplexity indicating greater confidence in answering the question. Simultaneously, forum view counts serve as a proxy for the value a question holds for the user community, representing the degree to which the question resonates with and benefits forum participants. This framework allows for the formalization of the incentives and strategic considerations of both GenAI and forum users, enabling the measurement of collaborative efficiency and potential gains from improved information exchange.
Perplexity, calculated as the exponential of the average negative log-likelihood of a language model predicting a sequence, functions as an internal signal to GenAI regarding its confidence in answering a given question; lower perplexity indicates higher confidence. Concurrently, forum view count provides a quantitative measure of a question’s value to the user community, reflecting its relevance and potential for generating discussion. This metric aggregates user interest, effectively representing external demand for information on a specific topic. The combination of these two metrics allows for a comparative analysis between GenAI’s internal assessment of question difficulty and the community’s perceived value of the question, forming the basis for quantifying collaborative potential.
Analysis of question data revealed a Spearman correlation of approximately 0 between GenAI perplexity and forum view counts, indicating a lack of association between the potential for GenAI to improve its responses and the perceived value of those questions to the forum community. To quantify the benefits of improved collaboration, a full-information collaborative scenario was modeled, establishing a benchmark against the current asymmetric information state. This modeling demonstrates that the framework recovers between 46-52% of GenAI’s potential learning gains and 56-66% of potential forum engagement, suggesting a substantial opportunity for optimization through enhanced information sharing between the GenAI system and the forum’s user base.
Optimizing Question Selection for Mutual Benefit
Two distinct strategies were investigated for question selection in a Generative AI (GenAI) and forum interaction scenario. The first, a greedy approach, focuses on maximizing information gain by consistently selecting questions that exhibit the highest perplexity – a measure of the model’s uncertainty, indicating areas where learning is most needed. In contrast, the utility maximization strategy moves beyond purely informational value and incorporates a predictive element, specifically the forum’s likelihood of accepting a given question. This acceptance probability is estimated using a Threshold Classifier, allowing the GenAI to prioritize questions not only for their informational content but also for their potential to be successfully integrated into the forum discussion, ultimately aiming for a higher rate of productive interaction and knowledge recovery.
The utility maximization strategy implemented within the GenAI system incorporates an Acceptance Probability Estimation method to predict the likelihood of a question being accepted by the target forum. This estimation leverages the forum’s pre-existing Threshold Classifier, a model trained to distinguish between acceptable and unacceptable questions based on established community guidelines. The output of this classifier – a probability score indicating acceptance – is then integrated into the GenAI’s decision-making process, allowing it to prioritize questions predicted to have a higher chance of being well-received and thus contribute positively to both learning and forum engagement. This predictive approach moves beyond simply identifying challenging questions, and instead focuses on maximizing the overall utility of each interaction.
Employing a utility maximization strategy for question selection demonstrably improves the Utility Recovery Rate (URR) in GenAI-forum interactions. Results indicate this approach recovers between 46% and 52% of potential GenAI learning, representing a significant gain over less strategic methods. Furthermore, forum engagement is also substantially increased, with the utility maximization strategy yielding a recovery rate of 56-66%. These gains are achieved by prioritizing questions that maximize both the GenAI’s learning and the forum’s acceptance probability, leading to a more balanced and mutually beneficial exchange.
Towards a Sustainable Future for Online Knowledge Ecosystems
Recent research indicates the potential for artificial intelligence to positively influence the health of online knowledge resources. Utilizing large language models – specifically LLaMA 3.1 8B and Pythia 6.9B – researchers have demonstrated a framework for AI systems designed to actively add to existing online knowledge, rather than simply consuming or potentially degrading it. This approach moves beyond the typical generative AI paradigm, focusing instead on bolstering established question-and-answer forums and similar platforms. The study highlights a pathway where AI can function as a collaborator in knowledge creation, identifying valuable questions and contributing to their resolution, thereby ensuring these vital online ecosystems remain robust and relevant in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Question-and-answer forums, once vibrant hubs of shared knowledge, face a growing challenge from generative AI capable of directly answering queries. This framework proposes a solution by actively incentivizing the selection of high-quality questions – those that demand nuanced reasoning, encourage detailed explanations, and avoid simple factual recall. By rewarding contributions that curate challenging and insightful prompts, the system shifts the focus from merely answering questions to asking better ones. This revitalization strategy doesn’t compete with generative AI; instead, it leverages its capabilities by providing it with richer, more complex problems to solve, simultaneously ensuring the continued relevance of human-driven Q&A platforms and fostering a dynamic cycle of learning and knowledge refinement.
