Author: Denis Avetisyan
As AI-generated images become increasingly realistic, a robust method for identifying them is crucial, and researchers have introduced a new dataset designed to rigorously evaluate the performance of current detection techniques.
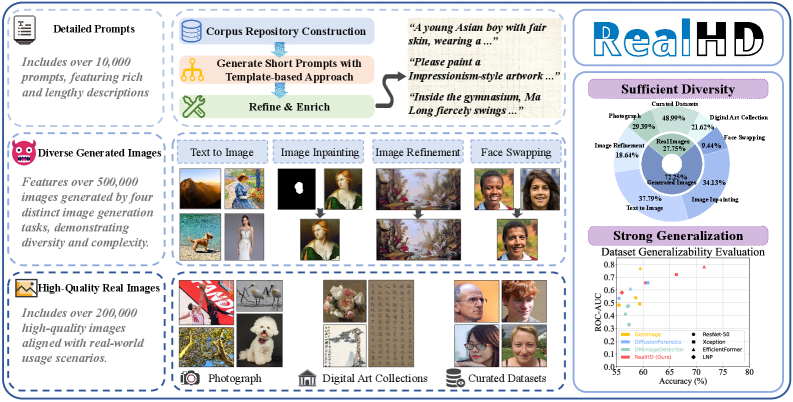
RealHD, a large-scale, high-quality dataset, combined with a noise entropy-based approach, significantly improves the accuracy and generalization of AI-generated image detection.
Despite advances in generative AI, reliably distinguishing between authentic and synthetic images remains a critical challenge due to limitations in existing datasets. To address this, we introduce RealHD: A High-Quality Dataset for Robust Detection of State-of-the-Art AI-Generated Images, a large-scale resource comprising over 730,000 images with rich annotations, designed to improve the generalization of detection models. Our analysis demonstrates that training on RealHD, coupled with a novel noise entropy-based detection method, significantly enhances performance and robustness compared to existing approaches. Will this dataset and methodology prove pivotal in establishing a new baseline for image forensics and mitigating the risks associated with increasingly realistic AI-generated content?
The Ascent of Synthetic Realism: Challenging Visual Authenticity
The rapid evolution of generative artificial intelligence models, such as Stable Diffusion, has unlocked an unprecedented capacity to create photorealistic imagery. These models, trained on massive datasets, don’t simply replicate existing images; they learn the underlying patterns and structures of visual data, allowing them to synthesize entirely new content with remarkable fidelity. The resulting images are increasingly difficult to distinguish from photographs or artwork created by humans, pushing the boundaries of what is considered authentic. This newfound realism isn’t achieved through simple pixel manipulation, but rather through complex diffusion processes that build images from noise, resulting in nuanced details and aesthetic qualities previously unattainable by algorithmic means. Consequently, the very definition of ‘real’ in the visual realm is being challenged, as synthetic creations seamlessly integrate with and potentially overshadow genuine photographic records.
Existing techniques for identifying artificially generated imagery are increasingly challenged by the rapid advancement of generative models. Historically, detection methods relied on identifying subtle artifacts or inconsistencies introduced during the generation process – flaws easily exploited as algorithms become more refined. These earlier approaches often focused on statistical anomalies in pixel patterns or frequency domains, but contemporary models, such as Stable Diffusion, produce outputs virtually indistinguishable from photographs captured by conventional means. This escalating sophistication necessitates a shift towards more robust detection strategies, including techniques that analyze semantic consistency, examine latent space characteristics, or leverage adversarial training to anticipate and counter evolving forgery methods. The development of such reliable tools is paramount, not merely for verifying authenticity, but also for maintaining trust in visual information within an increasingly synthetic media landscape.
The escalating creation of synthetic media, encompassing everything from subtly altered photographs to convincingly realistic deepfakes, presents a growing threat to information integrity and public trust. This proliferation isn’t merely a technological curiosity; it actively fuels the spread of misinformation, potentially influencing public opinion, damaging reputations, and even inciting real-world harm. Consequently, the development of reliable content authentication methods has become paramount. These techniques aim to verify the provenance of digital content, establishing whether an image or video is original or has been artificially generated or manipulated. Without such safeguards, discerning truth from fabrication becomes increasingly difficult, eroding confidence in visual media and demanding innovative solutions to preserve the authenticity of information in the digital age.
