Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new framework leverages the power of artificial intelligence to create more customized, sustainable, and equitable urban plans.
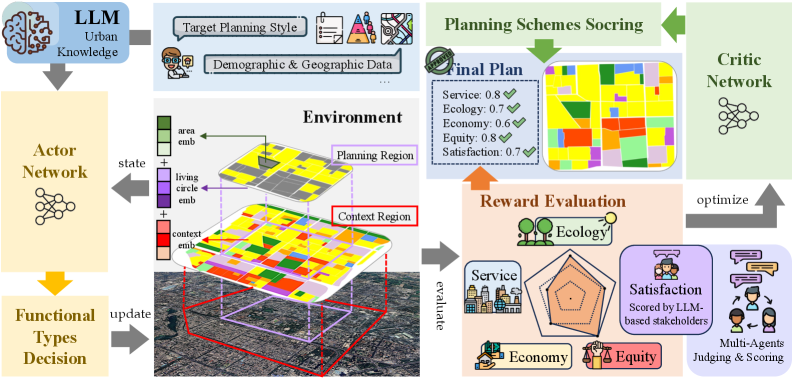
This paper presents Intelli-Planner, a system combining Large Language Models and Deep Reinforcement Learning for enhanced urban functional area allocation and participatory planning.
Effective urban planning often struggles to balance expert knowledge with participatory input, leading to time-consuming processes and potentially inequitable outcomes. This paper introduces ‘Intelli-Planner: Towards Customized Urban Planning via Large Language Model Empowered Reinforcement Learning’, a novel framework integrating Deep Reinforcement Learning and Large Language Models to generate optimized and customized urban plans. Through the incorporation of demographic data, planning preferences, and an LLM-based stakeholder evaluation system, Intelli-Planner surpasses traditional methods in both objective metrics and stakeholder satisfaction. Could this approach represent a paradigm shift towards more sustainable, equitable, and responsive urban design processes?
The Entangled Web of Modern Urbanism
Urban planning historically faced relatively contained challenges, but contemporary cities present a web of interconnected issues that defy simple solutions. Planners now grapple with simultaneously maximizing economic growth, ensuring environmental sustainability, and promoting social equity – objectives often in direct conflict. This complexity is compounded by increasingly diverse stakeholder groups, each with unique priorities and demands, ranging from developers and environmental advocates to local residents and transportation authorities. Successfully navigating these competing interests requires a shift away from traditional, siloed approaches toward integrated strategies capable of accommodating multiple objectives and fostering collaborative decision-making – a task proving exceptionally difficult given the inherent trade-offs and the dynamic nature of urban environments.
Conventional approaches to urban planning frequently stumble when attempting to simultaneously prioritize economic growth, environmental health, and social equity. Historically, development has often proceeded with a primary focus on financial returns, leading to ecological degradation and displacement of vulnerable populations. Conversely, purely conservation-focused planning can stifle economic opportunity and limit access to essential resources for residents. The inherent complexity lies in the interconnectedness of these objectives; a project that boosts the economy may simultaneously harm the environment or exacerbate existing inequalities. Consequently, many urban centers grapple with issues like pollution, resource scarcity, and widening socioeconomic gaps, demonstrating the limitations of planning models that fail to acknowledge and address these competing, yet crucial, considerations as a unified system.
Contemporary urban planning increasingly relies on sophisticated modeling and simulation tools to address the inherent trade-offs between competing priorities. These tools move beyond static, single-outcome projections, instead offering dynamic scenarios that visualize the consequences of various development choices on factors like traffic flow, environmental impact, and social equity. Crucially, successful implementation demands systems capable of incorporating real-time data – from citizen feedback platforms to sensor networks monitoring resource consumption – enabling planners to adapt strategies in response to evolving community needs and unforeseen circumstances. This iterative approach, facilitated by advanced analytical capabilities, allows for a more responsive and resilient urban environment, moving away from rigid master plans towards flexible frameworks that prioritize long-term sustainability and inclusive growth.
