Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new system dynamically optimizes deep learning inference to minimize delays and maximize reliability in shared autonomous vehicle environments.

PP-DNN improves the predictability of multi-tenant deep neural network inference by intelligently selecting critical frames and regions of interest for autonomous vehicle perception tasks.
Achieving consistent real-time performance remains a key challenge in deploying deep neural networks for autonomous vehicle perception, despite ongoing efforts to compress model size and accelerate inference. This paper, ‘Enhancing Predictability of Multi-Tenant DNN Inference for Autonomous Vehicles’ Perception’, introduces PP-DNN, a system that dynamically prioritizes critical image frames and regions of interest to improve the predictability and efficiency of multi-tenant DNN inference. By leveraging temporal locality and a FLOPs predictor, PP-DNN significantly reduces fusion delay and enhances detection completeness-achieving up to 7.3x more fusion frames and 75.4% improved detection-while maximizing cost-effectiveness. Can this approach to dynamic workload management unlock more robust and reliable perception systems for truly autonomous driving?
Unveiling the Patterns of Perception: The Challenge of Real-Time Awareness
The ambition of fully autonomous vehicles hinges on their ability to perceive and interpret the surrounding environment with unwavering reliability, yet this presents a considerable challenge for current deep neural networks (DNNs). While DNNs excel at tasks like object recognition, their computational demands are substantial, requiring significant processing power and time. Each frame captured by a vehicle’s sensors necessitates complex calculations, creating a latency issue that is unacceptable for real-time control-a delay of even milliseconds can have serious consequences. The very architectures that provide high accuracy often struggle to meet the stringent timing requirements of driving scenarios, forcing developers to seek innovative solutions that balance perceptual capability with operational speed. This fundamental tension between accuracy and latency remains a primary obstacle in the pursuit of truly self-driving technology.
The demand for instantaneous decision-making in autonomous vehicles creates a fundamental challenge: fully processing every captured frame with computationally intensive deep neural networks is simply impractical. Each frame contains a wealth of visual information, but subjecting all of it to complex analysis introduces unacceptable latency, hindering the vehicle’s ability to react to dynamic environments. Consequently, systems must selectively analyze incoming data, prioritizing critical information-such as nearby pedestrians or rapidly approaching vehicles-while intelligently filtering out less relevant details. This selective approach necessitates sophisticated algorithms capable of discerning importance in milliseconds, effectively balancing the need for comprehensive environmental awareness with the stringent real-time constraints of safe autonomous operation.
Current approaches to real-time perception for autonomous vehicles frequently encounter a fundamental trade-off between the desire for high accuracy, the need for processing speed, and the demand for consistent, predictable performance. Many systems achieve acceptable speeds by simplifying complex models or processing only a subset of incoming data, inevitably sacrificing some degree of accuracy in identifying and classifying objects. Conversely, prioritizing accuracy often introduces computational bottlenecks that compromise the vehicle’s ability to react quickly to changing conditions. This instability is particularly concerning; unpredictable latency or intermittent failures in perception systems present a critical safety risk, as the vehicle’s decision-making processes rely heavily on timely and reliable environmental understanding. Therefore, advancements in perception must simultaneously address all three of these factors – accuracy, speed, and predictability – to ensure the safe and dependable operation of autonomous vehicles.
Maintaining dependable autonomous vehicle operation hinges on consistent performance, yet fluctuating computational demands present a considerable challenge. As vehicles encounter diverse driving scenarios – from sun-drenched highways to dimly lit city streets, or sudden changes in traffic density – the workload on perception systems varies dramatically. This variability can lead to unpredictable latency and diminished accuracy in object detection and scene understanding. Current systems often exhibit performance degradation under peak loads, raising safety concerns about their ability to react reliably in critical situations. Research focuses on developing adaptive algorithms and hardware architectures capable of dynamically adjusting to these changing workloads, ensuring consistently stable and predictable performance – a prerequisite for public acceptance and widespread deployment of self-driving technology.
