Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new method leverages generative flow networks to create diverse and actionable counterfactual explanations, offering a deeper understanding of machine learning model decisions.
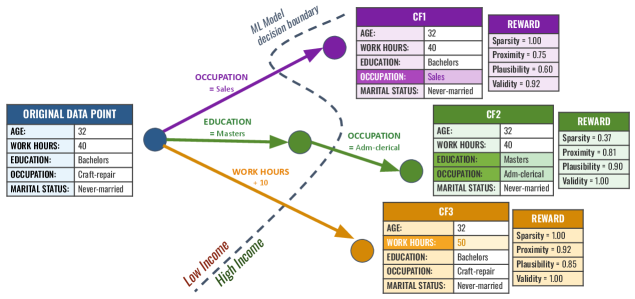
CounterFlowNet addresses limitations in existing counterfactual explanation techniques by improving sparsity, validity, and constraint handling.
Despite growing demand for interpretable machine learning, generating truly meaningful counterfactual explanations-those revealing minimal changes to input features that alter a model’s prediction-remains a significant challenge. This paper introduces ‘CounterFlowNet: From Minimal Changes to Meaningful Counterfactual Explanations’, a novel generative approach leveraging Generative Flow Networks to address limitations in existing methods concerning sparsity, validity, and the ability to incorporate user-defined constraints. CounterFlowNet formulates counterfactual generation as a sequential feature modification process, trained to sample explanations proportional to a reward function encoding desired qualities like plausibility and proximity. By seamlessly handling both continuous and categorical data and enabling actionability constraints without retraining, could this framework unlock more robust and user-centric explainable AI systems?
The Opaque Algorithm: Confronting the Black Box Problem
Even as machine learning algorithms achieve remarkable accuracy in diverse applications, a fundamental hurdle persists: the ‘black box’ problem. These complex models, particularly deep neural networks, often operate in ways that are opaque to human understanding, making it difficult to discern the reasoning behind their predictions. While a model might correctly identify an image as a cat, for example, it cannot easily articulate why it reached that conclusion – what specific features of the image triggered that response. This lack of transparency isn’t merely an academic concern; it poses significant challenges for deploying AI in critical domains like healthcare, finance, and criminal justice, where trust and accountability are paramount. The inability to interpret model decisions hinders debugging, prevents the identification of potential biases, and ultimately limits the broader adoption of these powerful technologies.
Many established machine learning techniques operate as “black boxes,” delivering predictions without revealing how those conclusions were reached. This opacity presents a critical issue, as it becomes difficult, if not impossible, to determine which specific input features most influenced a model’s decision. Consequently, stakeholders struggle to validate the logic behind automated systems, creating barriers to trust, especially in high-stakes applications like healthcare or finance. Without the ability to pinpoint causal factors, accountability becomes blurred, and potential biases embedded within the model remain undetected, ultimately limiting the responsible deployment of increasingly complex artificial intelligence.
Sequential Decision-Making: A Rigorous Approach to Counterfactual Generation
The generation of effective counterfactual explanations necessitates a systematic alteration of input features. This process involves iteratively modifying individual feature values and observing the corresponding change in the model’s output, continuing until the desired outcome is reached. Unlike random search methods, a systematic approach ensures comprehensive exploration of the feature space, increasing the likelihood of identifying minimal and plausible changes that would have resulted in a different prediction. The efficiency of this process is directly related to the method used to select and adjust features, with techniques prioritizing changes that have the greatest impact on the output generally performing best.
CounterFlowNet implements a sequential decision process for counterfactual generation by iteratively modifying input features. This is achieved through a series of discrete actions, where the network selects which feature to adjust at each step and the magnitude of that adjustment. Each action alters the input, and the model predicts the resulting outcome, allowing it to learn a policy for reaching the desired target outcome through a sequence of feature manipulations. This contrasts with methods that attempt to directly predict the necessary feature changes, and enables the exploration of multiple possible counterfactual explanations by allowing for branching decision paths.
Generative Flow Networks (GFNs) facilitate efficient exploration of the input feature space by learning a latent representation and an invertible mapping between the latent space and the feature space. This allows CounterFlowNet to generate counterfactual explanations through sampling from the latent space and decoding to obtain modified input features. The invertible mapping ensures that every sampled point in the latent space corresponds to a valid input, and the network’s generative capacity allows for the creation of diverse counterfactuals, avoiding solutions clustered around a single, potentially unrealistic, modification. By optimizing within this latent space, the search for minimal changes required to achieve a desired outcome is computationally streamlined compared to direct manipulation of the high-dimensional input features.
