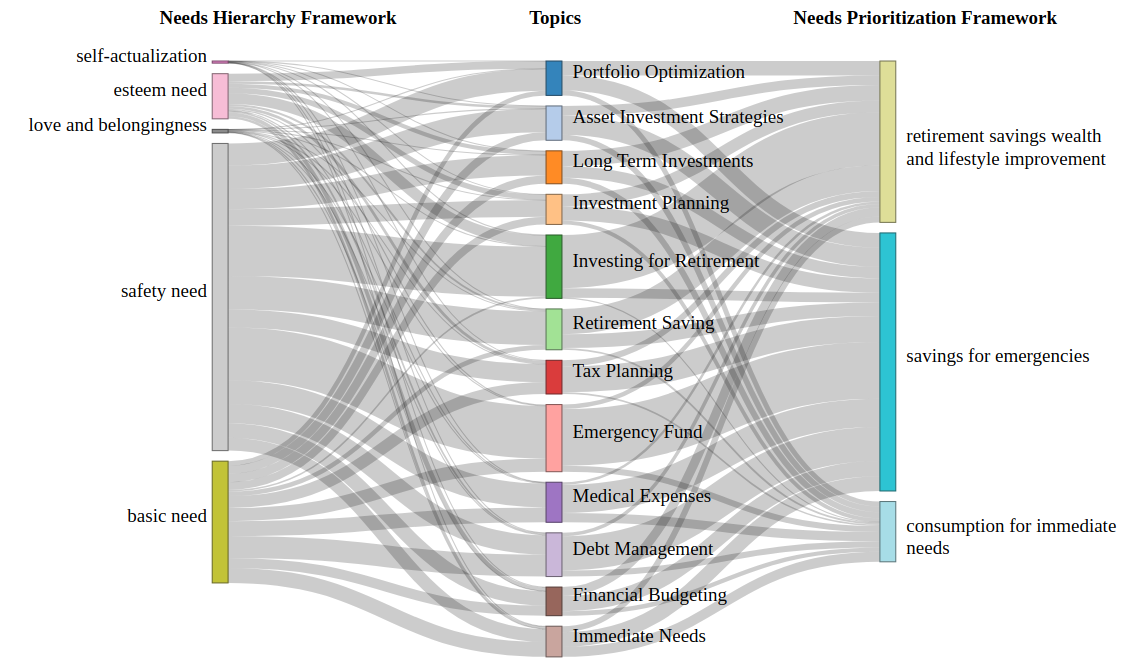
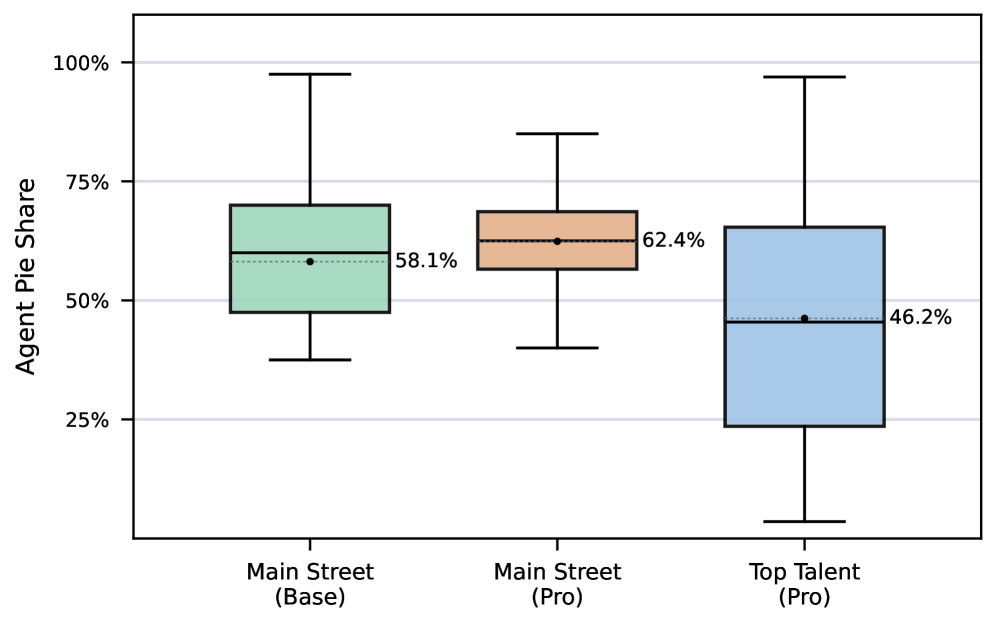
Decoding the Neural Network Mind: A New Approach to Understanding AI Behavior
Researchers have developed a novel diffusion model to map and interpret the complex internal states of large neural networks, offering new ways to control and analyze their decision-making processes.
