Decoding Galaxy Spectra with Deep Learning
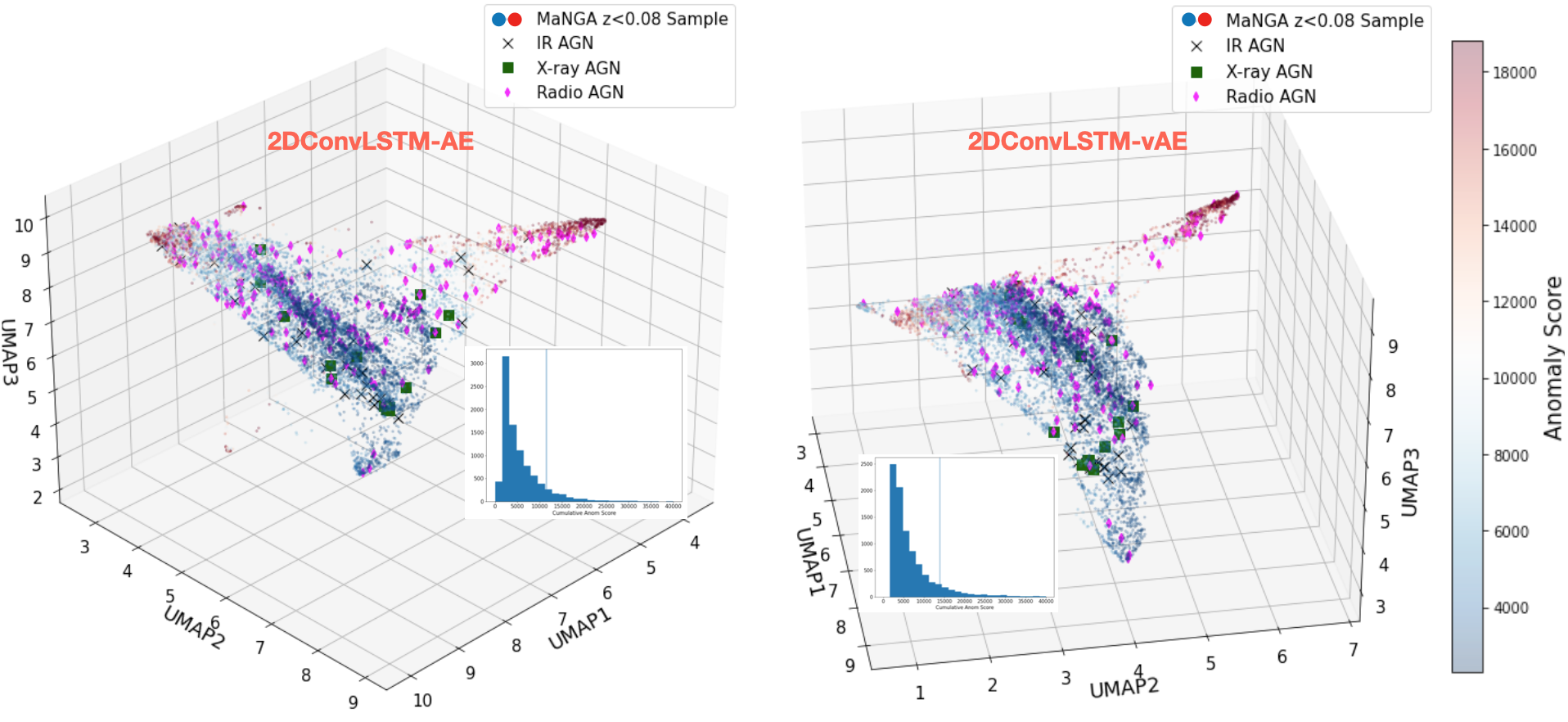
New research leverages unsupervised neural networks to analyze the complex spectral fingerprints of galaxies, paving the way for the discovery of unusual celestial objects.

New research leverages unsupervised neural networks to analyze the complex spectral fingerprints of galaxies, paving the way for the discovery of unusual celestial objects.