Establishing Rigorous Criteria: Defining a High-Quality Counterfactual
Validity in counterfactual explanations refers to the degree to which a proposed change to an input feature actually results in a different prediction from the machine learning model. A valid counterfactual must demonstrably flip the model’s output; alterations that do not affect the prediction are considered invalid and uninformative. Assessing validity requires evaluating the model’s response to both the original input and the perturbed, counterfactual input. High validity is paramount as it establishes a causal link between the feature change and the prediction change, forming the foundation of a reliable explanation. Without validity, any suggested feature modification is meaningless in the context of understanding the model’s behavior.
While a valid counterfactual explanation – one that demonstrably alters a model’s prediction – is foundational, several additional characteristics are critical for practical utility. Proximity measures the degree of change from the original input instance; minimizing this distance ensures the counterfactual remains a reasonable perturbation. Sparsity refers to the number of features modified to generate the counterfactual, with fewer changes generally preferred for interpretability and actionability. Finally, plausibility assesses whether the counterfactual instance conforms to the underlying data distribution; unrealistic counterfactuals, even if valid and sparse, provide limited insight. These attributes – proximity, sparsity, and plausibility – collectively enhance the trustworthiness and usefulness of counterfactual explanations beyond simple validity.
CounterFlowNet employs a Reward Function to identify high-quality counterfactual explanations by quantifying the desirability of generated examples based on multiple criteria. This function assigns scores reflecting validity – whether the change actually flips the model’s prediction – alongside proximity, sparsity, and plausibility. The Reward Function combines these metrics, weighted to prioritize desirable characteristics, and guides a gradient-based search process. This allows CounterFlowNet to iteratively refine candidate counterfactuals, maximizing the reward score and ultimately yielding explanations that are both effective at changing the prediction and meaningful in the context of the original input data.
