In just a few days before the 2024 Bitcoin halving, experts predict a major change in Bitcoin’s economic structure. This change will result in a decrease in Bitcoin’s inflation rate, which is the pace at which new Bitcoins enter circulation, to levels lower than those of gold – historically known for having low inflation.
This discovery warrants a more detailed analysis of its potential impact on Bitcoin, gold, and investors’ decisions regarding the future of digital and conventional asset classes.
Understanding the Halving
The Bitcoin network undergoes a halving approximately every four years, which is a built-in feature in its blockchain protocol. During this event, the reward given to miners for validating transactions and creating new blocks is decreased by half. For instance, the current reward is 6.25 bitcoins per block, but following the next anticipated halving on April 18th, this reward will be reduced to 3.125 bitcoins per block. This mechanism helps regulate the number of Bitcoins in circulation and replicates the scarcity characteristics of rare metals, thereby providing protection against inflation for Bitcoin as a currency.
Bitcoin’s Inflation Rate Post Halving
Now, every block mined on the Bitcoin network takes around 10 minutes and produces around 328,500 new bitcoins each year. After the next halving event, this number will decrease to roughly 164,250 bitcoins produced annually. At the time of the halving, it is predicted that around 19.7 million bitcoins will be in circulation, with a total supply limit of 21 million. This leads to an estimated post-halving inflation rate of about 0.83% per year.
Gold Vs Bitcoin: Inflation Rate Comparison
Instead of this: “In contrast, gold, which has long represented stability and a shield against inflation, experiences an annual increase of approximately 1% to 1.5% in its total above-ground supply, thanks to new mining production.”
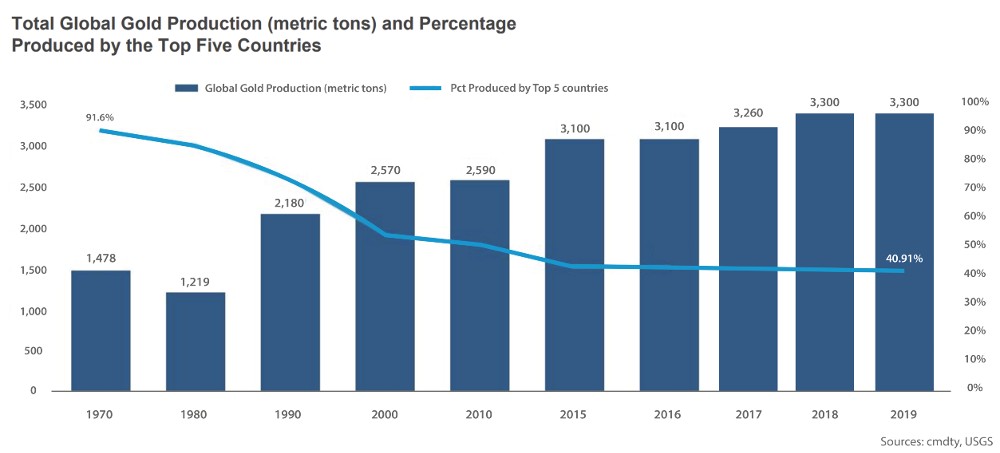
Global annual gold production has been consistent for decades. Source Barchart
Gold is added to the world’s supply through mining technology and geological availability, along with market demand and economic factors. Though these elements can cause variations, the rate at which gold enters the market has surprisingly stayed consistent. This consistency underlines gold’s role as a reliable “safe haven” asset.
After 2024, the projected annual inflation rate for Bitcoin is around 0.83%, which is lower than gold’s minimum inflation rate. This signifies an important shift for Bitcoin, moving from a risky investment to a more dependable form of value storage, a characteristic historically linked with gold.
Bitcoin – Finally The New Safe Haven?
As Bitcoin continues to gain traction, it raises the intriguing possibility: might this digital currency take on some of gold’s long-standing protective roles in uncertain economic conditions? Despite Bitcoin’s history of price fluctuations, its limited supply and diminishing inflation make it a strong contender for safe haven status.