The Algorithmic City: Introducing IntelliPlanner
IntelliPlanner is a computational framework designed to automate and optimize multiple facets of urban planning through the integration of Reinforcement Learning (RL) and Large Language Models (LLMs). The RL component enables the exploration of diverse planning scenarios and the iterative refinement of schemes based on defined reward functions, effectively navigating the complex solution space inherent in urban development. Simultaneously, LLMs process and interpret large volumes of data, including zoning regulations, demographic information, and infrastructure details, providing contextual understanding for the RL agent. This synergistic approach allows IntelliPlanner to move beyond traditional, manual planning processes, potentially identifying more efficient, sustainable, and equitable urban designs.
IntelliPlanner’s capacity to explore a vast solution space is achieved through the iterative process of Reinforcement Learning, where the framework evaluates numerous urban planning schemes based on simulated outcomes. This exploration, combined with the predictive capabilities of Large Language Models, allows IntelliPlanner to forecast the impact of different designs on various stakeholders. The framework quantifies stakeholder satisfaction through defined metrics, enabling a comparative analysis of proposed schemes. By repeatedly generating, evaluating, and refining plans, IntelliPlanner identifies those schemes predicted to yield the highest aggregate stakeholder satisfaction, exceeding the limitations of manual planning processes which are often constrained by resource limitations and cognitive biases.
IntelliPlanner integrates stakeholder preferences through a multi-stage process involving direct input mechanisms and preference modeling. Initial data collection utilizes surveys, public forums, and existing demographic information to establish a baseline of community needs. This raw data is then processed using Natural Language Processing techniques to extract key themes and prioritize concerns. A utility function is constructed, weighting these preferences based on frequency and stated importance, and this function serves as a core component of the Reinforcement Learning reward system. During scheme evaluation, IntelliPlanner explicitly optimizes for outcomes that maximize the calculated utility, ensuring that plans align with stated community priorities and effectively address identified needs. This process allows for iterative refinement of plans based on ongoing stakeholder feedback, further solidifying the prioritization of community needs.
The Logic of Reward and Policy: How IntelliPlanner Learns
The IntelliPlanner system utilizes a RewardFunction to numerically represent diverse planning goals, encompassing both qualitative and quantitative objectives. This function assigns scalar values to different outcomes, allowing the system to evaluate the effectiveness of various land use and resource management strategies. Specifically, the RewardFunction integrates metrics related to service accessibility – such as proximity to essential amenities – with indicators of ecological health, including biodiversity levels and habitat connectivity. The resulting aggregated score provides a unified measure of plan performance, enabling optimization algorithms to prioritize solutions that effectively balance competing objectives like economic development and environmental preservation. The function’s design allows for weighted contributions from each metric, providing flexibility in tailoring the system’s priorities to specific regional contexts and stakeholder values.
The RewardFunction within IntelliPlanner directly influences the learning process of the DRLPolicyNetwork by providing scalar values that represent the desirability of different land use allocation and resource management outcomes. This feedback signal enables the policy network to iteratively adjust its decision-making process, strengthening actions that yield higher rewards and discouraging those that result in lower rewards. Consequently, the DRLPolicyNetwork learns to identify and implement policies that effectively balance competing objectives as defined by the RewardFunction, optimizing for desired land use patterns and resource distribution strategies.
The Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm is employed as the training method for the DRLPolicyNetwork due to its efficiency in high-dimensional action spaces and its stability during learning. PPO is a policy gradient method that iteratively improves the policy by taking small steps to avoid drastic changes that could destabilize training. Crucially, IntelliPlanner leverages PPO within a MultiObjectiveOptimization framework, enabling the policy network to concurrently optimize for multiple, potentially conflicting, objectives – such as maximizing service provision while minimizing environmental impact. This is achieved by formulating a scalarized reward function, or by utilizing techniques like Pareto optimization to identify a set of non-dominated solutions representing the best trade-offs between objectives.
LLMKnowledgeEnhancement integrates data from Large Language Models to improve the DRLPolicyNetwork’s comprehension of complex urban systems. This process involves incorporating LLM-derived insights regarding factors such as population density, transportation networks, zoning regulations, and socioeconomic conditions. By supplementing the policy network’s training data with this contextual information, the system achieves a more nuanced understanding of urban dynamics and constraints, leading to improved land use allocation and resource management decisions. Specifically, LLM outputs are transformed into quantifiable features that are then used to augment the state representation provided to the policy network during training and inference.

