Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research reveals how to better understand and predict when customers decide not to buy, offering vital insights for marketers.
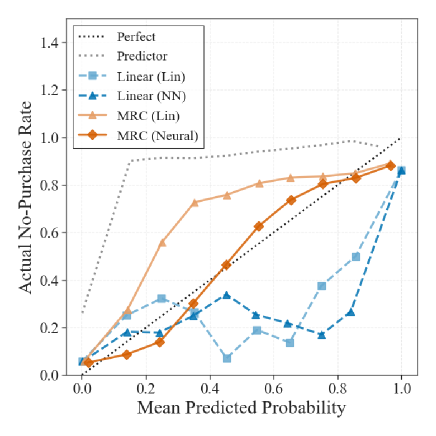
This paper presents an empirical study calibrating an imperfect auxiliary predictor to model unobserved no-purchase choice behavior and improve marketing strategy.
Estimating market size and consumer preferences is fundamentally challenged by the inability to observe unchosen alternatives, such as competitor purchases or simple non-purchase decisions. This paper, ‘Calibrating an Imperfect Auxiliary Predictor for Unobserved No-Purchase Choice’, addresses this issue by developing methods to refine predictions from external ‘auxiliary’ models that estimate the probabilities of these unobserved choices, even when those predictions are biased or miscalibrated. The authors demonstrate that, under certain conditions, a simple regression or rank-based approach can yield consistent and accurate no-purchase estimates using only observed purchase data, effectively translating imperfect predictions into statistically valid insights. How can these calibration techniques be extended to incorporate multiple auxiliary predictors and further improve downstream decision-making in assortment optimization and beyond?
Decoding the Consumer: Beyond Prediction to Understanding
The success of any marketing strategy hinges on the ability to anticipate what customers will buy, yet this seemingly straightforward goal presents a significant challenge for businesses. While historical sales data and demographic analysis offer some insight, these traditional methods frequently struggle to keep pace with the volatile nature of modern consumer preferences and the rapidly shifting market landscape. Customers are influenced by a complex interplay of factors – from social media trends and peer recommendations to economic conditions and even fleeting emotional states – making accurate prediction exceptionally difficult. Consequently, businesses must continually refine their analytical approaches, embracing more sophisticated modeling techniques and real-time data streams to move beyond simple observation and towards genuine predictive capability, all in pursuit of maximizing return on investment and maintaining a competitive advantage.
Historically, businesses relied on static demographic data and broad market segmentation to anticipate consumer needs, but these methods are increasingly proving inadequate. The accelerating pace of technological innovation, coupled with the proliferation of social media and readily available information, has fundamentally altered consumer behavior. Preferences now shift with remarkable speed, driven by trends, peer influence, and personalized experiences. Consequently, models built on past data quickly become obsolete, failing to capture the nuanced and dynamic nature of modern purchasing decisions. This necessitates a move beyond traditional analysis towards more agile and responsive strategies capable of tracking and interpreting these rapid market shifts to maintain relevance and accurately predict future demand.
For businesses navigating increasingly competitive landscapes, a nuanced comprehension of what motivates customer choices is no longer a luxury, but a fundamental requirement for sustained success. Superficial analyses of purchasing patterns prove insufficient; true advantage stems from identifying the core psychological, social, and emotional factors that underpin decision-making. This necessitates moving beyond simple demographic data and embracing methodologies that explore values, beliefs, and the intricate interplay between conscious and subconscious influences. Companies that prioritize this deeper understanding can tailor products, messaging, and experiences with remarkable precision, fostering stronger customer loyalty, driving innovation, and ultimately securing a significant competitive edge in the marketplace.
Empirical Dissection: How We Map the Path to Purchase
Empirical research forms the foundational methodology of this study, prioritizing evidence gathered through direct observation and measurement of actual purchasing behavior. This approach contrasts with theoretical or speculative analyses by focusing on quantifiable data – including transaction records, website analytics, and survey responses – to establish correlations and causal relationships. Data collection methods include both observational studies, tracking real-time consumer actions, and experimental designs, such as A/B testing of marketing interventions. The resulting dataset is then subjected to rigorous statistical analysis to validate findings and minimize the influence of subjective interpretation, thereby ensuring a practical and grounded understanding of customer behavior.
