Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research explores how intelligent, collaborative AI systems can optimize complex supply chain operations through learned experience.
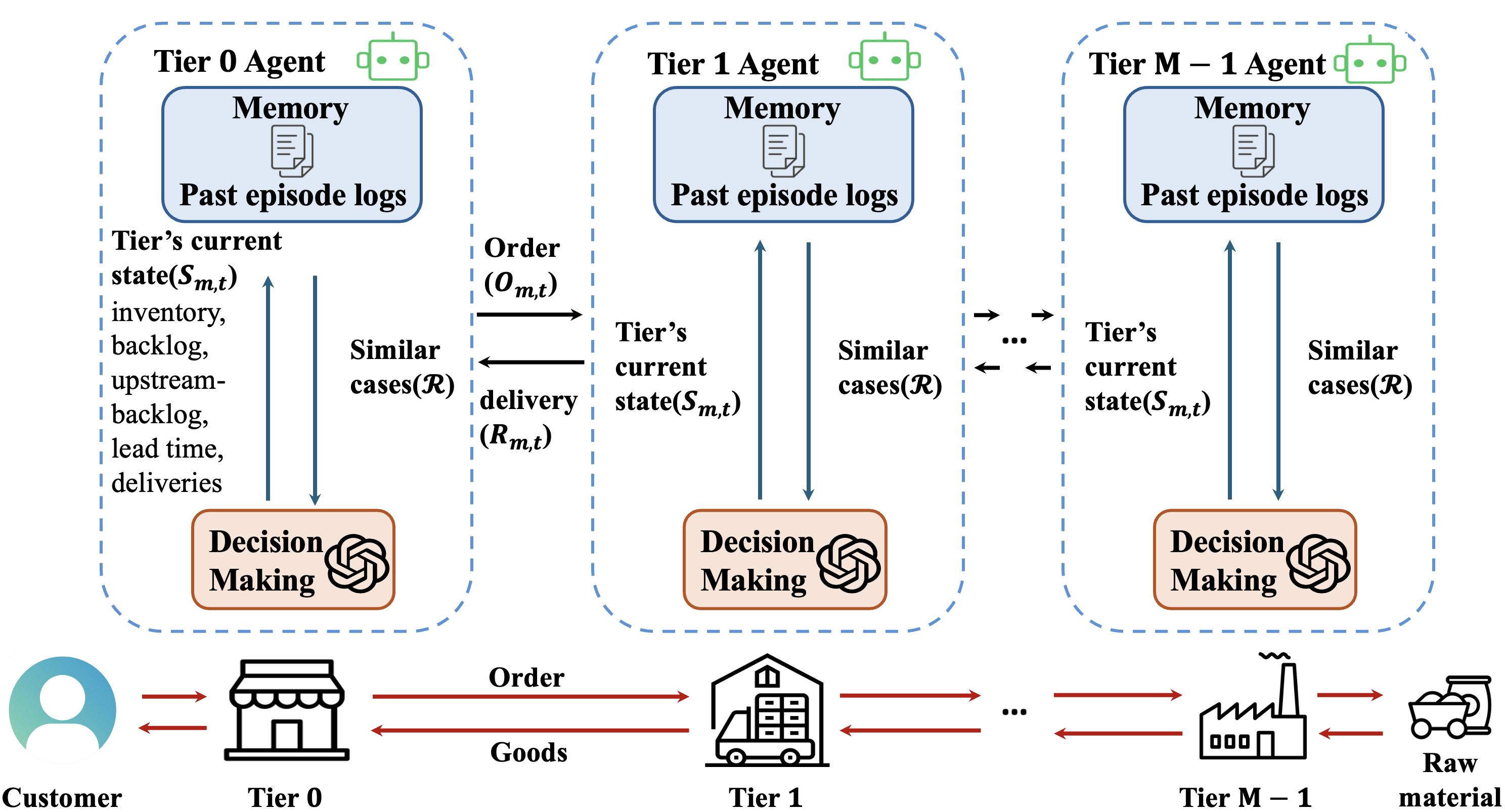
This review examines the application of large language model-based multi-agent systems to multi-echelon inventory management, demonstrating performance comparable to reinforcement learning approaches.
