On Tuesday, Jerome Powell, the Federal Reserve chair, hinted that planned interest rate reductions could be delayed past the originally anticipated timeline due to persisting high inflation figures. During a discussion with Bank of Canada Governor Tiff Macklem at the Wilson Center in Washington, Powell pointed out the surprising longevity of elevated inflation levels and indicated that the Federal Reserve would continue keeping interest rates at their current levels until there is clearer evidence indicating progress towards their 2% inflation goal.
Based on Bloomberg’s report, Powell made his remarks following three successive months of U.S. inflation figures surpassing forecasts by analysts, which weakened the burgeoning faith among policymakers.
The Consumer Price Index for Urban Consumers in the US, as previously announced, went up by 0.4% in March, similar to the increase experienced in February. This index has risen by a total of 3.5%, unadjusted for seasonal variations, over the past year.
In March, the major factors behind the overall index’s growth were the shelter and gasoline indexes. These two indexes contributed more than 50% to the index’s increase. Specifically, the energy index experienced a 1.1% rise, while the food index only went up by a slight 0.1%. It is worth mentioning that prices for food consumed at home remained constant. However, there was an uptick of 0.3% in the cost of dining out.
In March, the inflation rate for essentials excluding food and energy, known as the core Consumer Price Index (CPI), rose by 0.4 percent. This growth rate remained consistent with the previous two months. Notable increases were seen in sectors such as housing costs, motor vehicle insurance, healthcare, clothing, and personal care. Conversely, prices for used cars and trucks, recreational activities, and new vehicles decreased.
Each year, the overall index has shown a 3.5% growth for the twelve months up to March, which is slightly higher than the 3.2% increase observed in the previous period. The core index, without taking food and energy into account, went up by 3.8% over the same time frame. Prices for energy experienced a 2.1% rise for the first yearly increase since February 2023, while food prices surged by 2.2%.
According to Powell, the latest data doesn’t boost our faith and instead indicates that reaching the targeted inflation stability may take more time than initially thought.
Powell expressed concern over the latest figures, stating that they have not boosted our confidence and may suggest that reaching our goal will take longer than anticipated. He emphasized the need to give current restrictive measures more time before considering any changes. In simpler terms, he urged patience, suggesting the Federal Reserve wait longer before making adjustments based on new data and a changing economic landscape.
According to Bloomberg’s report, Powell’s cautious stance signifies a change in his perspective, indicative of a response to ongoing inflationary pressures that call for continued tight monetary policy. This view is consistent with the worries shared by other Federal Reserve officials regarding the economic data suggesting prolonged price increases.
Kathy Bostjancic, economist at Nationwide Mutual Insurance Company, spoke with Bloomberg News, sharing that Powell’s remarks had aligned with the market’s previous assumptions, causing a decrease in anticipated rate cuts due to improving economic signals. She admitted that these comments influenced investor feelings.
Reevaluating the schedule for interest rate cuts has caused Treasury yields to climb, momentarily pushing the two-year note yield above 5%, marking a new high since last November. The surge in yields indicates investors’ belief that the Federal Reserve might not act as swiftly in cutting rates as initially assumed.
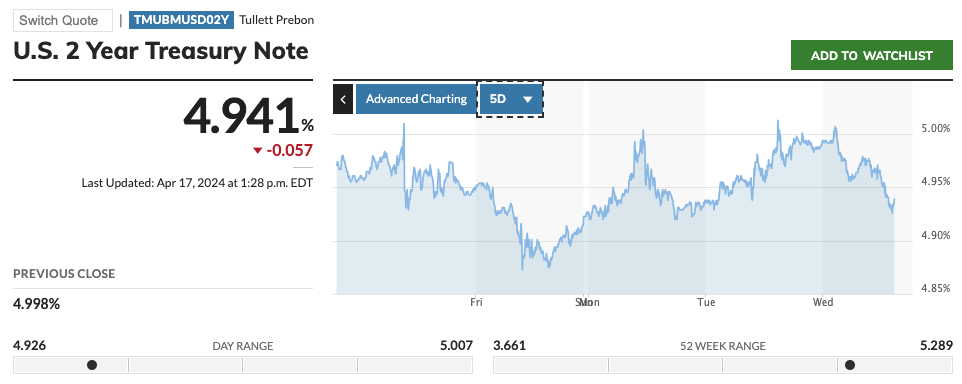
Based on Bloomberg’s latest report, the U.S. economy is showing signs of strength with more than 300,000 new jobs added in March and retail sales exceeding expectations. This comes as inflationary pressures are reemerging, making it harder for the Federal Reserve to achieve its inflation goals.
