Remembering is Key: How Agents are Building Long-Term Memory
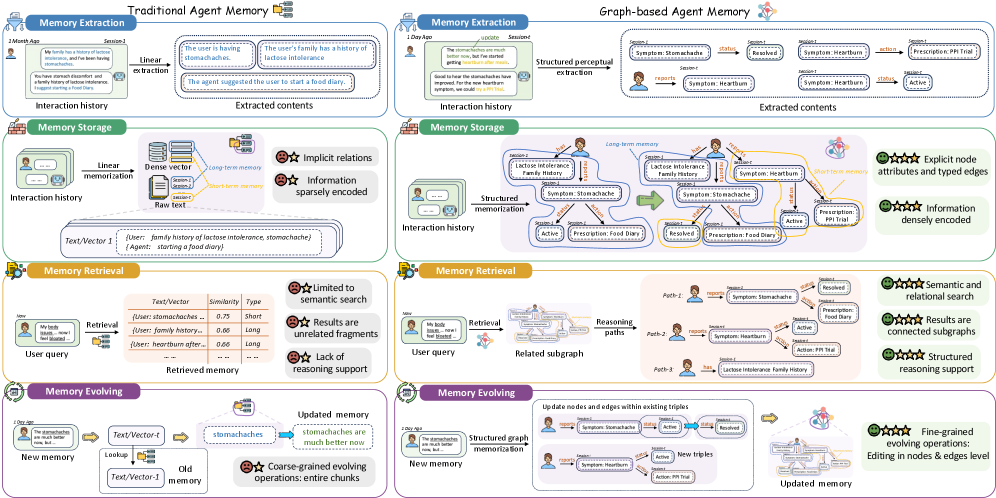
This review explores the emerging field of graph-based memory systems designed to equip AI agents with the ability to learn, adapt, and retain information over extended periods.

This review explores the emerging field of graph-based memory systems designed to equip AI agents with the ability to learn, adapt, and retain information over extended periods.
A new study evaluates the capacity of large language models to tackle both established and open challenges in graph theory, revealing limitations in original mathematical reasoning.
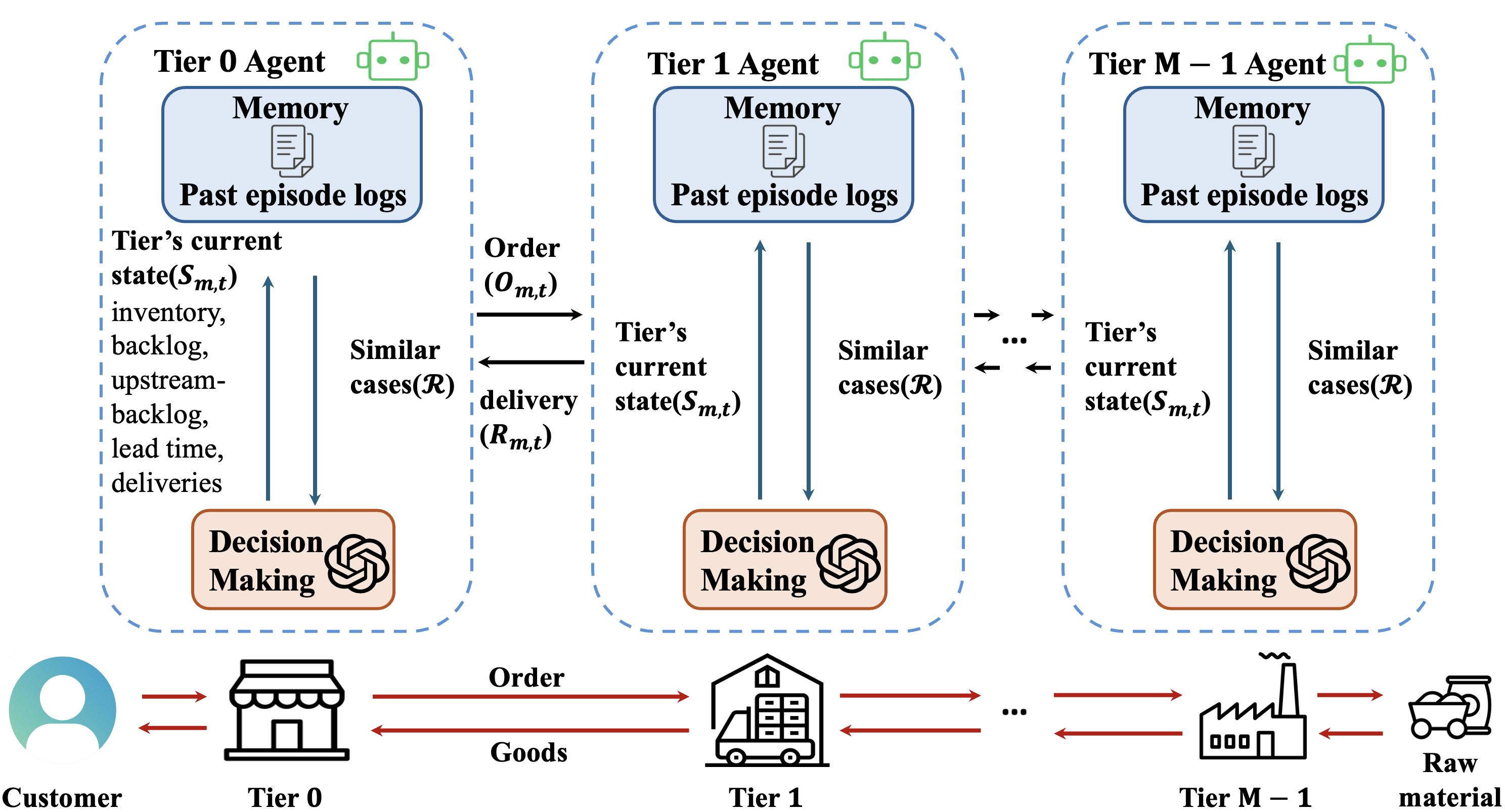