The analysis of purchasing patterns utilizes a combination of descriptive and inferential statistical techniques. Descriptive statistics, including measures of central tendency and dispersion, are employed to characterize purchasing behaviors across the dataset. Inferential statistics, such as regression analysis and correlation coefficients, are then used to identify statistically significant relationships between variables – for example, the correlation between demographic factors and purchase frequency, or the impact of promotional offers on average transaction value. Time series analysis is also implemented to detect trends and seasonality in purchasing data, while cluster analysis segments customers based on shared purchasing characteristics. Data sources include transaction records, customer demographics, and website activity logs, all subjected to rigorous data cleaning and validation procedures prior to analysis.
Cross-cultural comparison will be implemented by analyzing purchasing behavior data collected from at least five geographically and economically diverse regions – North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa. Within each region, data will be stratified by demographic factors including age, income, and education level to account for intra-regional variations. Statistical analysis, specifically ANOVA and regression modeling, will be employed to identify significant differences in purchasing preferences across these regions and to quantify the influence of cultural factors on consumer choices. This comparative approach will allow for the identification of both universal purchasing trends and region-specific anomalies, enriching the overall understanding of consumer behavior and informing localized marketing strategies.
Forecasting the Inevitable: Predictive Models and the Consumer Mind
Predictive modeling utilizes statistical techniques and historical data to forecast future sales volumes and revenue. This allows businesses to anticipate demand fluctuations, optimize inventory levels, and adjust production schedules accordingly. By analyzing past purchasing patterns, seasonality, promotional impacts, and external economic indicators, these models identify correlations and trends that inform future projections. Proactive application of these forecasts enables businesses to mitigate risks associated with overstocking or stockouts, capitalize on emerging opportunities, and ultimately improve resource allocation and profitability in response to evolving market dynamics.
Machine learning algorithms improve forecasting accuracy by identifying complex, non-linear relationships within sales data that traditional statistical methods may miss. Algorithms such as regression trees, random forests, and neural networks can process a larger volume of variables – including historical sales, promotional activity, economic indicators, and even weather patterns – to generate predictions. These algorithms aren’t limited to linear correlations; they can adapt and learn from data to identify subtle patterns and interactions, resulting in more granular and nuanced forecasts that account for a wider range of influencing factors. Furthermore, many machine learning models offer probabilistic outputs, providing not just a single point prediction, but a range of likely outcomes with associated probabilities, enabling better risk assessment and inventory management.
Longitudinal tracking of customer behavior involves the continuous monitoring of individual customer interactions and purchase histories over significant durations – typically exceeding one year. This extended observation period allows for the identification of patterns and trends that are not discernible through cross-sectional analysis. Specifically, it enables the differentiation between transient fluctuations and sustained shifts in purchasing preferences, improving forecast accuracy by accounting for seasonality, lifecycle effects, and evolving customer needs. Data collected through these methods include purchase frequency, monetary value of transactions, product categories purchased, and channel preferences, providing a comprehensive view of customer behavior and facilitating more reliable predictive modeling.
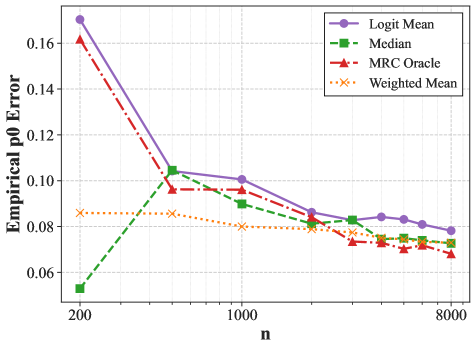
Beyond Correlation: Scaling Insight and the Pursuit of Validity
The foundation of reliable scientific insight increasingly relies on the breadth of data employed in analysis. Researchers are discovering that smaller datasets, while easier to manage, often fail to capture the full complexity of the phenomena under investigation, leading to findings that are specific to the sample rather than representative of the broader population. Utilizing large-scale datasets-those encompassing a significantly wider range of variables and observations-allows for the identification of subtle, yet critical, patterns that would otherwise remain obscured. This approach not only bolsters the robustness of the results-meaning they are less susceptible to random variations-but also dramatically enhances their generalizability, increasing confidence that the conclusions apply beyond the immediate study and to real-world scenarios. The sheer volume of information present in these datasets demands increasingly sophisticated analytical tools, but the potential rewards-more accurate, more reliable, and more broadly applicable knowledge-are substantial.