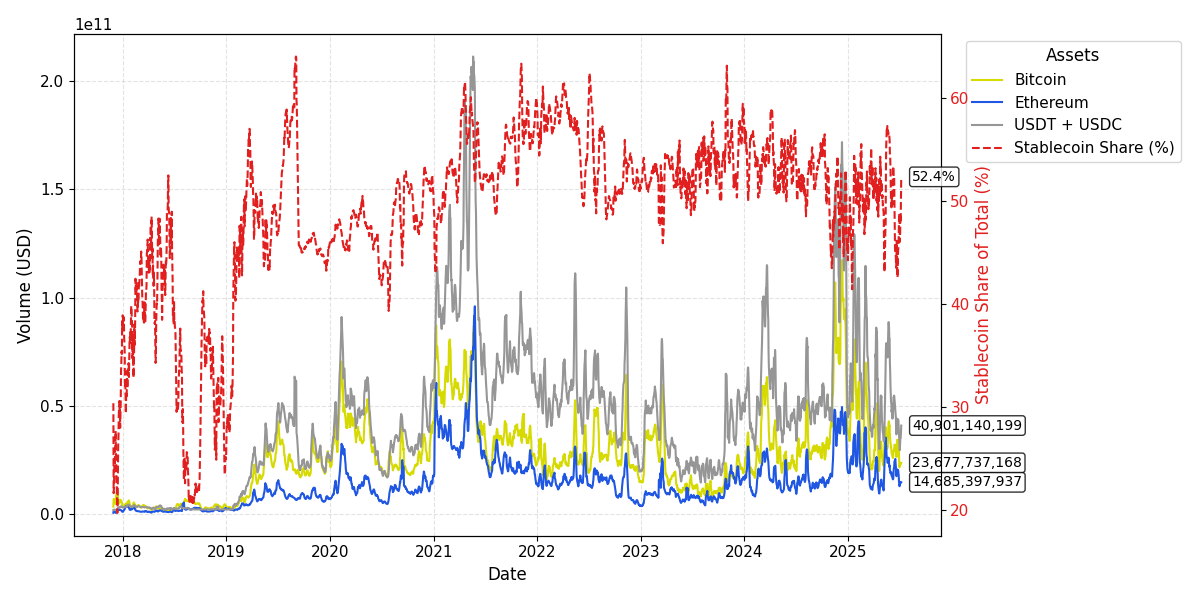
A new study reveals effective strategies for detecting money laundering within stablecoin transactions on the Ethereum blockchain.
![Information frictions arise from the interplay between the complexity of disclosure-quantified as [latex] \mathcal{D} [/latex]-and the unpredictability inherent in reporting, measured by [latex] \mathcal{U} [/latex], establishing a structural relationship that governs the efficient transmission of information.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17895v1/x1.png)
New research reveals that computational velocity, not just information access, now dictates price discovery, creating a growing disconnect between market efficiency and investor confidence.
![The TTS-GAN architecture, detailed in reference [18], leverages a generative adversarial network to synthesize speech, effectively bridging the gap between text and audible expression.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.17865v1/TTS-GAN.png)
A new approach leverages generative AI to expand limited financial datasets, improving the accuracy of deep learning models during market turbulence.
New research reveals that the methods used to align large language models create consistent, measurable patterns that can unintentionally amplify existing biases in complex AI systems.
