Author: Denis Avetisyan
Researchers have developed a novel framework, NetMamba+, that harnesses the power of the Mamba architecture to dramatically improve the speed and accuracy of identifying network traffic types.
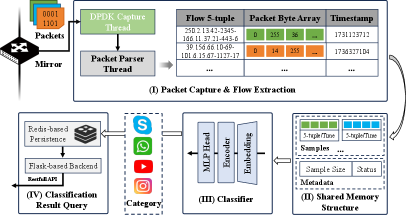
NetMamba+ leverages multimodal traffic representation and label distribution-aware pre-training for efficient and robust network traffic classification in both offline and online systems.
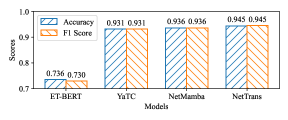
Effective network traffic classification is increasingly challenged by the proliferation of encrypted traffic and the limitations of existing machine learning approaches. This paper introduces ‘NetMamba+: A Framework of Pre-trained Models for Efficient and Accurate Network Traffic Classification’, a novel framework that addresses these challenges through the innovative application of the Mamba architecture, multimodal traffic representation, and label distribution-aware fine-tuning. Experiments demonstrate that NetMamba+ achieves state-of-the-art classification performance with improved efficiency and robustness across multiple datasets and even in real-world online deployments. Could this framework unlock new possibilities for efficient and accurate traffic analysis in increasingly complex network environments?
The Evolving Landscape of Network Visibility
Conventional methods of categorizing network traffic are increasingly challenged by the widespread adoption of encryption and anonymization technologies. As more data travels under the protection of protocols like HTTPS and VPNs, traditional deep packet inspection – which relies on examining the content of data packets – becomes ineffective, creating significant security blind spots for network defenders. This isn’t merely a technical hurdle; it represents a fundamental shift in the landscape of network security, as malicious activity can now be concealed within encrypted tunnels, bypassing conventional signature-based detection systems. Consequently, organizations face difficulty identifying and mitigating threats hidden within this encrypted traffic, potentially leaving networks vulnerable to attacks and data breaches. The rise of anonymization tools further compounds this issue, obscuring the origin and destination of traffic and hindering efforts to trace malicious actors.
Contemporary network defenses, historically reliant on identifying traffic based on known signatures, are increasingly challenged by proactive evasion techniques. Attackers now routinely employ methods like traffic obfuscation, fragmentation, and the dynamic alteration of malicious code to bypass signature-based detection systems. This necessitates a fundamental shift towards behavioral analysis and machine learning-driven approaches. Rather than seeking to recognize what a threat is, modern security focuses on identifying how traffic behaves – detecting anomalies and patterns indicative of malicious activity, regardless of whether a specific signature exists. This proactive stance allows for the identification of zero-day exploits and polymorphic malware that would otherwise slip past traditional defenses, enhancing overall network resilience in the face of evolving threats.
Raw network data presents a formidable analytical challenge due to its high dimensionality, velocity, and variety. Traditional methods often struggle to distill meaningful insights from this chaotic stream of packets, requiring innovative feature extraction techniques. Researchers are now exploring methods beyond simple packet inspection, including statistical analysis of inter-packet timings, flow-based analysis that aggregates packets into sessions, and machine learning algorithms capable of identifying subtle patterns indicative of malicious activity or network anomalies. These advanced approaches aim to reduce the dimensionality of the data while preserving critical information, enabling more effective real-time monitoring and threat detection. The development of robust and scalable feature extraction pipelines is therefore central to overcoming the limitations of conventional network analysis and achieving comprehensive traffic visibility.
Deep Learning: A Foundation for Intelligent Network Analysis
Deep learning techniques provide a robust framework for network analysis by leveraging multi-layered neural networks to automatically discover intricate, non-linear relationships within network data. Methods like pre-training, where models are initially trained on a related, often larger, dataset before fine-tuning on the specific network analysis task, enhance performance, particularly when labeled data is limited. This approach enables the model to learn generalizable features from the initial dataset, reducing the need for extensive task-specific training and improving generalization to unseen network patterns. The capacity to model complex dependencies, combined with automated feature extraction, distinguishes deep learning from traditional network analysis methods reliant on manually engineered features and simpler algorithms.
Class imbalance, a common characteristic of network datasets, significantly impacts deep learning model performance. When one class represents a substantially smaller proportion of the data than others-for example, malicious traffic comprising less than 1% of network activity-standard training procedures can lead to models biased towards the majority class. This results in poor detection rates for the minority class, despite potentially high overall accuracy. Mitigation strategies include data augmentation techniques to synthetically increase the representation of the minority class, cost-sensitive learning which assigns higher misclassification penalties to the minority class, and the utilization of evaluation metrics beyond simple accuracy, such as precision, recall, F1-score, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC), to provide a more nuanced assessment of model performance on imbalanced datasets.