The refinement of predictive models increasingly relies on sophisticated analytical techniques that move beyond traditional statistical methods. Approaches such as machine learning algorithms, including neural networks and support vector machines, are capable of identifying non-linear relationships and intricate interactions within complex datasets that might otherwise remain hidden. These methods not only enhance the precision of predictions but also reveal subtle patterns and previously unrecognized correlations, offering a more nuanced understanding of the phenomena under investigation. By leveraging these advanced tools, researchers can build models that are more robust, adaptable, and capable of generalizing beyond the specific data used for training, ultimately leading to more reliable and insightful conclusions.
The pursuit of statistically significant results is paramount to establishing the trustworthiness of any scientific investigation. Throughout the analytical process, researchers diligently monitor p-values and confidence intervals to confirm observed effects are unlikely due to random chance. Maintaining this statistical rigor isn’t merely about adhering to a threshold; it’s about building a robust foundation for conclusions, ensuring they represent genuine relationships rather than spurious correlations. Without consistent statistical significance, even large datasets or complex models can yield misleading interpretations, hindering the advancement of knowledge and potentially leading to flawed applications of research findings. Therefore, a commitment to statistical validity serves as a critical safeguard against uncertainty and a cornerstone of credible scientific discovery.

The study meticulously dissects customer purchasing behavior, revealing the inherent imperfections within predictive models-a necessary consequence of attempting to map complex human choices. This pursuit of understanding, even in the face of inevitable error, echoes Marvin Minsky’s assertion: “You can’t always get what you want, but if you try sometimes you find you get what you need.” The research doesn’t seek a flawless prediction, but rather a calibrated auxiliary predictor, acknowledging that a useful model often arises from recognizing and accounting for its limitations. Every exploit starts with a question, not with intent, and this paper skillfully questions the assumptions underpinning traditional marketing strategies, leading to potentially valuable insights despite the ‘imperfect’ nature of the data.
Beyond the Purchase: Avenues for Dissection
The effort to calibrate prediction of unobserved non-purchase isn’t about achieving flawless foresight. It’s about acknowledging the inherent noise, the ‘negative’ data points that so often get smoothed over in the pursuit of conversion rates. One wonders if the imperfections in the auxiliary predictor aren’t bugs, but signals-indications of latent preferences, unarticulated needs, or simply the beautiful messiness of human decision-making. Future work shouldn’t focus solely on minimizing error, but on interpreting it. What systematic deviations reveal more about the customer than successful predictions ever could?
The current framing, even in its empirical rigor, implicitly accepts purchase as the ultimate metric. But what if the true value lies in understanding why someone doesn’t buy? A shift towards modeling ‘non-choice’ with the same granularity as ‘choice’ could unlock entirely new dimensions of customer understanding. The challenge isn’t simply to predict behavior, but to reverse-engineer the internal calculus that leads to inaction.
Ultimately, this line of inquiry demands a more adversarial approach to marketing strategy. Rather than optimizing for immediate gains, the field might benefit from deliberately ‘stress-testing’ consumer models-seeking out the points of failure, the edge cases, the behaviors that defy prediction. It’s in these anomalies that the most profound insights are likely to be found.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.11505.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Securing the Agent Ecosystem: Detecting Malicious Workflow Patterns
- NEAR PREDICTION. NEAR cryptocurrency
- DOT PREDICTION. DOT cryptocurrency
- Wuthering Waves – Galbrena build and materials guide
- USD COP PREDICTION
- Silver Rate Forecast
- EUR UAH PREDICTION
- USD KRW PREDICTION
- Games That Faced Bans in Countries Over Political Themes
2026-02-14 17:44