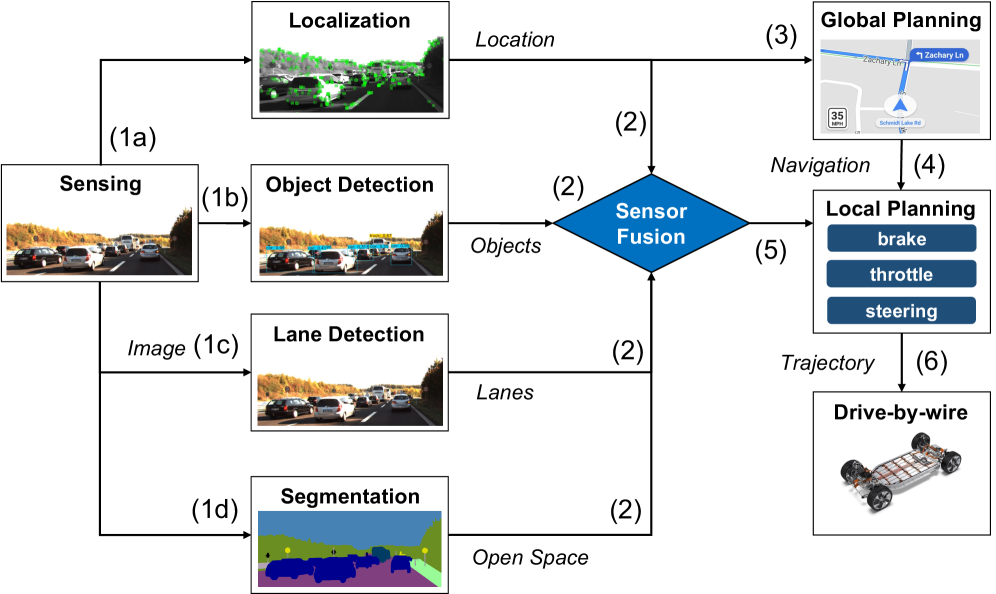
PP-DNN: Orchestrating Perception for Predictable Responsiveness
PP-DNN employs an adaptive perception pipeline designed to improve processing efficiency by focusing computational resources on the most relevant visual information. Rather than processing every frame equally, the system dynamically identifies and selects key frames and Regions of Interest (ROIs) for detailed analysis. This selective approach allows PP-DNN to prioritize areas exhibiting significant changes or critical features, reducing the overall computational load without sacrificing accuracy in perception tasks. The pipeline continuously adjusts its focus based on incoming data, enabling it to respond to dynamic scenes and varying levels of visual complexity.
The PP-DNN system employs the ROIGenerator and FrameScheduler to dynamically prioritize processing of incoming frames. The ROIGenerator identifies and defines Regions of Interest (ROIs) within each frame based on assessed criticality – areas likely containing relevant information for decision-making. Simultaneously, the FrameScheduler manages the processing queue, considering both the criticality of frames containing ROIs and the current availability of computational resources. This allows the system to allocate processing power preferentially to high-criticality regions and frames, ensuring that the most important data is analyzed promptly, even under fluctuating workloads or resource constraints. The combined operation of these two components facilitates efficient and targeted processing, maximizing throughput and minimizing latency.
PP-DNN incorporates a FLOPsPredictor module to estimate the floating-point operations (FLOPs) required for processing each incoming frame. This prediction, based on frame content and network complexity, allows the system to proactively allocate computational resources – including GPU time and memory – before processing begins. By anticipating FLOPs demands, PP-DNN avoids resource contention and bottlenecks, enabling dynamic adjustment of processing parameters and ensuring efficient utilization of hardware. The FLOPsPredictor’s output directly informs the FrameScheduler and ROIGenerator, facilitating prioritized frame selection and ROI analysis based on predicted computational cost and criticality.
PP-DNN’s adaptive perception pipeline demonstrably improves performance in multi-tenant Deep Neural Network (DNN) applications. Benchmarks indicate a 7.3x increase in the number of frames successfully processed in a fused manner, indicating improved throughput. Simultaneously, fusion delay-the time required to combine and process data from multiple sources-is reduced by a factor of greater than 2.6x. These gains contribute to predictable execution times, critical for safety-sensitive applications, and overall system reliability by ensuring consistent performance even under varying computational loads.

Leveraging Temporal Coherence: The Efficiency of Predicted Change
PP-DNNs are designed to minimize computational load by exploiting temporal locality inherent in video sequences. Consecutive frames in a video typically exhibit high degrees of similarity; therefore, redundant processing of identical or near-identical regions is inefficient. PP-DNN architecture leverages this by performing computations only on the changing elements between frames, rather than re-processing the entire frame. This is achieved through techniques that identify and cache previously computed features, and then reuse them in subsequent frames, significantly reducing the overall computational cost and enabling real-time performance on resource-constrained devices.