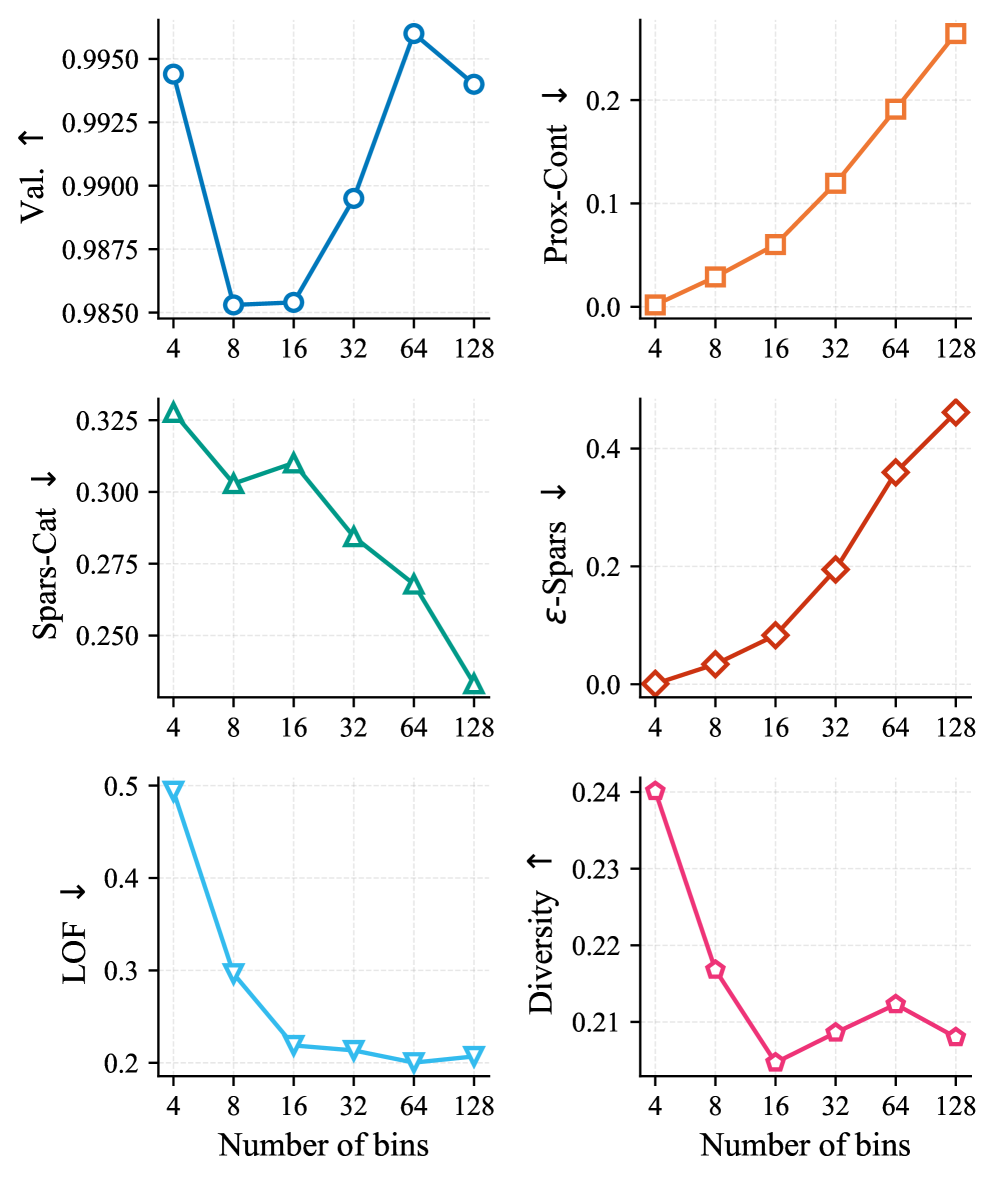
Action Masking and discretization are employed to optimize the counterfactual generation process within CounterFlowNet. Action Masking constrains the search space by preventing modifications to features deemed irrelevant or impossible to change, thereby enforcing realistic constraints on the generated counterfactuals. Discretization involves converting continuous feature values into a finite set of discrete bins; this reduces the complexity of the search space and improves computational efficiency by limiting the number of possible feature value combinations the algorithm must evaluate. Both techniques contribute to a more focused and efficient search for valid and plausible counterfactual explanations.
CounterFlowNet consistently achieves a validity rate exceeding 99% when tested across multiple datasets. This metric indicates the proportion of generated counterfactual examples that demonstrably alter the model’s original prediction. Rigorous evaluation procedures confirm that these generated instances are not simply noise, but represent genuine changes to the input that result in a different outcome from the machine learning model. The high validity score establishes CounterFlowNet as a highly reliable system for generating accurate and meaningful counterfactual explanations.
Advancing the State of the Art: CounterFlowNet and the Pursuit of Explainable Intelligence
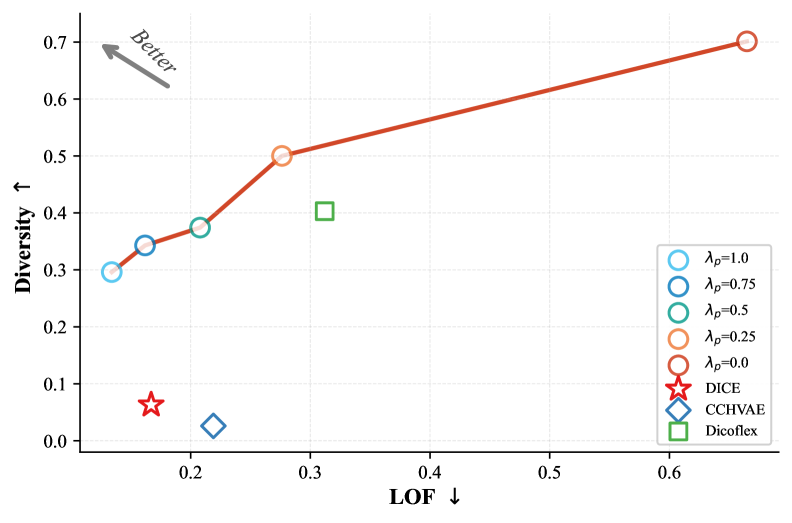
Current methods for generating counterfactual explanations – those minimal changes to an input that would alter a machine learning model’s prediction – frequently face a trade-off between several crucial qualities. Techniques like L2C, DiCE, and DiCoFlex often struggle to simultaneously produce explanations that are diverse – offering a range of possible changes – while also maintaining validity, meaning the altered input truly flips the model’s prediction, and sparsity, ensuring the changes are minimal and therefore more readily interpretable by humans. A lack of balance in these areas can result in explanations that are either unhelpful due to being implausible, fail to adequately explore the decision boundary, or are too complex to be easily understood, hindering trust and effective debugging of machine learning systems.