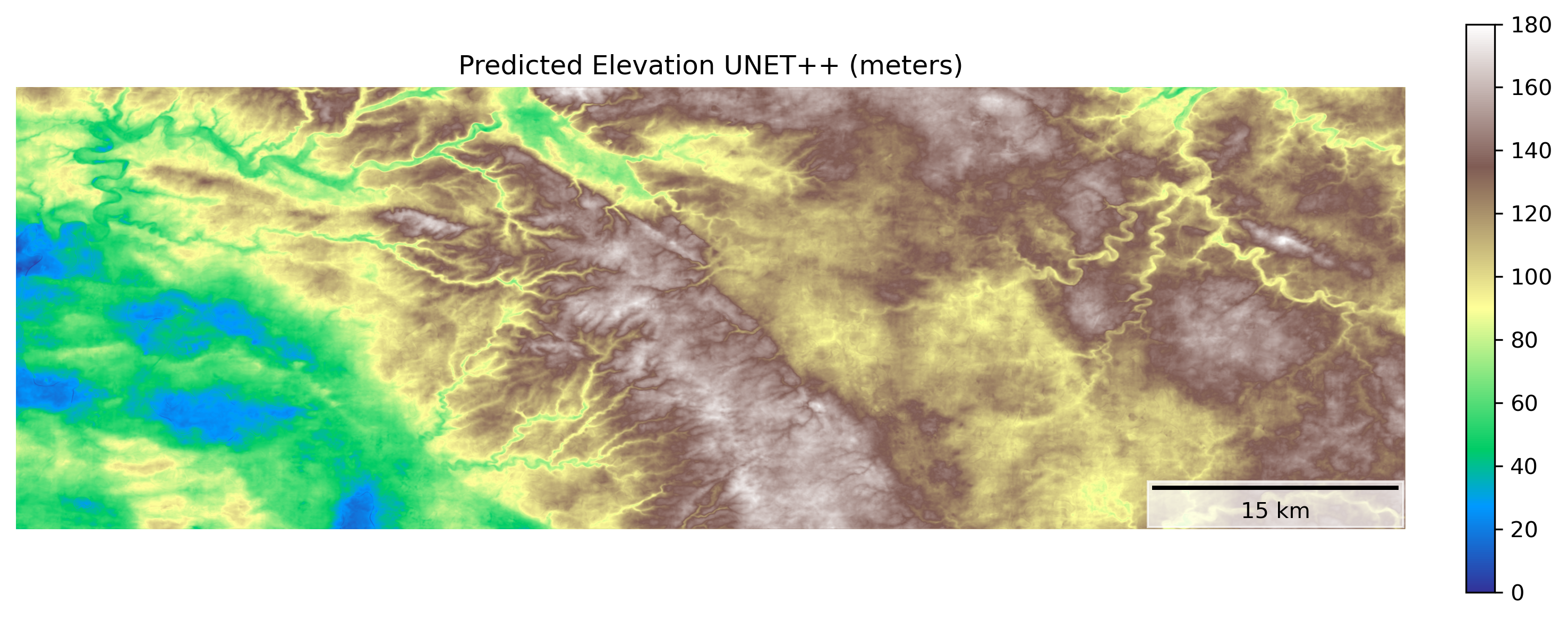
New research reveals how artificial intelligence can accurately infer elevation data from global geospatial embeddings.
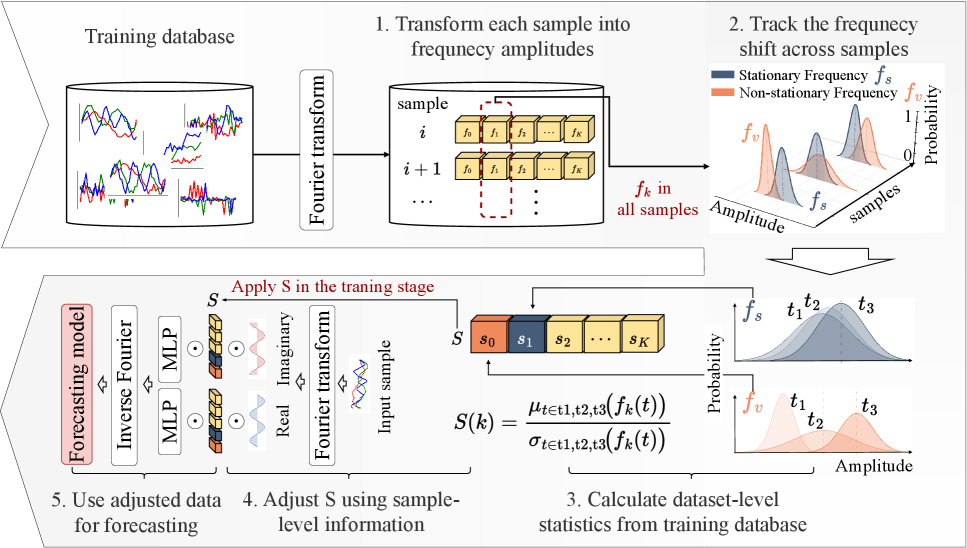
A new approach isolates stable frequency components in time series data to improve forecasting accuracy and resilience to changing conditions.