Effective supply chain management often struggles with dynamic, multi-echelon inventory control, despite advancements in optimization techniques. This paper, ‘AI Agent Systems for Supply Chains: Structured Decision Prompts and Memory Retrieval’, investigates large language model (LLM)-based multi-agent systems as a novel approach, demonstrating that incorporating historical experience via similarity matching significantly enhances adaptability and achieves performance comparable to reinforcement learning. Our results show that a carefully prompted LLM-based system can determine optimal ordering policies, even in restricted scenarios, and that a novel agent, AIM-RM, outperforms benchmarks across diverse supply chain conditions. Could this represent a viable pathway toward more robust and self-improving supply chain systems capable of navigating unforeseen disruptions?
Navigating the Complexities of Modern Supply Chains
Modern supply chains, extending across continents and involving numerous intermediaries, present a significant escalation in complexity beyond the scope of traditional inventory management techniques. Historically, businesses focused on managing stock within a single location or, at most, a simple two-tiered system; however, today’s multi-echelon networks-spanning raw material suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and ultimately, consumers-demand a fundamentally different approach. This intricacy arises not simply from the increased number of actors, but from the interconnectedness and dependencies between them. Delays or disruptions at any single point can cascade rapidly throughout the entire system, leading to stockouts, increased costs, and diminished customer satisfaction. Consequently, methods designed for linear, predictable flows are proving inadequate for navigating these dynamic, layered networks, necessitating innovative solutions that prioritize visibility, agility, and resilience.
Modern supply chains grapple with inherent volatility, demanding a shift from reactive strategies to proactive, intelligent systems. Consumer behavior, geopolitical events, and even unforeseen disruptions like pandemics introduce significant fluctuations in demand, while lead times – the delay between order and delivery – are increasingly subject to unpredictable variables. Traditional forecasting methods, built on historical data, often prove inadequate in these conditions, leading to either stockouts and lost sales or excessive inventory carrying costs. Consequently, businesses are turning to adaptive approaches, leveraging technologies like machine learning and real-time data analytics to dynamically adjust inventory levels, optimize routing, and anticipate potential disruptions before they impact the flow of goods. These intelligent systems aim not just to respond to change, but to anticipate it, creating resilient supply chains capable of navigating an increasingly uncertain world.
The pursuit of optimal inventory levels represents a perpetual balancing act for modern businesses. Effectively managing stock isn’t simply about minimizing holding costs; it’s equally crucial to ensure products are available when and where customers demand them, safeguarding service levels and preventing lost sales. This challenge is amplified by the inherent trade-offs involved: reducing inventory to cut costs increases the risk of stockouts, while maintaining high stock levels ties up capital and incurs storage expenses. Contemporary supply chains, characterized by globalization and intricate networks, further complicate this endeavor, requiring sophisticated strategies that move beyond traditional, static approaches to account for fluctuating demand, variable lead times, and the cascading effects of disruptions – ultimately, success hinges on a dynamic equilibrium between cost efficiency and superior customer service.
Conventional inventory management systems frequently employ static models-representations of supply chains assuming predictable conditions-but these approaches struggle when confronted with the realities of modern logistics. Real-world supply chains are rarely stable; they are characterized by fluctuating demand, variable lead times, and unforeseen disruptions-factors that render static models inaccurate and ineffective. These models often fail to account for the ripple effect of changes at one stage of the supply chain on others, leading to suboptimal inventory levels, increased costs, and potential service failures. Consequently, businesses are increasingly recognizing the need for dynamic models-those capable of adapting to changing conditions and incorporating real-time data-to achieve true supply chain resilience and efficiency.