Directly utilizing raw byte-level network data as input for deep learning models presents both opportunities and difficulties. While this approach avoids manual feature creation and potentially captures subtle anomalies, the high dimensionality and lack of inherent structure require specialized processing. Effective feature engineering often involves converting byte streams into numerical representations suitable for neural networks, such as character or byte n-grams, or employing techniques like word embeddings adapted for byte sequences. Simultaneously, model architectures must be optimized for handling sequential data and minimizing computational cost; recurrent neural networks (RNNs), particularly LSTMs and GRUs, and increasingly, transformer-based models, are commonly employed. Furthermore, data normalization and efficient batching strategies are critical for stable training and performance scaling.

NetMamba+: Scaling Network Classification with Novel Architecture
NetMamba+ utilizes a novel architecture that integrates state space models (SSMs) with efficient attention mechanisms, specifically Flash Attention, to achieve linear time complexity in network classification. Traditional attention mechanisms exhibit quadratic complexity with sequence length, hindering scalability. By replacing conventional attention with SSMs – which recursively model sequential data using hidden states – and optimizing the process with Flash Attention’s kernel fusion and tiling techniques, NetMamba+ reduces computational demands. This combination allows for processing longer sequences with significantly improved speed and reduced memory footprint compared to transformers, enabling effective classification of extensive network traffic data.
NetMamba+ utilizes a multimodal representation strategy to improve feature richness by processing network traffic data with techniques including byte allocation balancing and stride-based data cutting. Byte allocation balancing dynamically adjusts the partitioning of packet data into fixed-size blocks, optimizing resource utilization and preventing information loss from variable-length fields. Concurrently, stride-based data cutting extracts features at varying intervals within the packet payload, capturing both local and global dependencies. These methods facilitate a more comprehensive representation of network packets compared to traditional fixed-window approaches, enabling the model to discern subtle patterns and improve classification accuracy.
Label distribution-aware fine-tuning addresses the performance degradation commonly observed in network traffic classification when dealing with imbalanced datasets. Traditional fine-tuning methods can be biased towards majority classes, resulting in poor identification of rarer, yet potentially critical, traffic types. This technique modifies the training process to explicitly account for the frequency of each class, assigning higher weights to under-represented classes during loss calculation. Empirical results demonstrate that this approach yields up to a 6.44% improvement in F1 score across classification tasks, indicating a substantial gain in the accurate detection of minority traffic classes without significantly impacting performance on more prevalent traffic types.

Strengthening Security and Adaptability Through Intelligent Analysis
NetMamba+ significantly enhances network security through the incorporation of out-of-distribution (OOD) detection. This capability allows the system to move beyond simply classifying known traffic types and actively identify anomalous patterns that may indicate malicious activity or novel attacks. By flagging these unusual occurrences, NetMamba+ provides a crucial first line of defense, alerting security teams to potential threats that would otherwise bypass traditional signature-based systems. The system’s high accuracy, demonstrated by an AUROC of 0.9825 in OOD detection, minimizes false positives while maintaining a low false positive rate of 0.0463 at a 95% recall level, ensuring that genuine threats are prioritized and addressed efficiently. This proactive approach to threat detection is vital in the face of increasingly sophisticated and rapidly evolving cyberattacks.
NetMamba+ streamlines security operations by leveraging Redis, an in-memory data store, to maintain and rapidly access classification results. This integration moves beyond simple threat detection, enabling immediate responses to identified anomalies and facilitating seamless incorporation into pre-existing security information and event management (SIEM) systems. By storing results in Redis, NetMamba+ minimizes latency, allowing security teams to react to threats in real-time rather than being constrained by slower data retrieval methods. The system’s architecture supports dynamic updates and scaling, ensuring continued performance even with increasing network traffic and evolving threat landscapes, ultimately bolstering an organization’s overall security posture and incident response capabilities.
NetMamba+ showcases impressive performance metrics in real-world network analysis, achieving an average throughput of 261.87 Mb/s within a live system – a testament to its scalability. Critically, this system doesn’t just process data quickly, but also intelligently; inference speeds are up to 47.4 times faster than existing state-of-the-art methods. This speed is coupled with high accuracy in identifying unusual network activity, demonstrated by an Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.9825 and a False Positive Rate at 95% recall (FPR95) of just 0.0463, suggesting a robust ability to distinguish legitimate traffic from potential threats with minimal false alarms.