CounterFlowNet addresses the challenges of generating meaningful counterfactual explanations by integrating sequential decision-making with generative flow networks. Traditional methods often struggle to simultaneously achieve diverse, valid, and sparse counterfactuals, leading to explanations that are either unrealistic, inaccurate, or overly complex. This novel architecture frames the counterfactual generation process as a series of informed steps, allowing the model to strategically modify input features while maintaining plausibility and relevance. By leveraging the strengths of both sequential decision-making-which enables targeted alterations-and generative flow networks-which ensure the generated examples remain within the data distribution-CounterFlowNet produces counterfactuals that are demonstrably more interpretable and reliable than those created by existing techniques. This approach effectively navigates the trade-offs inherent in counterfactual generation, offering a balanced solution that enhances understanding of machine learning model behavior.
The advancement of machine learning model explainability hinges on the ability to generate counterfactual examples – plausible ‘what if’ scenarios that illuminate the reasoning behind a prediction. CounterFlowNet significantly improves upon existing methods by producing explanations that are not only accurate but also readily understandable by users. This heightened interpretability fosters greater trust in model outputs, as individuals can clearly see how a small change in input features would alter the outcome. By demystifying the decision-making process, CounterFlowNet moves beyond simply identifying a prediction to revealing the underlying logic, empowering stakeholders to confidently utilize and validate complex machine learning systems. This transparency is crucial for applications where accountability and user understanding are paramount, facilitating informed decision-making and responsible AI deployment.
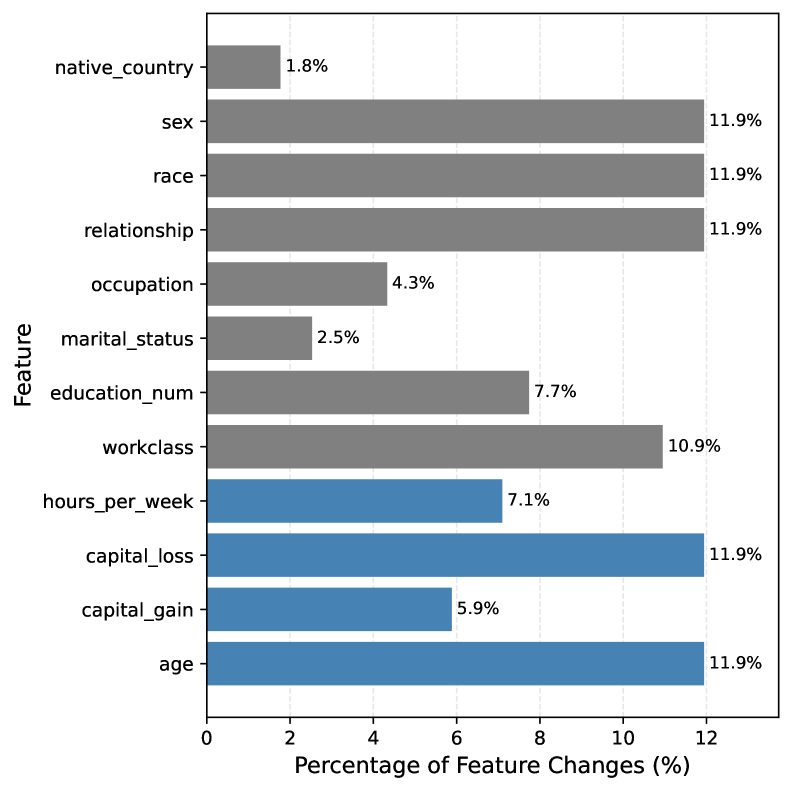
CounterFlowNet extends beyond simply explaining model predictions; it furnishes users with the means to proactively improve model robustness. By generating targeted counterfactual examples – minimal changes to input data that alter the prediction – the system illuminates potential vulnerabilities and biases embedded within machine learning models. This capability allows developers and data scientists to pinpoint specific features driving problematic predictions, fostering a deeper understanding of model behavior. Consequently, users can refine training data, adjust model parameters, or implement fairness-aware algorithms to mitigate identified issues, ultimately leading to more reliable and equitable artificial intelligence systems. The actionable nature of these insights transforms CounterFlowNet from a diagnostic tool into a catalyst for building more trustworthy machine learning applications.