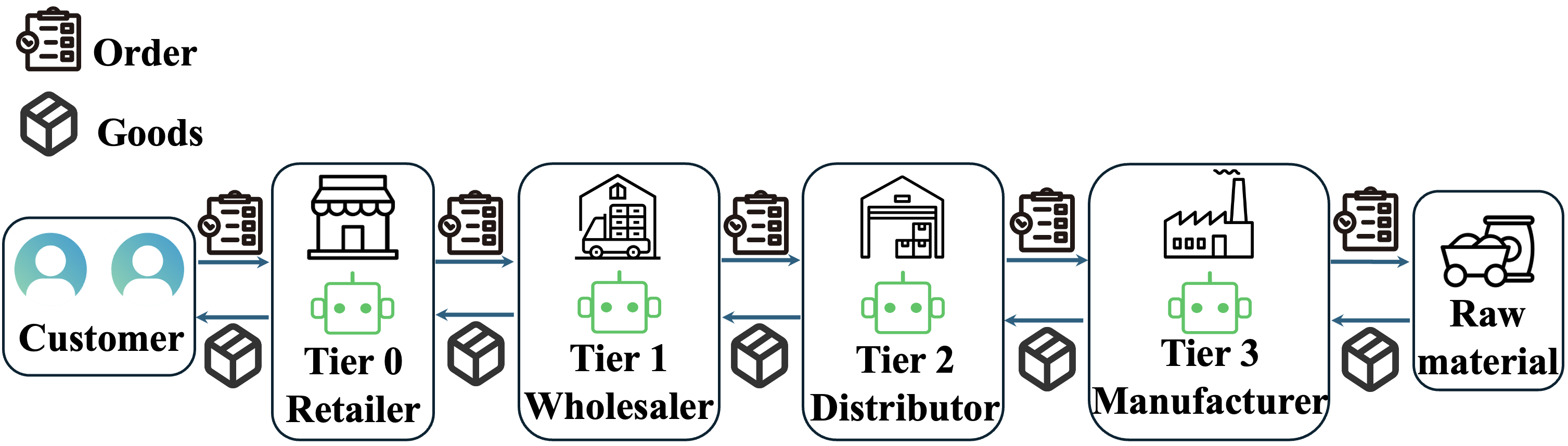
Introducing AIM-RM: An Adaptive, Intelligent System for Inventory Management
AIM-RM represents a novel approach to inventory management, leveraging a MultiAgentSystem architecture grounded in a Large Language Model (LLM) Foundation Model. This system departs from traditional methodologies by employing multiple interacting agents, each responsible for specific inventory-related tasks or data analysis. The LLMFoundationModel provides the core reasoning and predictive capabilities, enabling the agents to process complex data sets and generate informed decisions. This architecture is specifically designed to address the inherent complexities of inventory challenges, such as demand forecasting, lead time variability, and supply chain disruptions, offering a dynamic and scalable solution compared to static, rule-based systems.
Unlike traditional inventory management systems reliant on pre-defined parameters and static forecasts, AIM-RM incorporates a continuous learning mechanism fueled by historical data. The system analyzes HistoricalExperience, encompassing past demand, lead times, and supply disruptions, to identify patterns and refine its predictive capabilities. This allows AIM-RM to dynamically adjust inventory levels and replenishment strategies in response to evolving conditions such as seasonality, promotional activities, or unexpected shifts in customer behavior. The adaptive nature of the system minimizes reliance on manual intervention and improves resilience against unforeseen circumstances, leading to optimized inventory performance over time.
AIM-RM is designed for application within Multi-Echelon Inventory Management (MEIM) systems, addressing inventory optimization across multiple levels of a supply chain. Unlike traditional approaches that often optimize each echelon independently, AIM-RM considers the interdependencies between tiers – from raw material suppliers to manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. This holistic approach allows the system to make coordinated decisions regarding order quantities, safety stock levels, and replenishment policies at each echelon, minimizing total inventory costs and improving service levels across the entire supply chain. The system’s adaptive capabilities enable it to respond to fluctuating demand, lead times, and disruptions at any tier, ensuring optimized inventory positioning throughout the MEIM structure.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a key component of AIM-RM’s decision-making process. This technique combines the reasoning capabilities of a Large Language Model (LLM) with information retrieved from a knowledge base. Prior to generating a response or recommendation, the system queries relevant data sources to identify information pertinent to the current inventory challenge. This retrieved data is then incorporated into the LLM’s prompt, providing contextual grounding and ensuring that decisions are based on the most up-to-date and relevant information available, rather than solely on the LLM’s pre-trained knowledge. This process mitigates the risk of hallucination and improves the accuracy and reliability of the system’s output.