Looking Ahead: Future Directions and Broader Implications
Further refinement of NetMamba+ involves a strategic broadening of its analytical scope through the integration of diverse data streams. Current development prioritizes incorporating packet headers and associated metadata, enriching the model’s understanding of network traffic beyond simple payload analysis. This multimodal approach promises to reveal subtle patterns and anomalies currently obscured by a reliance on content alone. By leveraging information contained within packet structures-such as timestamps, source/destination addresses, and protocol types-the system can build a more holistic and context-aware representation of network behavior, potentially leading to enhanced threat detection and improved network management capabilities. This expanded representation isn’t limited to cybersecurity; the principles could prove valuable in fields requiring detailed sequential data analysis, such as financial modeling or complex systems monitoring.
Responsible deployment of network analysis tools like NetMamba+ necessitates robust techniques for packet anonymization and privacy preservation. The very nature of deep packet inspection, while powerful for anomaly detection, risks exposing sensitive user data if not carefully managed. Researchers are actively investigating methods such as differential privacy, data masking, and secure multi-party computation to obfuscate identifying information within network traffic. These approaches aim to strike a balance between maintaining the utility of network data for security purposes and safeguarding individual privacy rights. Further development in this area is not merely a technical challenge, but an ethical imperative to ensure that advancements in network monitoring do not come at the expense of user confidentiality and trust.
The architectural innovations within NetMamba+ – specifically its state space model and selective scan mechanism – aren’t limited to network traffic analysis. These principles offer a compelling pathway for advancements across diverse fields reliant on efficient sequence modeling. Applications range from financial time series analysis, where identifying anomalous patterns is critical, to bioinformatics, where understanding protein folding and genomic sequences demands robust, yet computationally lean, methods. Furthermore, the model’s ability to rapidly process sequential data makes it well-suited for real-time anomaly detection in industrial control systems, predictive maintenance, and even natural language processing tasks where context and temporal dependencies are paramount. By decoupling sequence length from computational cost, NetMamba+’s core concepts promise to unlock new possibilities in any domain where extracting meaningful insights from extended sequential data presents a significant challenge.
The NetMamba+ framework, with its focus on multimodal representation and label distribution-aware fine-tuning, embodies a principle of holistic system design. The architecture isn’t merely about achieving high accuracy in network traffic classification; it’s about creating a robust and efficient system for online systems – one that considers the entire pipeline from representation to deployment. This approach mirrors the understanding that structure dictates behavior; a well-considered architecture anticipates and accommodates real-world complexities. As Linus Torvalds once stated, “Talk is cheap. Show me the code.” NetMamba+ doesn’t simply present theoretical improvements; it delivers a concrete framework demonstrably effective in practical, live network environments, prioritizing functional implementation over abstract speculation.
Where the Stream Leads
The pursuit of efficient network traffic classification, as exemplified by NetMamba+, reveals a persistent tension: the desire for increasingly granular accuracy clashes with the inherent ambiguity of real-world data. While the framework demonstrates commendable performance, the underlying challenge remains: can a model truly understand traffic patterns, or merely approximate them with sufficient fidelity? The multimodal approach is a logical progression, acknowledging that packets are but one facet of a complex interaction, yet it introduces the problem of effective feature integration – what constitutes meaningful correlation amidst the noise?
Further refinement will likely necessitate a shift from purely accuracy-focused metrics to those that better reflect operational cost – the energy expenditure of inference, the latency introduced by complex models, and the resilience to adversarial manipulation. The framework’s success in online systems is encouraging, but scaling such deployments introduces new pressures. The label distribution-aware fine-tuning represents a pragmatic step, but the very act of labeling implies a predefined categorization – a constraint that may ultimately limit the system’s adaptability.
The elegance of any such system lies not in its immediate capabilities, but in its capacity to degrade gracefully. Good architecture is invisible until it breaks, and only then is the true cost of decisions visible.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.21792.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- TON PREDICTION. TON cryptocurrency
- 2025 Crypto Wallets: Secure, Smart, and Surprisingly Simple!
- The 11 Elden Ring: Nightreign DLC features that would surprise and delight the biggest FromSoftware fans
- 10 Hulu Originals You’re Missing Out On
- 17 Black Voice Actors Who Saved Games With One Line Delivery
- Is T-Mobile’s Dividend Dream Too Good to Be True?
- The Gambler’s Dilemma: A Trillion-Dollar Riddle of Fate and Fortune
- Walmart: The Galactic Grocery Giant and Its Dividend Delights
- Gold Rate Forecast
- ‘A Charlie Brown Thanksgiving’ Tops Apple TV+’s Top 10 Most-Watched Movies List This Week
2026-02-01 23:24