RealHD: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating Generative Adversarial Networks
The RealHD dataset consists of 730,000 high-resolution images compiled to provide a comprehensive resource for AI-generated image detection research. Image selection prioritized diversity in both depicted scenes – encompassing a broad spectrum of everyday environments and objects – and the generative techniques used for their creation. This curation process includes images produced by various models and parameter settings, reflecting the rapidly evolving landscape of AI image synthesis and ensuring the dataset’s ability to challenge and evaluate the robustness of detection algorithms across multiple generation methods. The high-quality nature of the images, combined with this diversity, is intended to facilitate more accurate and generalizable detection models.
The RealHD dataset utilizes state-of-the-art generative models, specifically Flux and Stable Diffusion, to synthesize its artificial images. This approach ensures the creation of highly realistic and challenging test cases for AI-generated image detection algorithms. Images were generated using diverse parameters and settings within these models to maximize variation and represent the evolving capabilities of generative AI. The resulting synthetic data mirrors the complexity and fidelity of images commonly produced by current generative techniques, providing a robust evaluation environment that moves beyond simpler, less realistic datasets.
RealHD builds upon the foundations of existing AI-generated image detection datasets, specifically GenImage and DiffusionForensics, to provide a more extensive and reliable evaluation platform. While prior datasets offered initial benchmarks, RealHD significantly increases the scale and diversity of test images, incorporating a wider range of generative methods and scene complexities. This expansion is crucial for assessing the generalization capabilities of detection algorithms; models trained and tested solely on limited datasets often exhibit poor performance when confronted with images generated by novel techniques or depicting unfamiliar content. Empirical results demonstrate that algorithms evaluated on RealHD exhibit improved performance across a broader spectrum of generative models compared to those assessed using earlier datasets, indicating a more robust and comprehensive evaluation process.
Dissecting the Synthetic: Forensic Approaches to Image Authentication
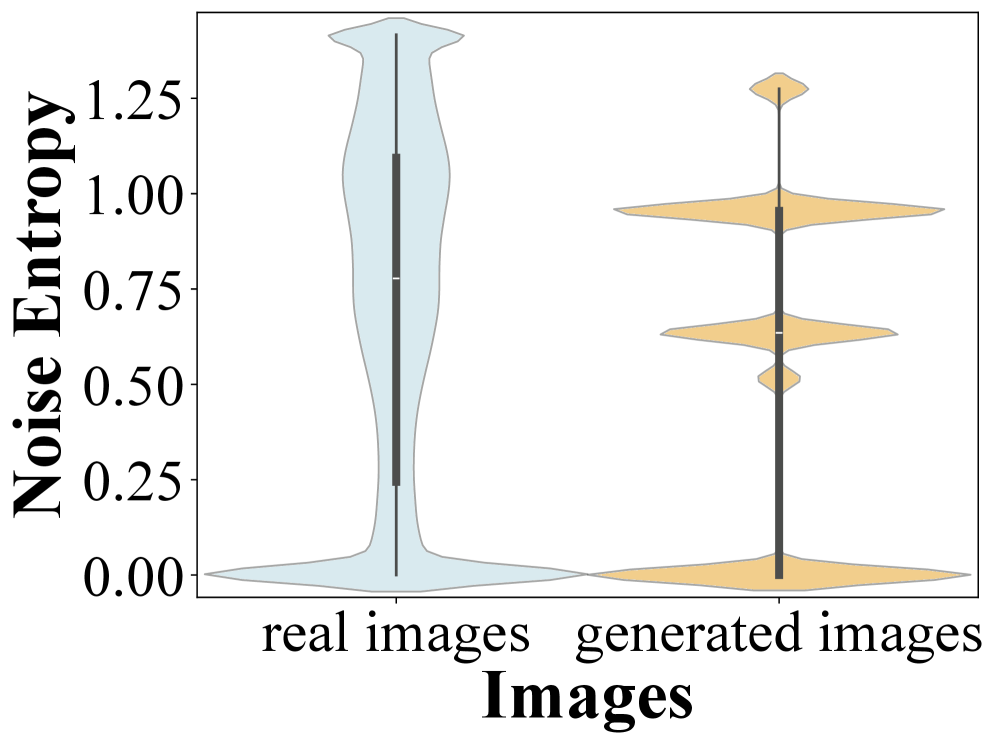
Learned Noise Pattern (LNP) algorithms operate on the principle that real and synthetic images possess distinct noise characteristics. Natural images accumulate noise during capture and processing, resulting in complex, statistically predictable patterns. Generative models, conversely, often produce images with different noise profiles, typically exhibiting less complexity or patterns unique to the generative process. LNP algorithms are trained on datasets of both real and generated images to learn these differentiating noise patterns. During detection, the algorithm analyzes the noise present in a given image and compares it to the learned patterns to classify the image as either real or synthetic. The efficacy of LNP relies on the diversity and representativeness of the training data, as well as the algorithm’s ability to accurately model and distinguish subtle variations in noise characteristics.