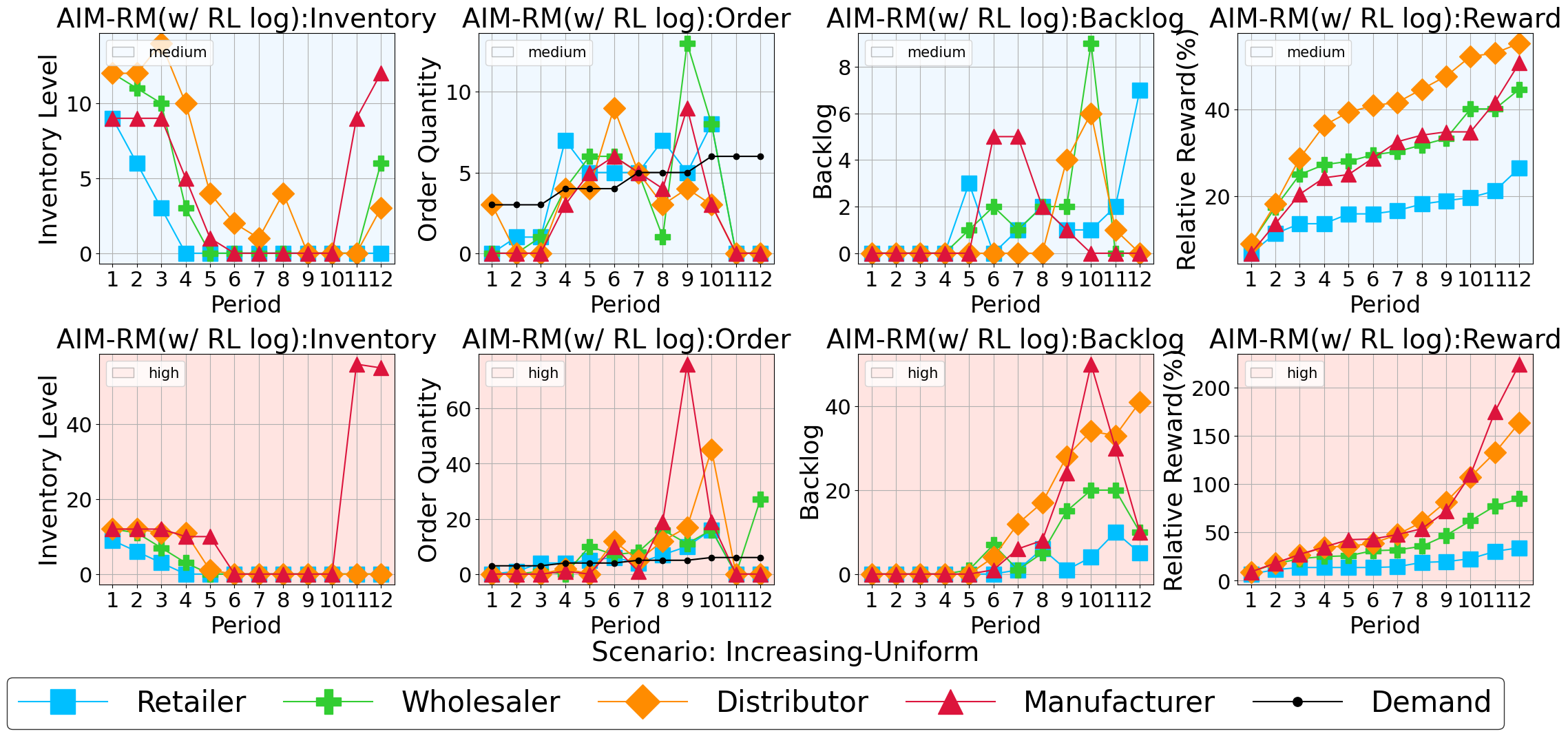
Demonstrating Intelligent Optimization Through Rigorous Testing
AIM-RM employs Reinforcement Learning (RL) to iteratively improve its inventory management decisions. The system functions by defining a state space representing inventory levels and demand forecasts, an action space encompassing order quantities, and a reward function that quantifies cost reduction and efficiency gains. Through interaction with a simulated supply chain environment, the RL agent learns an optimal policy – a mapping from states to actions – that maximizes cumulative rewards. This adaptive learning process allows AIM-RM to dynamically adjust ordering strategies based on observed performance, leading to minimized costs associated with holding inventory, stockouts, and order placement, and ultimately enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
The system employs a Constraint Programming Satisfiability (CP-SAT) solver to calculate optimal inventory levels by formulating the inventory management problem as a set of constraints and objectives. These constraints incorporate factors such as warehouse capacity, supplier lead times, demand forecasts, and ordering costs. The solver then identifies inventory configurations that satisfy these constraints while maximizing a defined objective function, typically minimizing total inventory holding and ordering costs or maximizing service levels. This approach allows for the consideration of complex, interconnected dependencies within the supply chain and facilitates the determination of feasible and cost-effective inventory policies.
AIM-RM builds upon established inventory management techniques, specifically the BaseStockPolicy, by integrating adaptive learning capabilities. Rather than relying on static, pre-defined parameters for reorder points and order quantities, AIM-RM utilizes Reinforcement Learning to dynamically adjust these values based on observed demand patterns, lead times, and cost factors. This extension allows the system to move beyond the limitations of traditional BaseStockPolicy implementations, which require manual recalibration and are less responsive to changing market conditions. The adaptive learning component effectively transforms the static BaseStockPolicy into a dynamic, self-optimizing strategy, improving inventory control and reducing associated costs.