DeepCache and SelfCueingAttention are techniques employed within PP-DNN to exploit temporal locality for performance gains. DeepCache operates by storing and reusing feature maps from previous frames, effectively caching redundant computations when consecutive frames exhibit high similarity. SelfCueingAttention, conversely, dynamically focuses processing on regions within a frame that have changed significantly since the previous frame; this is achieved through attention mechanisms that prioritize updating only the differing elements, rather than reprocessing the entire frame. Both techniques reduce computational load by minimizing redundant operations and concentrating resources on the evolving aspects of video sequences, resulting in accelerated processing and reduced latency.
The ROIGenerator employs the Structural Similarity Index Metric (SSIM) to assess the perceptual difference between consecutive video frames. SSIM provides a quantitative measure of image fidelity, considering luminance, contrast, and structure, and outputs a value between -1 and 1, where 1 indicates perfect similarity. This metric is crucial for identifying regions exhibiting significant change; lower SSIM scores correlate with greater dissimilarity and, therefore, highlight areas requiring detailed processing. The ROIGenerator utilizes these SSIM-derived values to dynamically select Regions of Interest (ROIs), focusing computational resources on the most visually distinct portions of the video sequence and minimizing redundant analysis of static or minimally changing areas.
Exploiting temporal locality enables alert systems to perform DNN execution at any time, adjusting processing detail based on computational resources and latency requirements. Rather than requiring full frame analysis for every alert trigger, systems can prioritize processing only the changing regions between consecutive frames. This is achieved by dynamically scaling the DNN’s operational complexity; for instance, utilizing lower-resolution inputs or fewer DNN layers when speed is critical, and increasing detail when resources allow. This adaptive approach facilitates real-time responsiveness without compromising accuracy, as the system leverages inherent redundancies within video sequences to minimize redundant computations.
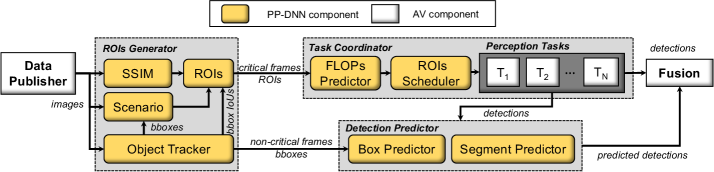
Optimizing for Deployment: The Pursuit of Efficient Computation
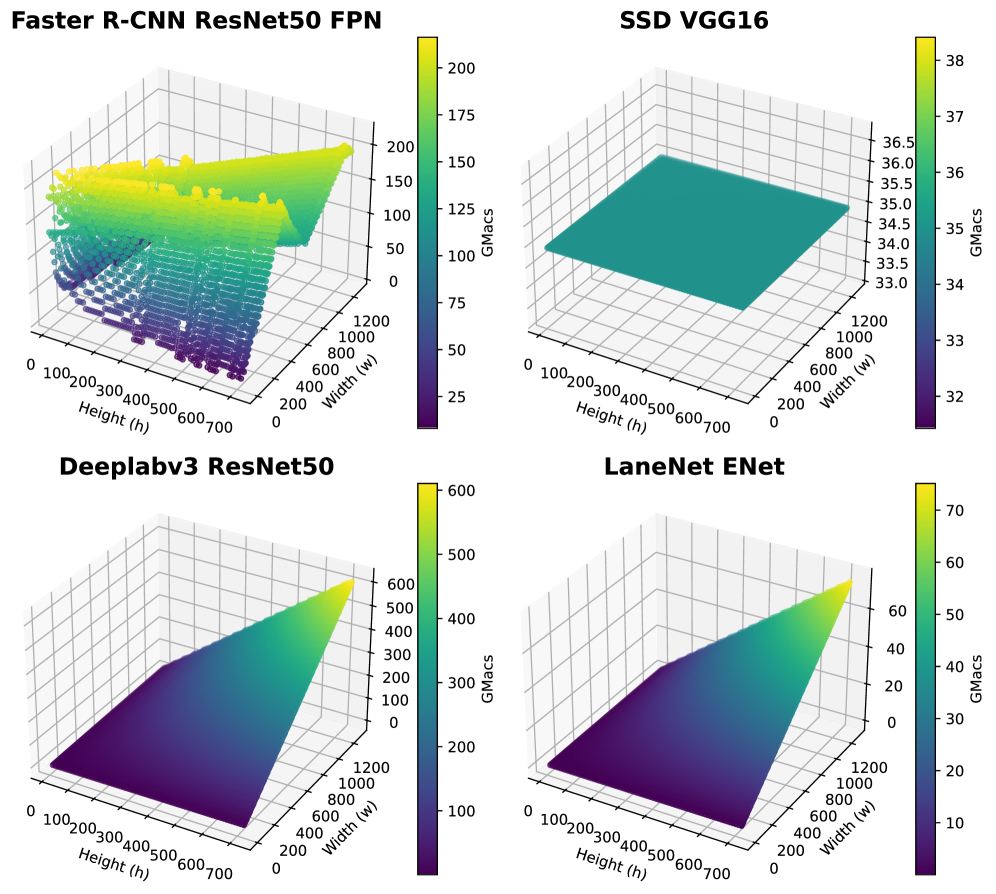
Model compression techniques, specifically pruning and precision reduction, are core components in optimizing Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) for resource-constrained environments. Pruning systematically removes unimportant weights or connections within the network, decreasing the number of computations required during inference. Precision reduction lowers the numerical precision used to represent weights and activations – for example, transitioning from 32-bit floating point to 8-bit integer – which directly reduces memory footprint and accelerates computation, particularly on hardware designed for lower-precision arithmetic. These methods are applied to DNN architectures such as YOLOv3, FasterRCNN, and Deeplabv3+ to minimize computational demands without substantial degradation in model accuracy.