New research explores how intelligent, collaborative AI systems can optimize complex supply chain operations through learned experience.
New research shows artificial intelligence can assess how appealing and easy to understand a visualization is, but struggles to automatically identify intentional deception.
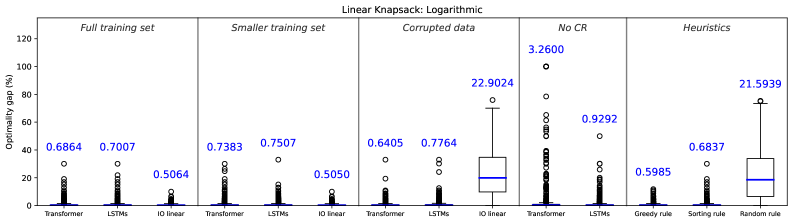
A new approach leverages the power of transformer models to directly predict solutions for discrete optimization problems, sidestepping the need for traditional inverse optimization techniques.
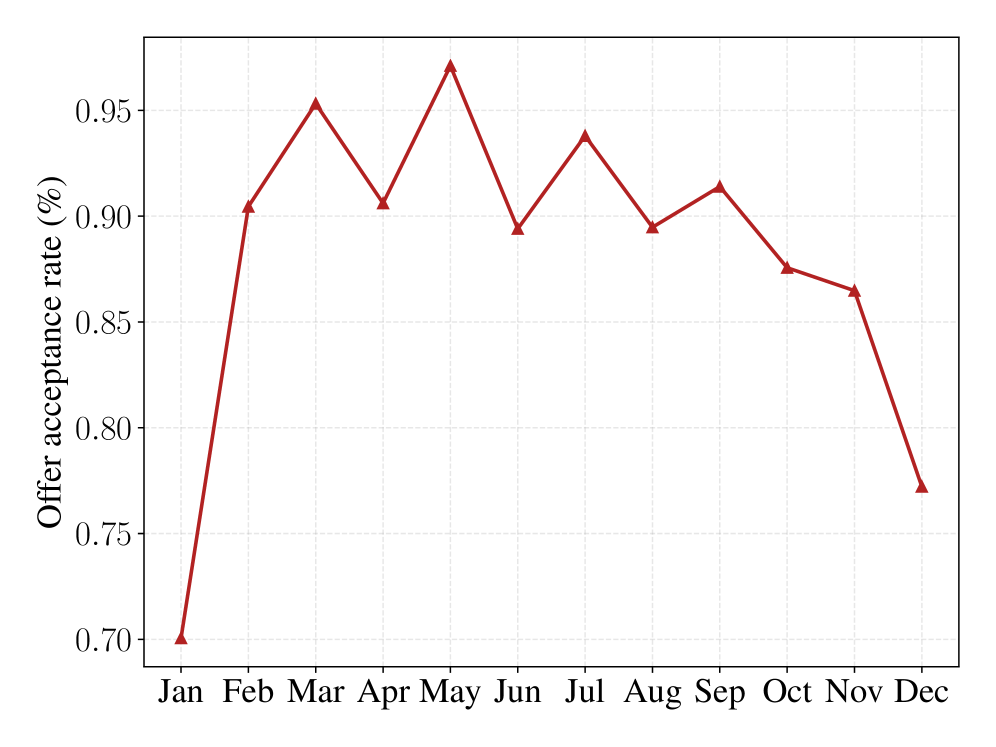
Current heart transplant policies can be gamed, and new research argues that machine learning must account for strategic behavior to ensure fair and efficient organ distribution.
