Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research demonstrates how artificial intelligence can analyze prediction markets to uncover relationships between different contracts, potentially leading to better forecasts and trading strategies.

This paper explores the use of agentic AI, powered by large language models, to cluster prediction market contracts and discover hidden relationships for improved information aggregation.
Prediction markets, while powerful tools for aggregating information, are often fragmented by overlapping questions and hidden relationships between contracts. This limitation motivates the research presented in ‘Semantic Trading: Agentic AI for Clustering and Relationship Discovery in Prediction Markets’, which introduces an agentic AI pipeline capable of autonomously identifying coherent topical groupings and uncovering dependencies-both correlated and anti-correlated-within these markets. Results demonstrate that this approach accurately predicts relational outcomes and translates them into trading strategies yielding significant returns. Could agentic AI unlock a more efficient and profitable paradigm for navigating and exploiting the latent semantic structure of prediction markets?
The Fragility of Human Forecasting: A Foundation for Rationality
Conventional forecasting methods frequently falter when addressing intricate, real-world occurrences, largely because of systematic cognitive biases embedded within human judgment. These biases-such as confirmation bias, where individuals favor information confirming existing beliefs, or anchoring bias, where initial information unduly influences subsequent estimates-distort assessments of probability and potential outcomes. Furthermore, traditional approaches often rely on limited datasets and expert opinions, failing to adequately capture the full spectrum of relevant information dispersed across various sources. This reliance on narrow perspectives can lead to inaccurate predictions, particularly in rapidly evolving situations where unforeseen factors play a significant role. Consequently, attempts to anticipate future events, whether in financial markets, geopolitical landscapes, or scientific advancements, are frequently plagued by systematic errors and an underestimation of inherent uncertainty.
Prediction markets represent a departure from traditional forecasting methods by harnessing the collective intelligence of a diverse group of participants. Platforms like Polymarket allow individuals to place wagers on the outcome of future events, effectively creating a continuously updated probability assessment. This mechanism incentivizes accurate predictions because those who correctly anticipate outcomes profit from their knowledge, while incorrect predictions result in financial loss. The resulting market prices, therefore, reflect the aggregated beliefs of numerous independent forecasters, often outperforming expert opinions or simple extrapolations. This dispersed information aggregation is particularly valuable when dealing with complex, uncertain events where no single individual possesses all the relevant knowledge, offering a dynamic and potentially highly accurate signal for anticipating future realities.
The true power of prediction markets hinges not just on gathering predictions, but on understanding the intricate web of connections between events. Identifying correlated occurrences – where one outcome meaningfully influences another – is crucial for refining forecasts and uncovering hidden risks or opportunities. Sophisticated analytical techniques, including network analysis and machine learning algorithms, are being employed to map these relationships, revealing how seemingly disparate events might be linked through complex causal chains. By accurately modeling these correlations, prediction markets can move beyond simple point predictions to offer nuanced probabilistic assessments, enhancing their utility for strategic decision-making and proactive risk management. This ability to discern patterns and dependencies represents a significant step towards harnessing collective intelligence for more effective foresight.
The reliability of prediction markets hinges critically on the swift and precise determination of event outcomes, a function largely entrusted to entities known as oracles. These oracles act as bridges between the market and the real world, gathering and verifying information to definitively resolve predictions. Without accurate and timely resolution, incentives within the market become misaligned, eroding trust and diminishing predictive power. A delayed or incorrect resolution can lead to disputes, reduced participation, and ultimately, a less efficient aggregation of knowledge. Consequently, significant effort is devoted to developing robust oracle mechanisms – ranging from decentralized networks of data providers to sophisticated algorithms – that ensure the integrity and trustworthiness of prediction market outcomes, allowing these markets to function as genuine signals of collective intelligence.
Agentic Systems: The Pursuit of Autonomous Insight
Traditional artificial intelligence systems have largely relied on static models trained on fixed datasets, limiting their adaptability and requiring retraining for new information. Agentic AI signifies a departure from this approach by implementing dynamic, autonomous agents. These agents are not simply predictive models but rather entities capable of independent reasoning, planning, and execution within defined environments. This shift enables continuous learning and adaptation without explicit reprogramming, allowing the system to respond to changing conditions and discover novel insights. The core difference lies in the agent’s ability to proactively gather information, formulate hypotheses, and test them through interaction with its environment – a capability absent in conventional static models.
The Agentics Framework facilitates the construction of autonomous agents through a structured data management system utilizing typed schemas, termed ATypes. These ATypes define the permissible data types and relationships for each agent, ensuring data integrity and enabling efficient processing. Specifically, ATypes allow for the categorization and validation of market data, agent interactions, and discovered relationships. This structured approach contrasts with traditional unstructured data handling, enabling more reliable and scalable agent operation. The framework’s use of typed schemas supports modularity, allowing for the easy integration of new data sources and agent capabilities without compromising system stability or data accuracy.