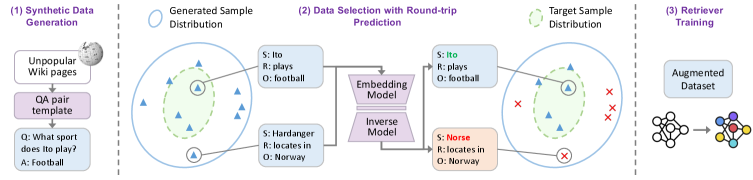
Researchers have developed a data augmentation framework that leverages round-trip prediction to significantly improve the performance of dense retrieval systems on challenging, long-tail question answering tasks.
New research reveals how accounting for incomplete demand information can drastically improve inventory management and reduce costly overstocking or stockouts.
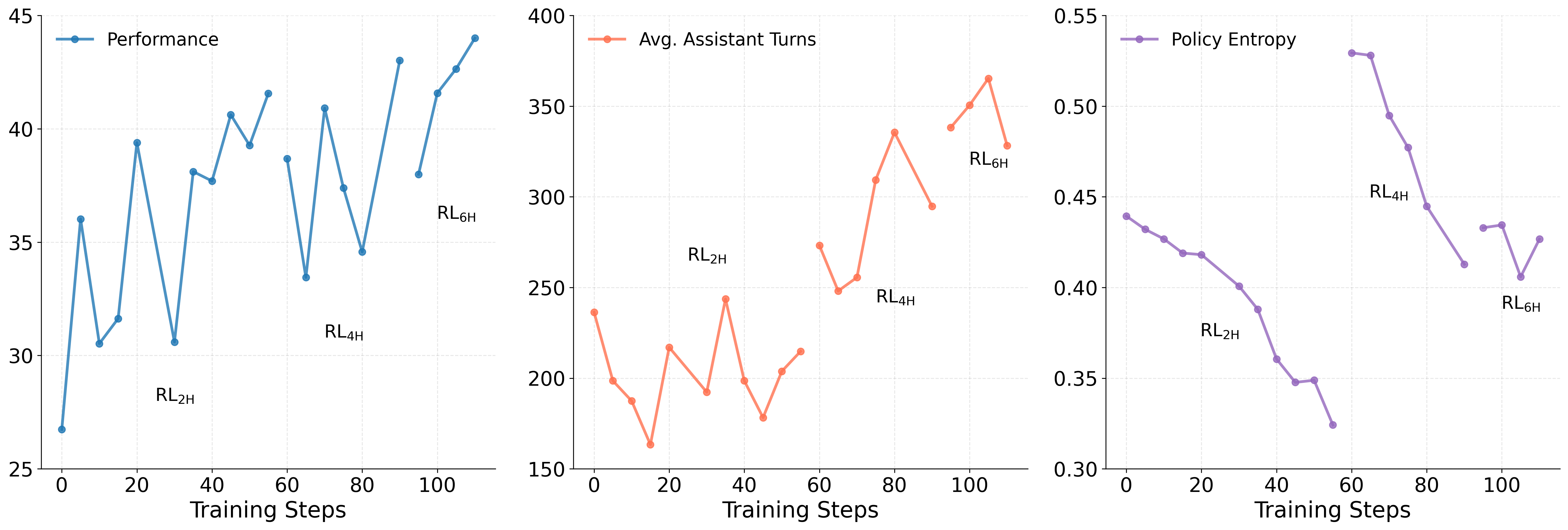
Researchers have developed a new agent capable of planning and executing tasks that require extended reasoning and action sequences, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with large language models.