Evaluations demonstrate CounterFlowNet’s superior performance across multiple datasets, consistently achieving the highest Harmonic Mean when compared to existing counterfactual explanation methods. This metric highlights a robust balance between the diversity of generated explanations and their validity – ensuring that the proposed changes meaningfully alter the model’s prediction without introducing unrealistic or irrelevant features. Importantly, CounterFlowNet doesn’t sacrifice sparsity in pursuit of this balance; it delivers competitive results in minimizing the number of feature changes needed to generate effective counterfactuals, contributing to improved interpretability and user trust. This combination of high Harmonic Mean, competitive sparsity, and balanced diversity establishes CounterFlowNet as a significant advancement in the field of explainable artificial intelligence.
The utility of counterfactual explanations hinges on their similarity to the original data point; explanations that are too distant become difficult to understand and may not represent realistic alterations. CounterFlowNet addresses this critical need by generating counterfactuals exhibiting competitive proximity – meaning the minimal changes required to alter a model’s prediction are both effective and readily comprehensible. This focus on closeness ensures that the explanations remain grounded in the original instance, offering actionable insights rather than abstract modifications. By maintaining a strong connection to the input data, CounterFlowNet facilitates trust in the explanations and enables users to confidently identify the key features driving model decisions, thereby enhancing the overall interpretability of complex machine learning systems.
The pursuit of robust counterfactual explanations, as demonstrated by CounterFlowNet, necessitates a commitment to mathematical rigor. The framework’s emphasis on generative flow networks and reward shaping isn’t merely about achieving functional results; it’s about establishing a provably valid transformation from the original input to a counterfactual. This aligns perfectly with the sentiment expressed by Barbara Liskov: “Programs must be right first before they are fast.” The elegance of CounterFlowNet lies not simply in its ability to generate diverse explanations, but in the underlying mathematical principles ensuring those explanations are both actionable and, crucially, correct. The network’s constraints aren’t arbitrary; they’re invariants designed to guarantee the logical consistency of the counterfactual, mirroring the pursuit of provable correctness in algorithmic design.
What’s Next?
The pursuit of ‘explainable AI’ frequently resembles alchemy – a desire to transmute opaque functionality into readily understandable terms. CounterFlowNet represents a step towards a more rigorous formulation, shifting the emphasis from merely producing explanations to ensuring their mathematical validity. However, the problem of counterfactual generation is not simply one of finding a different input that alters the prediction; it is a problem of defining what constitutes a meaningful difference. The current reliance on reward shaping, while pragmatic, introduces subjective elements that ultimately detract from the desired purity. Future work must address the challenge of formalizing ‘actionability’ and ‘diversity’ – concepts presently reliant on ill-defined heuristics.
A critical limitation remains the implicit assumption that small perturbations are inherently preferable. While intuitively appealing, this is not necessarily logically sound. A truly robust explanation should not shy away from demonstrating the model’s sensitivity to even substantial changes in input space, if such sensitivity exists. To achieve this, a deeper investigation into the geometry of the model’s decision boundaries is required – a move away from generating ‘plausible’ counterfactuals and towards discovering the fundamental constraints governing the model’s behavior.
Ultimately, the field requires a shift in perspective. The goal should not be to ‘explain’ machine learning models to humans, but to construct models that are, by their very design, inherently transparent and self-documenting. CounterFlowNet, while a valuable contribution, is still a workaround. The true elegance lies not in post-hoc justification, but in foundational correctness.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.17244.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Securing the Agent Ecosystem: Detecting Malicious Workflow Patterns
- Silver Rate Forecast
- DOT PREDICTION. DOT cryptocurrency
- 4 Reasons to Buy Interactive Brokers Stock Like There’s No Tomorrow
- EUR UAH PREDICTION
- NEAR PREDICTION. NEAR cryptocurrency
- Top 15 Insanely Popular Android Games
- Did Alan Cumming Reveal Comic-Accurate Costume for AVENGERS: DOOMSDAY?
- USD COP PREDICTION
2026-02-22 09:13