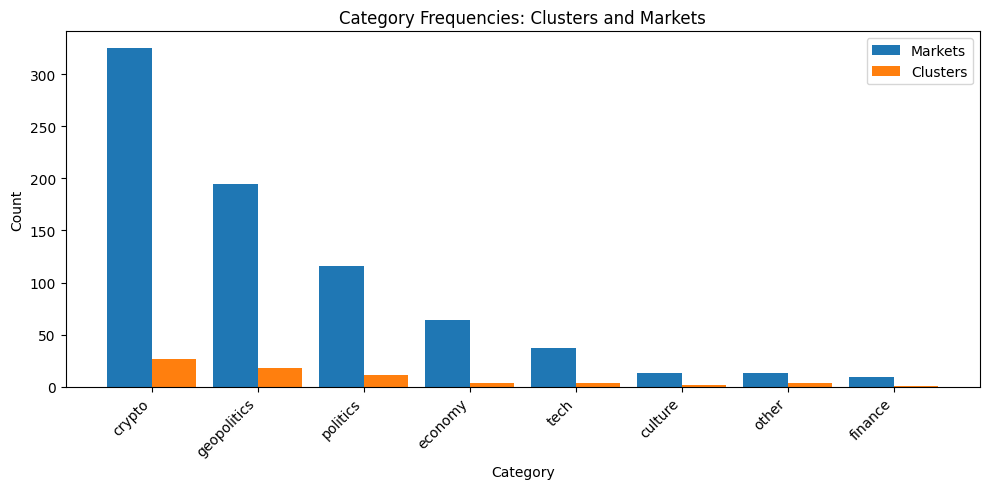
Market clustering is performed by LLM-based Agents utilizing a Vector Space Model to determine semantic similarity between markets. This process involves embedding market descriptions into a high-dimensional vector space, where proximity indicates similarity. Clustering algorithms then group markets based on these vector representations. Evaluation during April-June trials demonstrated an average cluster accuracy of 63.9%, indicating the system’s capacity to correctly group markets with related characteristics. Accuracy is determined by comparing the agent-generated clusters against a pre-defined ground truth of known market relationships.
The system facilitates Relationship Discovery by identifying economically meaningful links between distinct markets. Utilizing the clustered market data generated via the Vector Space Model, the agentic AI analyzes semantic similarities beyond immediately apparent connections. This analysis results in the proposal of relationships, representing potential correlations that may not be evident through traditional methods. These proposed relationships are not simply statistical coincidences; they are grounded in semantic analysis of market characteristics, suggesting potential avenues for economic insight and strategic decision-making. The system outputs these relationships as structured data, allowing for further investigation and validation by domain experts.

Decoding Market Interdependence: Beyond Correlation to Causation
The agentic approach to market analysis systematically identifies predicted correlations through the establishment of two link types: Same-Outcome Links and Different-Outcome Links. Same-Outcome Links denote instances where two events are predicted to result in the same market outcome, despite potentially differing causal paths. Conversely, Different-Outcome Links indicate predictions of divergent market outcomes following two related events. This systematic identification is achieved through computational modeling and allows for a structured representation of predicted relationships, moving beyond simple correlative observation to highlight anticipated directional dependencies between market factors.
Identified links between events, as determined by the agentic approach, represent more than correlational data; they indicate potential causal mechanisms or shared underlying dependencies. While statistical association merely observes events occurring together, these links attempt to model why events co-occur. This distinction is critical because causal relationships allow for predictive power beyond simple pattern recognition; understanding dependencies enables the agent to anticipate outcomes even when observed patterns are disrupted. The framework prioritizes identifying these substantive connections, moving beyond surface-level statistical observations to infer the functional relationships between events within a modeled system.
The Model Context Protocol facilitates improved predictive accuracy by enabling the agent to integrate and analyze data from heterogeneous sources. This protocol defines a standardized method for accessing, validating, and converting data formats, including structured databases, unstructured text, and real-time data streams. By establishing a consistent framework for data ingestion and preprocessing, the agent minimizes errors arising from data inconsistencies and maximizes the utility of available information. The protocol also incorporates mechanisms for data provenance tracking, allowing the agent to assess data reliability and prioritize information based on source credibility and temporal relevance, ultimately leading to more robust and accurate predictions of market correlations.
Logical transduction within the framework functions as a process of converting data from heterogeneous sources into a standardized, interpretable format. This involves applying defined rules and algorithms to resolve semantic differences, handle varying data granularities, and address inconsistencies in representation. Specifically, it enables the system to map diverse input data – including time series, textual reports, and structured databases – into a common logical language suitable for reasoning and analysis. The process ensures data compatibility and facilitates the identification of relationships between events, ultimately supporting the prediction of market correlations by enabling consistent data interpretation across all sources.