The labeling of Bitcoin as a “safe haven” asset akin to gold is a contentious issue among finance professionals. To determine the correlation between Bitcoin and gold, it’s important to examine various aspects and viewpoints.
Price Behavior and Correlation
- Volatility: Bitcoin is known for its high volatility compared to traditional safe haven assets like gold. This volatility stems from various factors including market sentiment, regulatory news, technological developments, and macroeconomic factors that do not typically affect gold prices in the same manner.
- Market Dynamics: The market dynamics of Bitcoin are considerably different from those of gold. Bitcoin’s market is relatively young, having been around since 2009, and it experiences large swings in price due to its nascent industry status and speculative interest. Gold, by contrast, has been a recognized store of value for millennia and is integrated into various sectors such as jewelry and electronics, in addition to its investment attributes.
- Reaction to Economic Stress: Gold has historically risen in times of economic uncertainty or inflation since it is considered a tangible asset with intrinsic value. Bitcoin, sometimes referred to as “digital gold,” has had instances where it has increased in value during times of market stress, but its reaction to such events is less consistent. For example, during the initial months of the COVID-19 pandemic, Bitcoin initially fell sharply in March 2020 before recovering and eventually starting a significant bull run, whereas gold displayed more consistent growth during the same period.
Statistical Correlation
- Empirical Data: Over the last five years, statistical analyses show that the correlation between Bitcoin and gold is generally weak. There are periods of slight positive correlation, particularly during times of heightened market stress, but these are not consistently maintained.
- Correlation Coefficient: The correlation coefficient between Bitcoin and gold fluctuates, typically ranging from slightly negative to mildly positive. This indicates that while both assets can sometimes react similarly to certain macroeconomic stimuli, their price movements are not strongly aligned.
Narrative vs. Reality
- Investor Perception: The perception of Bitcoin as a safe haven may be driven more by narrative and investor sentiment than by fundamental attributes. While some investors treat Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation, similar to gold, this usage is not universally accepted or observed in market data.
- Market Maturity: Bitcoin’s market is evolving, and its role may also change over time. What it is today could be different in the next decade, potentially aligning more closely with traditional assets or carving out a unique niche.
Conclusion
According to real-world information over the past five years, the idea that Bitcoin functions similarly to gold as a safe haven investment isn’t consistently true. Although both assets can be seen as shields against specific risks, their market actions and underlying foundations vary greatly. As a result, Bitcoin stands out as a distinct asset class, unlike traditional safe havens such as gold.
As the Bitcoin halving in 2024 draws near, a significant decrease in Bitcoin’s inflation rate compared to gold is expected. This momentous occasion signifies an important milestone for Bitcoin as it strives for market stability akin to gold. While it remains uncertain if Bitcoin will eventually match gold in terms of stability, the halving event is certain to impact Bitcoin’s evolution as a valuable asset class. Keeping a close eye on these developments is advisable for investors and market observers, as they have the power to shape Bitcoin’s future trajectory and possibly redefine what it means to be a safe-haven asset in the digital realm.
Read More
- Apothecary Diaries Ch.81: Maomao vs Shenmei!
- 30 Best Couple/Wife Swap Movies You Need to See
- Gachiakuta Chapter 139: Rudo And Enjin Team Up Against Mymo—Recap, Release Date, Where To Read And More
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Netflix’s ‘You’ Season 5 Release Update Has Fans Worried
- Every Minecraft update ranked from worst to best
- Batman and Deadpool Unite: Epic DC/Marvel Crossover One-Shots Coming Soon!
- Who was Peter Kwong? Learn as Big Trouble in Little China and The Golden Child Actor Dies at 73
- Ncuti Gatwa Exits Doctor Who Amidst Controversy and Ratings Crisis!
- Mobile MOBA Games Ranked 2025 – Options After the MLBB Ban
2024-04-17 10:54