The principles guiding this research – incentivized contribution and quality assessment within knowledge-sharing platforms – extend far beyond question-and-answer forums. Investigating applications in fields such as scientific literature review, legal precedent analysis, or even technical documentation promises to cultivate more robust and reliable online resources. By adapting this framework to diverse knowledge-intensive domains, a collaborative ecosystem can emerge, where artificial intelligence actively supports and enhances human expertise, rather than simply replicating or replacing it. This broader implementation is crucial for ensuring the long-term sustainability of online knowledge, promoting accuracy, and fostering a future where information remains a shared and evolving asset.
The pursuit of sustainable interaction, as detailed in this work, necessitates a holistic understanding of system dynamics. It’s not merely about patching declines in forum participation with AI-generated content; it’s about re-evaluating the underlying incentive structures. This echoes Carl Friedrich Gauss’s observation: “If others would think as hard as I do, they would not have so many questions.” The paper demonstrates that by incentivizing AI to pose challenging questions-effectively stimulating intellectual demand-a significant portion of lost utility can be recovered. This isn’t simply about information retrieval; it’s about fostering a collaborative ecosystem where AI and human intellect mutually reinforce each other, much like a well-designed city infrastructure evolves without necessitating complete reconstruction.
The Road Ahead
This work suggests a path toward stabilizing a symbiotic relationship between generative AI and human knowledge ecosystems, but it does not offer a final solution. The presented framework, while demonstrating the potential of incentivized questioning, rests on assumptions about rational actors and predictable utility functions. One cannot simply transplant a heart – even a perfectly engineered one – without considering the circulatory system’s existing condition, its capacity for adaptation, and the potential for rejection. The current model simplifies the complexities of human motivation; intrinsic rewards, reputation, and the simple joy of knowledge exchange are not easily quantified or replicated in an algorithmic incentive structure.
Future work must address the inherent asymmetries of information. The AI ‘knows’ what it does not know, but accurately gauging the informational needs – and existing knowledge – of a diverse forum population remains a considerable challenge. Furthermore, the long-term consequences of shaping question quality through incentives deserve scrutiny. A system optimized for ‘challenging’ questions may inadvertently discourage simpler inquiries, potentially creating a knowledge bottleneck.
Ultimately, the sustainability of this collaboration hinges not merely on elegant game theory, but on a deeper understanding of how information flows, how knowledge is valued, and how humans and machines can best complement each other’s strengths – and mitigate each other’s weaknesses. A truly robust system will be one that adapts, learns, and evolves, not one rigidly defined by initial conditions.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.04572.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Gold Rate Forecast
- 2025 Crypto Wallets: Secure, Smart, and Surprisingly Simple!
- HSR 3.7 story ending explained: What happened to the Chrysos Heirs?
- The 10 Most Beautiful Women in the World for 2026, According to the Golden Ratio
- ETH PREDICTION. ETH cryptocurrency
- Uncovering Hidden Groups: A New Approach to Social Network Analysis
- Here Are the Best TV Shows to Stream this Weekend on Paramount+, Including ‘48 Hours’
- Games That Faced Bans in Countries Over Political Themes
- ‘Zootopia+’ Tops Disney+’s Top 10 Most-Watched Shows List of the Week
- The Labyrinth of Leveraged ETFs: A Direxion Dilemma
2026-02-06 02:46