Neighboring Pixel Relationships (NPR) represent a class of image forensic techniques that operate on the premise that natural images exhibit statistical dependencies between adjacent pixels due to the physics of image capture and sensor limitations. Synthetic images, generated by algorithms, often lack these nuanced correlations, or exhibit patterns inconsistent with naturally occurring images. NPR methods analyze these local structures – specifically, the relationships between pixel values and their neighbors – to detect anomalies. These analyses frequently involve calculating statistical measures, such as the variance or correlation, of pixel differences within a defined neighborhood. Deviations from expected statistical distributions, characteristic of real images, can indicate manipulation or artificial generation. The effectiveness of NPR methods relies on the ability to accurately model these local image characteristics and identify subtle inconsistencies that differentiate synthetic from authentic content.
The Xception model demonstrates high accuracy in detecting synthetic images when evaluated on the GenImage dataset, achieving 99.00%. However, performance significantly decreases when tested against the more complex RealHD dataset, with accuracy dropping to 85.21%. This disparity indicates a limitation in the model’s generalization capability and necessitates the development of more robust detection techniques. Integrating a noise entropy method with the Xception architecture yields a substantial performance improvement, boosting accuracy by 15.90% and increasing the Area Under the Curve (AUC) by 5.00%, suggesting that incorporating noise analysis enhances the model’s ability to discern synthetic content.
Ensuring Reliability: Evaluating Robustness in Content Authentication Systems
Detection algorithms, while often effective in controlled laboratory settings, frequently encounter challenges when deployed in real-world scenarios characterized by imperfect image quality. To rigorously evaluate their resilience, researchers employ techniques that deliberately degrade image data, mirroring the conditions of everyday capture and transmission. A common method involves applying JPEG compression, a ubiquitous process that reduces file size by discarding image information; the extent of this compression serves as a quantifiable measure of degradation. By systematically varying the compression level, scientists can assess how gracefully a detection algorithm maintains its accuracy as image fidelity diminishes, revealing its robustness to common forms of real-world visual noise and potential failure points before practical deployment.
The creation of truly robust forgery detection systems demands training data that mirrors the complexity of real-world manipulations. Consequently, researchers are moving beyond simple synthetic forgeries to employ techniques like image inpainting and refinement. Image inpainting skillfully fills in missing or damaged regions of an image, creating seamless reconstructions that mimic authentic edits. Simultaneously, image refinement algorithms subtly alter existing pixels, introducing realistic artifacts and blurring the lines between genuine and manipulated content. By combining these methods, the generative process produces synthetic images that are far more challenging for detection algorithms, pushing them to discern increasingly subtle discrepancies and ultimately improving their reliability when faced with real-world forgeries. This approach ensures that detection systems aren’t simply memorizing patterns from easily identifiable synthetic data, but rather learning to analyze the underlying visual characteristics indicative of manipulation.
Comparative evaluations reveal that advanced models, specifically FatFormer and SAAN, exhibit promising capabilities in both object detection accuracy and aesthetic quality assessment. When tested against established baseline models, these architectures demonstrate the potential to significantly enhance performance in challenging visual tasks. Of particular note is the performance on the RealHD dataset, where SAAN consistently achieves the highest aesthetic scores, indicating a superior ability to preserve and even enhance visual fidelity – a crucial factor for applications demanding both precision and pleasing visual output. This suggests that these models not only identify objects more effectively but also deliver results with improved perceptual quality, paving the way for more robust and user-friendly systems.
Towards Universal Content Authentication: Charting a Course for the Future
Current content authentication methods often falter when faced with sophisticated manipulations, prompting researchers to revisit the subtle fingerprints left by image acquisition processes – specifically, image noise. Techniques leveraging Image Noise Entropy and Non-Local Means (NLM) analyze the statistical properties of this noise, as each camera sensor introduces a unique pattern during capture. By characterizing these patterns, it becomes possible to discern whether an image has been tampered with, even if the alterations are visually seamless. Further investigation into these noise-based detection methods holds the potential to create remarkably robust authentication tools, capable of identifying even skillfully crafted forgeries by analyzing discrepancies in noise characteristics between different image regions or comparing them to a database of known sensor profiles. This approach moves beyond pixel-level analysis, focusing instead on the inherent physical properties of the image itself, promising a new era of reliable content verification.