Model compression techniques applied to deep neural networks, including architectures such as YOLOv3, FasterRCNN, SSD, Deeplabv3+, and LaneNet, demonstrably reduce both model size and computational complexity. This reduction is achieved through methods like pruning, which removes redundant parameters, and precision reduction, which lowers the numerical precision of weights and activations. Critically, these optimizations are designed to minimize any corresponding decrease in accuracy; evaluations have shown that substantial compression can be achieved with only marginal performance degradation, allowing for efficient deployment on resource-constrained platforms.
PP-DNN utilizes a combined strategy of adaptive sampling and model compression techniques to optimize performance across multiple key metrics. Adaptive sampling dynamically adjusts the input data volume processed by the network, focusing computational resources on the most informative regions. Simultaneously, model compression, including pruning and precision reduction, minimizes the computational demands of the Deep Neural Network (DNN) itself. This synergistic approach allows PP-DNN to achieve a functional trade-off, maintaining high accuracy while significantly reducing latency and resource consumption, and ultimately improving overall system efficiency.
Performance evaluations demonstrate that the implemented optimizations result in a 75.4% improvement in Detection Completeness, signifying a substantial increase in the system’s ability to accurately identify all relevant objects or features within a given dataset. Concurrently, a 98% Cost-Effectiveness Improvement has been achieved, indicating a significant reduction in computational resources required to maintain the same level of performance. These gains are sustained even under high workload conditions, ensuring consistent and reliable operation without performance degradation as processing demands increase.
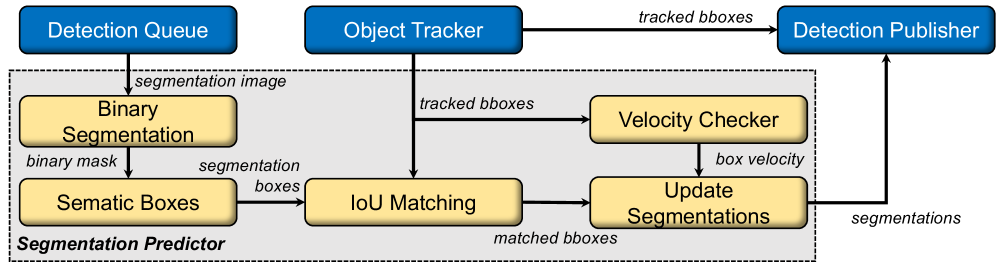
Towards Safe and Reliable Autonomous Driving: A System of Predictable Awareness
Autonomous vehicles operate in a world of constant change, demanding perception systems that don’t just detect objects, but do so with consistent, predictable timing. The PP-DNN – Predictable Performance Deep Neural Network – tackles a fundamental limitation of existing systems by dynamically adjusting its perception pipeline. Rather than employing a fixed approach, PP-DNN intelligently balances the need for comprehensive detection with the critical constraint of minimizing processing delay. This adaptability is achieved through a sophisticated architecture that prioritizes consistent performance even when faced with varying environmental conditions or computational loads. The result is a system less prone to unexpected failures or erratic behavior, fostering greater safety and reliability in complex driving scenarios, and representing a crucial advancement towards truly self-driving technology.