A new framework, CFRecs, uses graph neural networks and counterfactual reasoning to deliver more effective and actionable recommendations for both buyers and sellers in the competitive real estate market.
A new deep learning framework, Multi-AD, boosts anomaly detection performance by transferring knowledge between seemingly unrelated imaging applications.
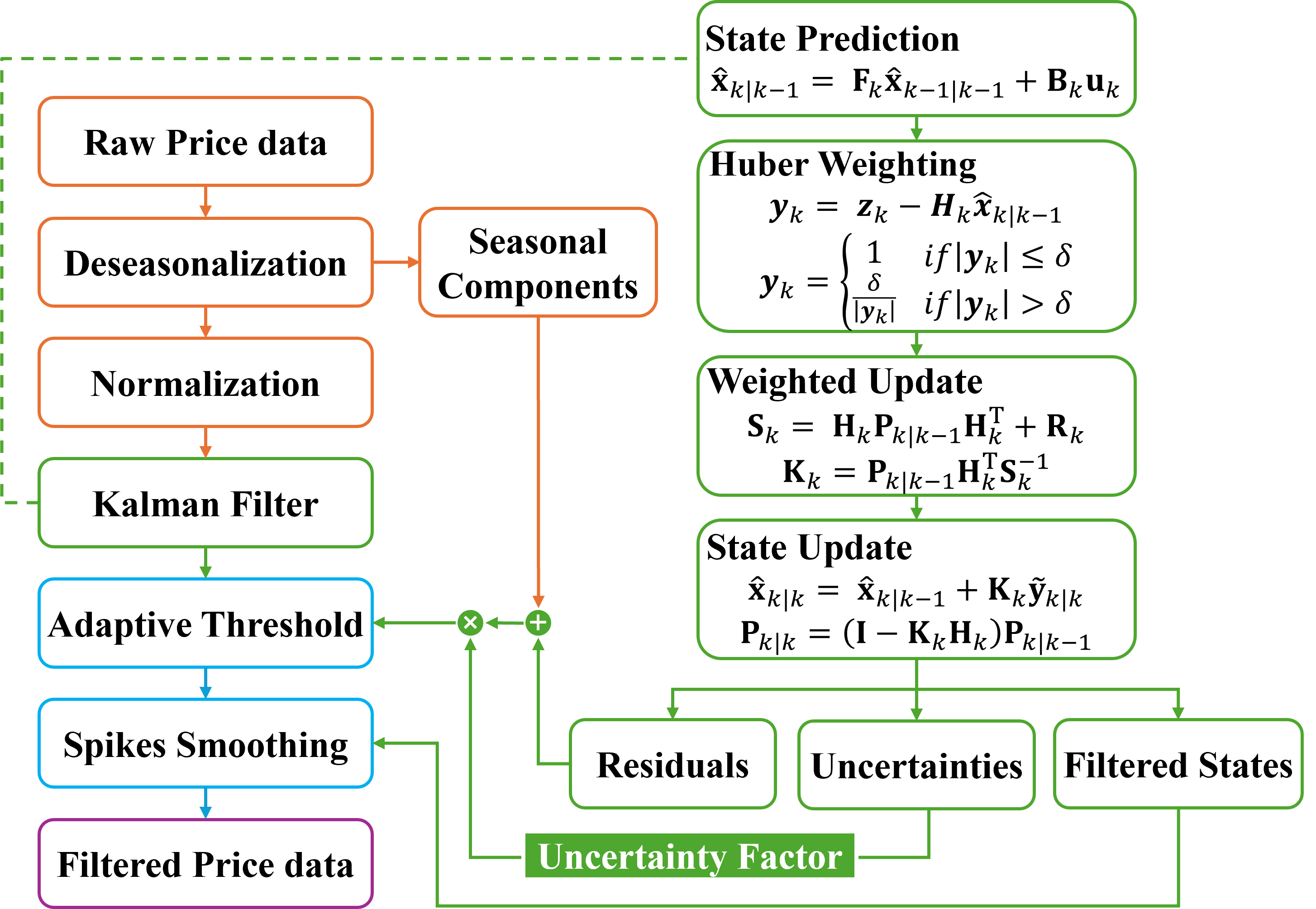
New research demonstrates the power of advanced time series models to accurately forecast day-ahead electricity prices, even in highly dynamic environments.
A new system leverages graph-based learning and reinforcement learning to dramatically accelerate and improve the efficiency of systematic literature reviews.