Towards Resilient Futures: The Impact of IntelliPlanner
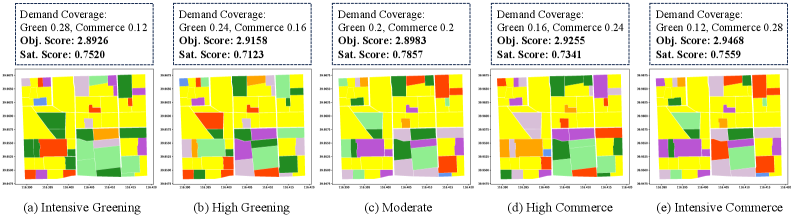
IntelliPlanner presents a novel approach to urban development focused on maximizing accessible green spaces and, consequently, enhancing the quality of life for city dwellers. The framework systematically integrates environmental considerations into the planning process, moving beyond traditional methods that often prioritize economic factors. By intelligently allocating land and resources, IntelliPlanner facilitates the creation of more parks, gardens, and natural areas within urban landscapes. This increased GreenSpaceCoverage isn’t merely aesthetic; it directly correlates with improved air quality, reduced urban heat island effects, and increased opportunities for recreation and social interaction, fostering healthier and more vibrant communities. The system’s capacity to balance competing urban needs ensures that green space expansion doesn’t come at the expense of essential infrastructure or economic development, but rather complements it for a truly sustainable and equitable urban future.
IntelliPlanner operates on the principle that truly sustainable urban development necessitates a holistic approach, moving beyond single-objective optimization. The framework actively balances competing priorities – such as maximizing green space, ensuring affordable housing, and optimizing transportation networks – to avoid inadvertently disadvantaging certain communities. This systematic balancing isn’t merely about compromise; it’s about identifying synergistic solutions that enhance overall well-being. By considering a multitude of factors simultaneously, IntelliPlanner aims to distribute resources and opportunities more equitably, fostering inclusive growth and reducing disparities in access to essential services and amenities. The result is urban planning that doesn’t just improve aggregate scores, but actively works to uplift all residents and create a more just and livable city for everyone.
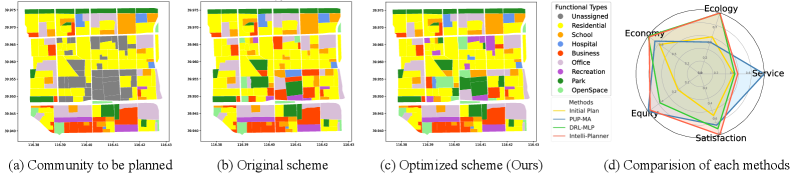
A compelling demonstration of IntelliPlanner’s efficacy occurred within the Beijing community, where the AI-driven framework yielded a substantial 44.63% increase in overall score when contrasted with previously established, human-designed urban plans. This improvement wasn’t simply theoretical; the scoring system comprehensively evaluated key metrics related to GreenSpaceCoverage, equitable resource allocation, and quality of life indicators. The significant gain suggests that IntelliPlanner’s systematic approach to balancing competing urban objectives-such as maximizing green spaces while optimizing infrastructure-outperforms conventional planning methodologies. This result highlights the potential for artificial intelligence to not only streamline the urban planning process but also to generate demonstrably superior outcomes for city residents and the environment.
Evaluations across diverse urban landscapes reveal the broad applicability of IntelliPlanner, demonstrating substantial gains in overall urban planning effectiveness. In Chicago, the framework achieved a 31.65% increase in total score when compared to existing planning schemes, signifying marked improvements in areas like resource allocation and community well-being. Similarly, implementation in Madrid yielded a significant 27.07% increase, highlighting the system’s ability to adapt to varying city structures and priorities. These results, obtained through rigorous testing in geographically and culturally distinct communities, suggest that IntelliPlanner is not merely a localized solution, but a potentially transformative tool for urban development worldwide.