The pursuit of truly autonomous driving hinges on a vehicle’s ability to perceive its surroundings accurately and consistently. PP-DNN addresses this challenge not by maximizing a single perceptual metric, but by intelligently balancing three crucial factors: DetectionCompleteness, FusionDelay, and cost-effectiveness. DetectionCompleteness ensures a thorough identification of all relevant objects, while minimizing FusionDelay – the time lag between sensing and understanding – is vital for real-time responsiveness. Critically, PP-DNN achieves this balance without demanding prohibitively expensive computational resources. This careful orchestration allows the system to maintain robust and reliable perception even in complex and rapidly changing environments, representing a key advancement toward safe and dependable autonomous operation.
Recent advancements in autonomous vehicle perception aren’t solely focused on increasing accuracy, but crucially, on guaranteeing predictable performance. Systems like Prophet achieve this by incorporating uncertainty estimation directly into the perception pipeline. Rather than simply outputting a detection, Prophet provides a confidence interval alongside each object identified, allowing the vehicle’s planning systems to account for potential errors. This probabilistic approach doesn’t diminish the system’s ability to accurately perceive the environment; instead, it quantifies the likelihood of accuracy, enabling more conservative and reliable decision-making. By explicitly modeling uncertainty, Prophet facilitates safer navigation, particularly in challenging conditions where sensor data might be ambiguous or incomplete, representing a vital step towards truly dependable autonomous operation.
The advancement of perception systems like PP-DNN and Prophet isn’t merely incremental; it signals a crucial stride towards unlocking the transformative promise of fully autonomous vehicles. By prioritizing predictable performance alongside accuracy, these innovations directly address longstanding safety concerns that have hindered widespread adoption. This heightened reliability isn’t just about preventing accidents – it’s about broadening access to mobility for individuals who currently face transportation limitations, including the elderly, those with disabilities, and residents of underserved areas. Ultimately, these developments pave the way for a future where autonomous vehicles enhance independence, reduce congestion, and fundamentally reshape how people and goods move, creating a more inclusive and efficient transportation ecosystem.
The pursuit of predictable performance in multi-tenant DNNs, as detailed in the paper, necessitates a careful examination of temporal locality and its impact on fusion delay. This mirrors Geoffrey Hinton’s observation: “The basic idea is that we need to move beyond memorization and towards understanding.” The system’s dynamic adjustment of critical frames and ROIs isn’t simply about processing data faster; it’s about discerning which data truly contributes to understanding the scene. By focusing on these key elements-effectively prioritizing information-PP-DNN moves beyond rote processing and towards a more insightful interpretation of visual data, mirroring the shift Hinton advocates for in machine learning. The selection of ROI demonstrates a pattern-recognition approach to identifying the most impactful inputs for accurate autonomous vehicle perception.
Beyond the Horizon
The presented system, PP-DNN, addresses a practical constraint – the unpredictable latency inherent in shared deep neural network inference. Yet, achieving predictability does not equate to understanding the fundamental limits of this shared resource. Future work must move beyond dynamic adjustment of regions of interest and critical frames to explore the intrinsic characteristics of multi-tenant interference. Is the observed improvement merely a clever redistribution of delay, or a genuine reduction in computational entanglement? The current emphasis on temporal locality, while beneficial, begs the question of whether truly independent inference is achievable in a heavily contended system.
A crucial, largely unexplored area lies in the interplay between model architecture and tenancy. Does a model designed for single-tenant operation simply resist efficient sharing, or can architectural innovations mitigate interference at a deeper level? Furthermore, the notion of a ‘critical frame’ relies on a predefined importance metric. Exploring adaptive criticality – where the system learns to prioritize frames based on real-time contextual understanding – represents a significant, if challenging, avenue for investigation.
Ultimately, the promise of efficient multi-tenant inference rests not just on clever algorithms, but on a rigorous understanding of the underlying physics of computation. If a pattern cannot be reproduced or explained, it doesn’t exist.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.11004.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Silver Rate Forecast
- Securing the Agent Ecosystem: Detecting Malicious Workflow Patterns
- DOT PREDICTION. DOT cryptocurrency
- 4 Reasons to Buy Interactive Brokers Stock Like There’s No Tomorrow
- NEAR PREDICTION. NEAR cryptocurrency
- EUR UAH PREDICTION
- Did Alan Cumming Reveal Comic-Accurate Costume for AVENGERS: DOOMSDAY?
- Top 15 Insanely Popular Android Games
- USD COP PREDICTION
2026-02-13 03:09