
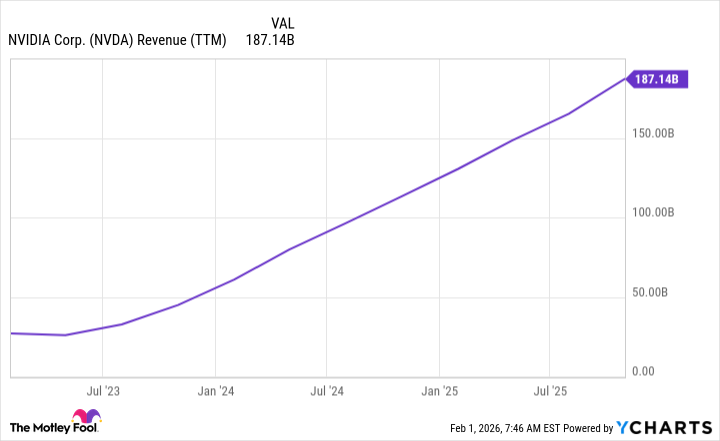
Nvidia (NVDA +8.01%) has, in recent periods, demonstrated substantial equity appreciation. While comparative performance metrics can always be identified, the company’s ascent has positioned it as a leading entity by market capitalization. The sustainability of this trajectory, however, warrants rigorous examination.
Past performance is, naturally, not indicative of future results. Nvidia’s current dominance in providing computational resources for artificial intelligence (AI) workloads is predicated on maintaining a technological and logistical advantage. Continued expansion is also contingent upon sustained capital investment by AI hyperscalers.
This analysis will explore potential revenue projections for Nvidia over the next five years, assessing the underlying assumptions and associated risks.
Current Market Position and Growth Drivers
Nvidia’s graphics processing units (GPUs) have become the de facto standard for AI computing due to their parallel processing capabilities. The company’s hardware is frequently integrated into new data center infrastructure, reflecting its established position in the market. While competitive pressures are increasing, Nvidia currently maintains a lead in terms of overall performance and ecosystem support.
Capital expenditure announcements by AI hyperscalers suggest continued demand for computational resources. This trend, if sustained, bodes well for Nvidia. The company anticipates this pattern to continue through at least 2030, representing a significant opportunity for revenue growth.
Revenue Projections and Underlying Assumptions
Estimates suggest global data center capital expenditures will reach $600 billion in 2025, potentially expanding to $3 trillion to $4 trillion by 2030. If these projections materialize, Nvidia could theoretically exceed $1 trillion in annual revenue. This, however, is contingent upon maintaining a substantial market share.
Wall Street analysts currently forecast $213 billion in revenue for fiscal year 2026. Assuming a 36% share of the $600 billion data center spending figure for 2025, Nvidia’s revenue would align with this estimate. Maintaining this share through 2030, at the midpoint of its projections, could result in revenue exceeding $1.24 trillion. The validity of this projection, however, requires further scrutiny.
Risk Factors and Considerations
Several factors could impede Nvidia’s projected growth. These include:
- Increased Competition: Alternative hardware architectures and the emergence of new competitors could erode Nvidia’s market share.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Ongoing geopolitical instability and component shortages could impact production and delivery.
- Macroeconomic Conditions: A slowdown in global economic growth could reduce demand for AI-related infrastructure.
- Technological Advancements: The emergence of disruptive technologies could render Nvidia’s current hardware obsolete.
Furthermore, the projected growth in data center capital expenditures is based on optimistic assumptions about the continued expansion of AI applications. A failure to realize these applications could lead to a reduction in investment.
While Nvidia’s current trajectory is impressive, extrapolating this growth over a five-year timeframe requires a degree of caution. The company’s success is contingent upon navigating a complex and evolving landscape.
Whether Nvidia will achieve $1 trillion in annual revenue by 2030 remains to be seen. However, continued demand for AI computing resources suggests that the company will remain a significant player in the technology sector.
Read More
- 21 Movies Filmed in Real Abandoned Locations
- 2025 Crypto Wallets: Secure, Smart, and Surprisingly Simple!
- The 11 Elden Ring: Nightreign DLC features that would surprise and delight the biggest FromSoftware fans
- 10 Hulu Originals You’re Missing Out On
- 39th Developer Notes: 2.5th Anniversary Update
- Gold Rate Forecast
- The 10 Most Beautiful Women in the World for 2026, According to the Golden Ratio
- Rewriting the Future: Removing Unwanted Knowledge from AI Models
- PLURIBUS’ Best Moments Are Also Its Smallest
- Leaked Set Footage Offers First Look at “Legend of Zelda” Live-Action Film
2026-02-08 21:02