Rigorous evaluation of the IntelliPlanner framework across three major global cities – Beijing, Chicago, and Madrid – reveals substantial gains in urban planning efficacy when contrasted with traditional methods. Specifically, the framework achieved a quantifiable 5.40% improvement in its objective score within the Beijing community, indicating a more optimized allocation of resources and enhanced urban functionality. While gains varied across locations reflecting unique urban complexities, Chicago experienced a 1.64% increase, and Madrid demonstrated a 3.92% improvement. These results, consistently observed across diverse urban landscapes, suggest that IntelliPlanner provides a demonstrably superior approach to urban development, moving beyond subjective assessments to deliver measurable improvements in city planning outcomes.
IntelliPlanner represents a shift in urban development, offering planners a powerful toolkit for data-driven decision-making. By leveraging artificial intelligence, the framework analyzes complex urban systems and identifies optimal strategies for balancing competing priorities – from maximizing green spaces to ensuring equitable resource allocation. This isn’t about replacing human expertise, but rather augmenting it with objective insights derived from vast datasets, allowing for more informed and effective planning. The result is a move towards cities that are not only more sustainable and environmentally responsible, but also demonstrably more resilient in the face of future challenges, ultimately fostering improved quality of life for all residents through strategically optimized urban landscapes.
IntelliPlanner represents a fundamental shift in urban development, moving beyond traditional, often siloed, planning approaches towards a holistic and integrated system. The framework’s capacity to simultaneously optimize for economic vitality and environmental sustainability positions it as a key tool for future city design. By leveraging artificial intelligence, it facilitates the creation of urban spaces that not only foster economic growth and opportunity, but also prioritize ecological health and resource management. This convergence of objectives promises cities that are demonstrably more resilient, equitable, and capable of adapting to the challenges of a changing world, ultimately redefining the standards for responsible and forward-thinking urban planning.
The pursuit of optimized urban landscapes, as detailed within Intelli-Planner, echoes a fundamental truth about complex systems. It isn’t about imposition of will, but about nurturing potential. As Grace Hopper observed, “It’s easier to ask forgiveness than it is to get permission.” This sentiment applies directly to the iterative process of reinforcement learning; the system learns through experimentation, occasionally charting unforeseen paths. The framework doesn’t dictate a perfect city, but rather proposes possibilities, adapting and refining its approach based on the ‘confessions’ logged from stakeholder interactions and the ‘revelations’ gleaned from the resulting designs. The system, like any living ecosystem, will inevitably reveal imperfections, but it is through these explorations that true growth – and sustainable, equitable urban planning – takes root.
What Lies Ahead?
The deployment of Intelli-Planner, or systems like it, isn’t a solution, but a carefully constructed prelude to new categories of urban problems. The framework optimizes for stated goals – sustainability, equity – but those are moving targets, defined by stakeholders who themselves are subject to change. Each iteration of the model learns not just optimal city layouts, but also enshrines the biases and priorities of its current participants. The system will inevitably amplify those biases, creating legible, quantifiable patterns of inequity, even while striving for the opposite.
The real challenge isn’t better algorithms, but better documentation of failure. No one writes prophecies after they come true, and the inevitable compromises, unforeseen consequences, and outright errors embedded within these systems will accumulate faster than any corrective action. The value won’t be in predicting the future, but in creating auditable trails of how the system arrived at its current, flawed state.
Future work will likely focus on ‘explainable AI’ – a term that implicitly acknowledges the black box it attempts to illuminate. But perhaps the more pressing question isn’t ‘why did the system do this?’, but ‘what new constraints will be necessary to contain the fallout?’. The city, after all, is not a problem to be solved, but a system to be perpetually managed – and each deploy is a small apocalypse.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.21212.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- TON PREDICTION. TON cryptocurrency
- 2025 Crypto Wallets: Secure, Smart, and Surprisingly Simple!
- 10 Hulu Originals You’re Missing Out On
- The 11 Elden Ring: Nightreign DLC features that would surprise and delight the biggest FromSoftware fans
- 17 Black Voice Actors Who Saved Games With One Line Delivery
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Is T-Mobile’s Dividend Dream Too Good to Be True?
- The Gambler’s Dilemma: A Trillion-Dollar Riddle of Fate and Fortune
- Walmart: The Galactic Grocery Giant and Its Dividend Delights
- Is Kalshi the New Polymarket? 🤔💡
2026-02-01 04:58