The Adaptive Inventory Management with Reinforcement learning (AIM-RM) agent demonstrated performance levels statistically equivalent to established Reinforcement Learning algorithms, specifically Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) and Multi-Agent PPO (MAPPO), when applied to multi-echelon inventory management challenges. Evaluation across diverse supply chain scenarios confirmed the AIM-RM agent’s robust adaptability and consistent performance. Quantitative analysis revealed the AIM-RM system achieved the highest average reward among all tested configurations in a significant number of tested scenarios, indicating its capacity to optimize inventory control and minimize associated costs under varying conditions.
Maintaining optimal inventory levels necessitates careful management of Safety Stock, which represents a buffer against uncertainties in supply and demand. The AIM-RM system addresses this through dynamic adjustment of Safety Stock based on real-time data streams encompassing order fulfillment rates, lead times, and demand forecasts. Predictive analytics, utilizing historical data and identified trends, are employed to anticipate potential disruptions and proactively modify Safety Stock levels. This contrasts with static Safety Stock policies which fail to account for fluctuating conditions. By continuously evaluating and adapting Safety Stock, AIM-RM aims to minimize stockouts and associated costs while simultaneously reducing excess inventory and holding expenses.
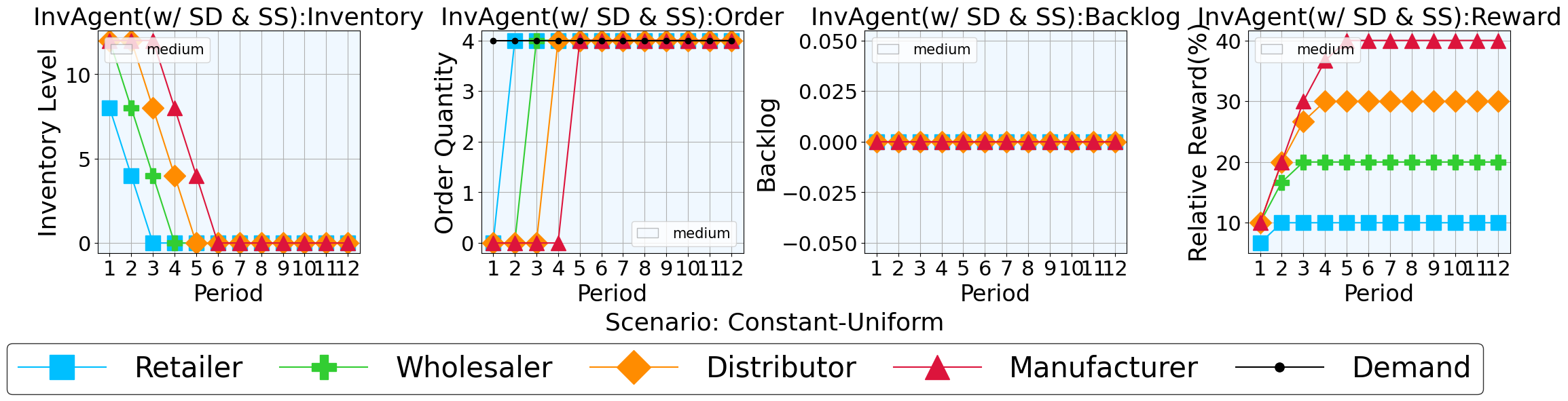
Mitigating the ‘Overthinking’ Problem in Large Language Models
Interestingly, even sophisticated Large Language Models aren’t always aided by extensive reasoning; a phenomenon dubbed ‘overthinking’ can actually decrease performance. This counterintuitive result stems from the models becoming lost in complex chains of thought, leading to errors that simpler, more direct approaches would have avoided. The foundation of AIM-RM, like many LLMs, is susceptible to this issue, where the drive to thoroughly analyze a problem inadvertently introduces inaccuracies or irrelevant details. Essentially, the model can become paralyzed by possibilities, ultimately hindering its ability to arrive at the most practical and correct solution – a testament to the fact that more computation doesn’t always equate to better results.
The architecture of this system intentionally mitigates the tendency of large language models to overthink, a phenomenon where increased reasoning steps paradoxically diminish performance. This is achieved through integrated computational limits and a focus on streamlined decision-making processes. Rather than allowing unbounded recursion or exhaustive analysis, the system employs mechanisms to curtail excessive computation, prioritizing efficient problem-solving. This design choice ensures the model converges on practical solutions without getting bogged down in irrelevant details or speculative tangents, ultimately fostering robust and reliable outputs even in complex scenarios.