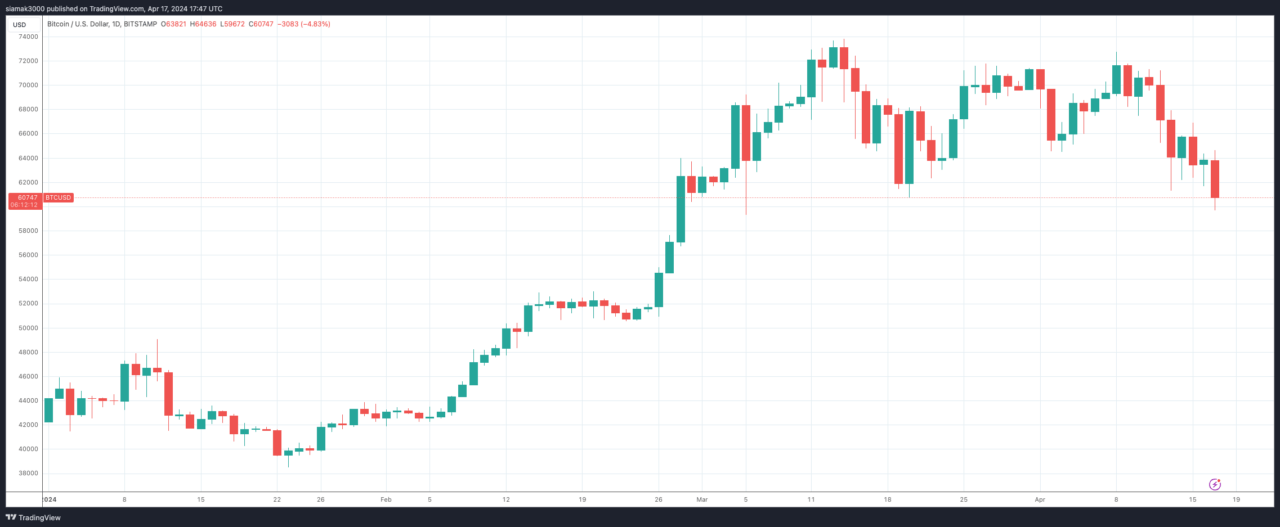
Once again, large returns on U.S. Treasury bonds tend to harm riskier investments like cryptocurrencies. It’s no shock then that Bitcoin, which is currently priced at $60,724 as of 5:47 p.m. UTC on 17 April 2024, has dropped by 2.9% in the last day despite the upcoming Bitcoin halving event being just under three days away.
Read More
- Apothecary Diaries Ch.81: Maomao vs Shenmei!
- 30 Best Couple/Wife Swap Movies You Need to See
- USD ILS PREDICTION
- Everything We Know About DOCTOR WHO Season 2
- DC: Dark Legion The Bleed & Hypertime Tracker Schedule
- 9 Kings Early Access review: Blood for the Blood King
- Summoners War Tier List – The Best Monsters to Recruit in 2025
- Clair Obscur: Expedition 33 – All Act 3 optional bosses and where to find them
- Netflix’s ‘You’ Season 5 Release Update Has Fans Worried
- 10 Shows Like ‘MobLand’ You Have to Binge
2024-04-17 21:00