![Specular reflections, proving difficult to replicate in forged faces due to the mathematical foundations of the Phong illumination model [latex]I = r + a\cos\theta [/latex], are leveraged by the proposed SRI-Net to identify inconsistencies and expose manipulations undetectable by spatial or frequency-based forgery detection methods.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.06452v1/x1.png)
![The study demonstrates a robust linear relationship between the [latex]W1W1[/latex] magnitude and stellar mass for galaxies lacking spectral energy distribution estimates, with propagated uncertainties on [latex]log_{10}(M_{\star})[/latex] typically around ±0.05 dex-though peaking at intermediate masses where dust content and star-formation histories introduce greater diversity.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.06492v1/figs/predicted_err_vs_mass.png)
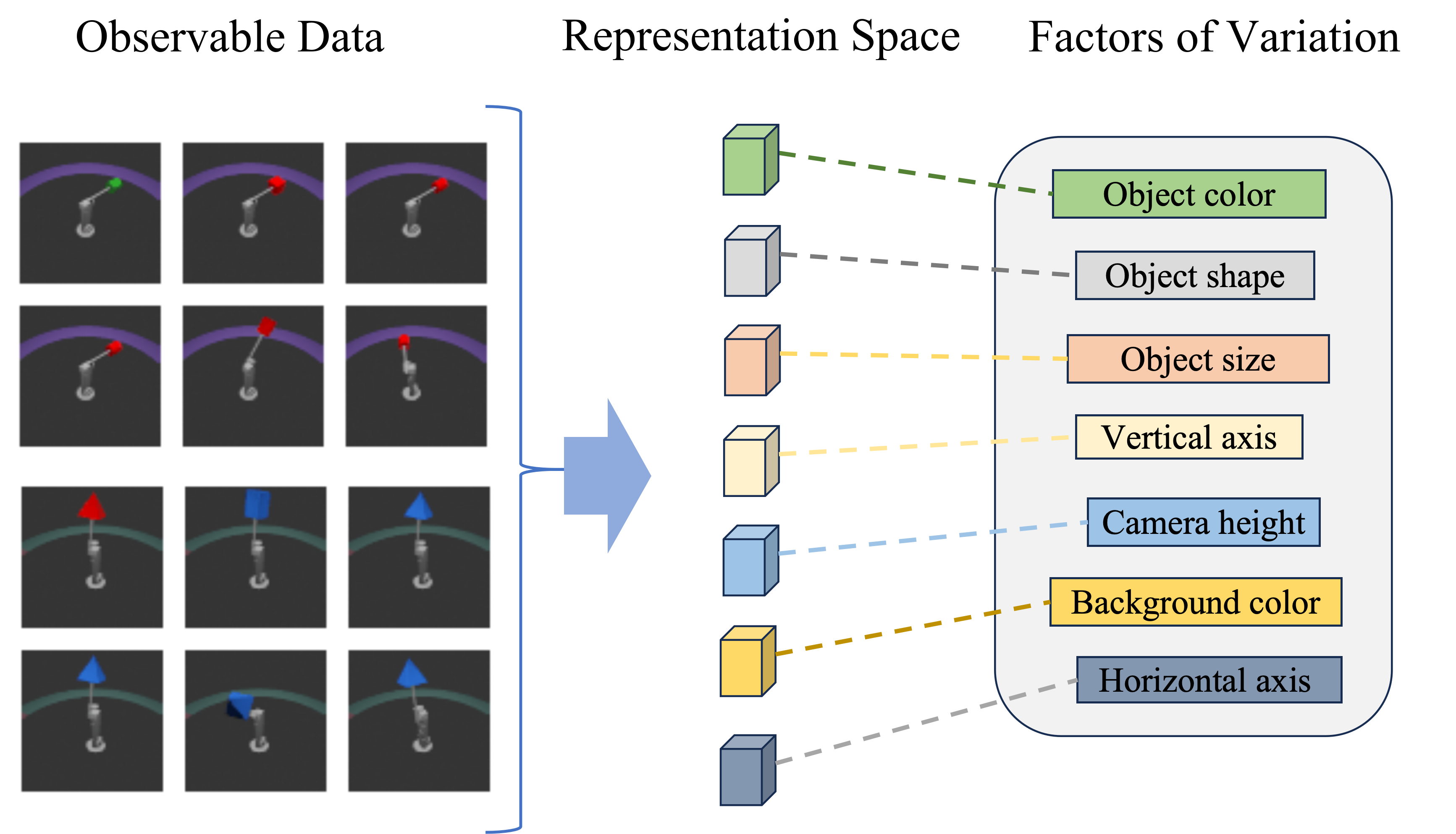
![Spatially-adaptive mixture-of-experts leverage Sobel edge detection [latex] \nabla I [/latex] to dynamically refine feature maps, enabling a nuanced understanding of image structure and localized processing within a neural network.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.05100v1/x2.png)