AIM-RM distinguishes itself through a deliberate focus on pragmatic solutions, eschewing the tendency of some Large Language Models to get lost in convoluted reasoning. This system is engineered to prioritize actionable results over exhaustive analysis, recognizing that unnecessary complexity often diminishes performance. By streamlining the decision-making process and concentrating on core objectives, AIM-RM consistently delivers robust and reliable outputs, proving that effective problem-solving doesn’t always require the most intricate approach. This commitment to simplicity translates into a system capable of consistently meeting demands, even within dynamic and unpredictable environments.
A key indicator of AIM-RM’s reliability lies in its remarkably consistent performance, demonstrated by a standard deviation of rewards equal to zero. This signifies an absence of stochasticity – or randomness – in the large language model’s output, meaning the system consistently delivers optimal results without unpredictable variations. Unlike many LLMs prone to fluctuating performance, AIM-RM exhibits a deterministic quality, ensuring predictable and dependable outcomes across repeated evaluations. This level of consistency is not merely a statistical curiosity; it’s fundamental to building trust in the system’s decision-making, particularly in applications where even minor inconsistencies could have significant consequences.
The architecture incorporates a crucial responsiveness to fluctuating real-world conditions, specifically by monitoring both DemandTrend and LeadTime. This dynamic adaptation isn’t merely reactive; the system proactively adjusts its decision-making processes based on predicted shifts in customer demand and the anticipated duration for fulfilling requests. Consequently, the model maintains a high degree of relevance even within unstable environments characterized by unpredictable surges or declines in activity. This ensures the system consistently delivers practical solutions, rather than relying on static calculations that may quickly become outdated, ultimately enhancing its overall effectiveness and reliability in the face of volatility.
The pursuit of adaptive systems, as demonstrated by this work on multi-agent LLMs for supply chain management, echoes a fundamental principle of effective design. The study highlights how incorporating historical experiences-a form of memory retrieval-allows agents to navigate complexity and achieve performance akin to reinforcement learning. This resonates deeply with Claude Shannon’s observation that “The most important thing in communication is to convey meaning, not to transmit information.” Here, the ‘meaning’ is optimal inventory management, and the system’s ability to learn from the past – to distill essential patterns from accidental noise – is paramount to achieving it. Structure, in this case, the agent’s memory and decision-making process, dictates the system’s behavioral adaptability and ultimate success.
The Road Ahead
The pursuit of adaptive supply chains through multi-agent systems reveals a predictable pattern: initial gains from clever prompt engineering eventually encounter the limitations of static knowledge. This work, by grounding agents in retrieved experience, offers a partial, yet significant, mitigation. However, it subtly shifts the core challenge. The system’s performance now hinges not simply on what is remembered, but on the fidelity of the memory itself – and the mechanisms for discerning relevant from irrelevant experience. Documentation captures structure, but behavior emerges through interaction; the true test lies in long-term performance under genuinely novel disruptions.
A natural extension involves exploring memory architectures beyond simple retrieval. The human supply chain manager doesn’t just recall past events; they construct narratives, identifying causal links and anticipating second-order effects. Replicating this capacity – a form of embedded simulation – demands more than just larger datasets. It requires agents capable of abstraction, counterfactual reasoning, and, crucially, the ability to forget – to prune irrelevant or misleading experiences before they calcify into rigid, maladaptive behaviors.
Ultimately, the focus must move beyond optimizing for a single metric – inventory cost, for example. True resilience arises from systems that can gracefully degrade, reconfigure, and even redefine their objectives in the face of unforeseen circumstances. The question isn’t simply whether an agent can respond to disruption, but whether it can learn from it, evolving its very understanding of the system it inhabits.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.05524.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Top 15 Insanely Popular Android Games
- Did Alan Cumming Reveal Comic-Accurate Costume for AVENGERS: DOOMSDAY?
- 4 Reasons to Buy Interactive Brokers Stock Like There’s No Tomorrow
- Gold Rate Forecast
- EUR UAH PREDICTION
- ELESTRALS AWAKENED Blends Mythology and POKÉMON (Exclusive Look)
- Silver Rate Forecast
- New ‘Donkey Kong’ Movie Reportedly in the Works with Possible Release Date
- Core Scientific’s Merger Meltdown: A Gogolian Tale
- DOT PREDICTION. DOT cryptocurrency
2026-02-07 09:00