The increasing sophistication of generative artificial intelligence presents a significant threat to the trustworthiness of visual content, particularly through techniques like face swapping and deepfake creation. These manipulations, often imperceptible to the human eye, can seamlessly replace one person’s likeness with another in images and videos, potentially leading to misinformation, reputational damage, and even security breaches. Consequently, robust methods for detecting these alterations are paramount; future research must prioritize algorithms capable of identifying subtle inconsistencies introduced during the manipulation process – focusing on biophysical impossibilities, inconsistencies in lighting or shadows, and discrepancies in facial expressions. Successfully mitigating the risks posed by such manipulations requires not only technical advancements in detection, but also the development of tools that empower individuals and organizations to verify the authenticity of visual information and safeguard against the spread of synthetic falsehoods.
The proliferation of increasingly realistic synthetic media demands a unified approach to content verification, necessitating the development of universal authentication standards. Currently, a fragmented landscape of detection methods hinders widespread adoption and effective defense against manipulated content. Establishing these standards requires more than just algorithms; it demands comprehensive, high-quality datasets like RealHD, which provide the necessary ground truth for training and evaluating authentication techniques. Such datasets, capturing the nuances of real-world image and video capture, are crucial for distinguishing authentic content from sophisticated forgeries. A standardized framework, built upon these datasets, will empower developers, platforms, and consumers with the tools to confidently assess the integrity of digital information and mitigate the growing risks associated with deceptive synthetic media.
The pursuit of robust AI-generated image detection, as exemplified by RealHD, aligns with a fundamental principle: verifiable accuracy. The dataset’s emphasis on high-quality images and rigorous evaluation methods isn’t merely about achieving higher scores, but about establishing a provable foundation for distinguishing authentic content from synthetic creations. This resonates with Yann LeCun’s assertion: “The real promise of AI is not to replace humans, but to augment them.” RealHD, by providing a solid benchmark and improved detection via noise entropy analysis, facilitates this augmentation, offering tools to verify digital authenticity and bolster human oversight in an increasingly synthetic world. The dataset’s focus on generalization, minimizing vulnerabilities to novel generation techniques, underscores the importance of algorithms built on mathematical purity, not simply empirical success.
Future Directions
The introduction of RealHD represents a necessary, if incremental, step towards quantifiable progress in the field of AI-generated image forensics. The dataset’s scale and quality address a critical deficiency in prior evaluations, yet the underlying problem remains stubbornly resistant to complete resolution. Current reliance on statistical artifacts – noise entropy, in this instance – is inherently fragile. As generative models mature, these statistical fingerprints will inevitably diminish, requiring a continual arms race of increasingly subtle feature extraction. The true test will not be detection against current diffusion models, but against those yet conceived – those that fundamentally alter the generative process.
A more fruitful avenue lies in abandoning the pursuit of “detection” altogether. Rather than seeking to identify the origin of an image, research should focus on verifiable properties of the depicted scene. Can the physical plausibility of the image be mathematically proven? Can semantic consistency be guaranteed? This shifts the focus from a statistical game of cat and mouse to a problem of formal verification – a realm where elegance and provability, not mere accuracy on a benchmark, are paramount.
Ultimately, the value of such work is not in preventing the creation of synthetic imagery – an exercise in futility – but in establishing a framework for trustworthy visual information. Each additional parameter in a generative model introduces a potential for subtle manipulation, and only rigorous mathematical analysis can hope to expose – and ultimately, neutralize – these vulnerabilities. The pursuit of ‘realism’ is a distraction; the pursuit of truth is the only logical imperative.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2602.10546.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- 2025 Crypto Wallets: Secure, Smart, and Surprisingly Simple!
- 🚨 Kiyosaki’s Doomsday Dance: Bitcoin, Bubbles, and the End of Fake Money? 🚨
- Monster Hunter Stories 3: Twisted Reflection launches on March 13, 2026 for PS5, Xbox Series, Switch 2, and PC
- Here Are the Best TV Shows to Stream this Weekend on Paramount+, Including ‘48 Hours’
- The 10 Most Beautiful Women in the World for 2026, According to the Golden Ratio
- 20 Films Where the Opening Credits Play Over a Single Continuous Shot
- Crypto’s Comeback? $5.5B Sell-Off Fails to Dampen Enthusiasm!
- 39th Developer Notes: 2.5th Anniversary Update
- 10 Hulu Originals You’re Missing Out On
- 10 Underrated Films by Ben Mendelsohn You Must See
2026-02-12 17:02