Translating Insight into Action: A Predictive Trading Strategy
A predictive market strategy, framed as a leader-follower approach, leverages identified relationships to exploit momentary pricing discrepancies and generate alpha-that is, excess return-from market inefficiencies. This strategy doesn’t rely on predicting the absolute outcome, but rather on anticipating how market participants will react to information as it unfolds; the ‘leader’ identifies potential mispricings based on predictive signals, initiating trades before broader market consensus solidifies, while the ‘follower’ component adapts to and profits from the subsequent price correction. By consistently capitalizing on these subtle, short-lived inefficiencies, the system aims to deliver consistent, positive returns, effectively extracting value where others perceive only noise. The success of such a strategy hinges on speed and accuracy in resolving event outcomes, enabling timely trade execution and payoff calculations.
The successful implementation of a predictive trading strategy is fundamentally dependent on the swift and accurate resolution of events. Delays or inaccuracies in determining event outcomes directly impact payoff calculations, potentially negating any predictive advantage. A strategy predicated on identifying relationships between events requires definitive confirmation – or denial – of those relationships to trigger appropriate trades and realize profits. Without timely event resolution, the system struggles to differentiate between correct and incorrect predictions, leading to miscalculated returns and eroding the strategy’s overall effectiveness. Consequently, the infrastructure supporting the trading strategy must prioritize rapid and reliable event outcome reporting to ensure the integrity of the system and maximize potential gains.
The successful implementation of a predictive trading strategy hinges on a robust and flexible market infrastructure, and Polymarket provides precisely that. Its Limit Order Books enable traders to specify desired entry and exit prices, allowing for precise execution of trades based on predicted outcomes. Crucially, the platform’s Conditional Token Framework automates the payoff process; tokens are minted and distributed to successful predictions, and conversely, tokens are burned or redistributed in cases of incorrect predictions. This automated system minimizes counterparty risk and ensures transparent, verifiable outcomes. By combining these features, Polymarket facilitates the seamless execution of complex trading strategies predicated on probabilistic forecasts, effectively translating predictive accuracy into quantifiable financial returns and creating a dynamic environment for information discovery.
The predictive model demonstrated a 72.6% accuracy in identifying relationships within the target market, initially translating to a substantial return on investment. June trials showcased a peak ROI of 47.5%, indicating a potentially lucrative trading strategy. However, subsequent performance in July revealed a significant downturn, with ROI declining to -12.3%. This fluctuation highlights the dynamic nature of market conditions and suggests that while the model possesses predictive capability, consistent profitability requires ongoing adaptation and risk management. The observed variance underscores the importance of continuous monitoring and refinement of the trading strategy to maintain positive returns in evolving environments.

The pursuit of discerning relationships within prediction markets, as detailed in the study, echoes a fundamental tenet of computational elegance. Donald Knuth once stated, “Premature optimization is the root of all evil.” While not directly about trading, the sentiment applies profoundly; hastily implemented strategies, lacking a provable understanding of the underlying market relationships, are unlikely to yield sustainable results. The agentic AI approach, by focusing on relationship discovery and market clustering, prioritizes establishing a solid, logically sound foundation – a ‘correct’ understanding – before attempting optimization. This methodical approach, valuing provability over mere empirical success, aligns perfectly with a mathematically pure perspective on efficient systems.
What’s Next?
The demonstrated capacity of agentic AI to discern relationships within prediction markets, while promising, merely scratches the surface of a far more fundamental challenge. Current approaches treat the identification of these relationships as largely empirical – a pattern-finding exercise. A truly elegant solution, however, demands a shift towards provable causal inference. The correlations observed are insufficient; a rigorous mathematical framework is needed to establish why certain contracts cluster and influence each other, not simply that they do. This necessitates moving beyond the descriptive power of large language models and integrating formal methods of reasoning.
A critical limitation lies in the inherent noisiness of prediction market data. The signal, representing genuine insight, is often obscured by the random fluctuations of human sentiment and irrational exuberance. Future work must prioritize the development of robust filtering techniques, potentially drawing upon tools from information theory and statistical mechanics, to isolate the underlying mathematical structure. The current reliance on LLMs, while effective for initial exploration, risks enshrining spurious correlations as predictive features.
Ultimately, in the chaos of data, only mathematical discipline endures. The true potential of agentic AI in economic forecasting will not be realized until these systems move beyond pattern recognition and embrace the principles of formal verification. A predictive model is not merely one that appears to work on historical data; it is one whose correctness can be mathematically guaranteed.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2512.02436.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- 2025 Crypto Wallets: Secure, Smart, and Surprisingly Simple!
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Brown Dust 2 Mirror Wars (PvP) Tier List – July 2025
- Banks & Shadows: A 2026 Outlook
- ETH PREDICTION. ETH cryptocurrency
- HSR 3.7 story ending explained: What happened to the Chrysos Heirs?
- The 10 Most Beautiful Women in the World for 2026, According to the Golden Ratio
- Gay Actors Who Are Notoriously Private About Their Lives
- 9 Video Games That Reshaped Our Moral Lens
- Zack Snyder Shares New Ben Affleck Batman Image: ‘No Question — This Man Is Batman’
2025-12-03 07:33