Author: Denis Avetisyan
A new forensic approach leverages subtle inconsistencies in AI-created videos to reliably distinguish them from authentic footage.

Researchers demonstrate a framework based on ‘Manifold Projection Fluctuations’ to detect forgeries by analyzing residual patterns and temporal inconsistencies.
Despite rapid advances in generative AI, distinguishing between authentic and synthetic video remains a critical challenge as macro-level artifacts diminish. This work, ‘MPF-Net: Exposing High-Fidelity AI-Generated Video Forgeries via Hierarchical Manifold Deviation and Micro-Temporal Fluctuations’, addresses this by positing that AI-generated videos, unlike physical recordings, exhibit inherent ‘Manifold Projection Fluctuations’ (MPF) in their residual frames. Our novel framework leverages a hierarchical dual-path approach to detect these subtle, structured patterns-spatial anomalies and micro-temporal inconsistencies-even in visually flawless forgeries. Can these low-level computational fingerprints provide a robust foundation for reliable forensic analysis in an era of increasingly realistic synthetic media?
The Illusion of Authenticity: When Seeing Isn’t Believing
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence has ushered in a new era of video creation, with models like Sora2, Veo, and Wan capable of generating strikingly realistic content. This proliferation of high-fidelity synthetic media presents a growing challenge to conventional methods of verifying authenticity; discerning between genuine footage and AI-generated simulations is becoming increasingly difficult, even for experts. These models don’t simply stitch together existing clips, but create entirely new scenes with nuanced details, mimicking human movement, lighting, and camera work with unprecedented accuracy. Consequently, the very foundation of visual evidence is being questioned, demanding innovative approaches to media forensics and raising critical concerns about the potential for manipulation and deception in the digital realm.
Established techniques for verifying the authenticity of digital media are rapidly becoming obsolete in the face of increasingly sophisticated AI video generation. Previously reliable forensic methods, such as analyzing compression artifacts or examining subtle inconsistencies in lighting and shadow, are now easily circumvented by models capable of producing remarkably realistic synthetic content. These advanced generators effectively mimic the nuances of real-world video, making it exceedingly difficult to identify telltale signs of manipulation. Consequently, researchers are actively developing novel detection strategies, focusing on identifying unique “fingerprints” embedded within the generated content-perhaps tracing characteristics of the AI’s underlying architecture or searching for subtle statistical anomalies imperceptible to the human eye-to counteract this growing threat to media integrity.
The increasing sophistication of synthetic media presents profound risks extending far beyond simple deception. The ability to fabricate realistic video and audio carries significant implications for societal trust, potentially eroding faith in established institutions and journalistic integrity. Nation-state actors and malicious groups could leverage these technologies to create and disseminate disinformation campaigns, influencing elections, inciting social unrest, or damaging international relations. Furthermore, the creation of “deepfake” evidence poses a severe threat to legal proceedings and personal reputations, as fabricated content could be used to falsely accuse individuals or manipulate investigations. Beyond these broad societal impacts, national security concerns are heightened by the potential for synthetic media to be used in espionage, blackmail, or the creation of convincing propaganda, demanding urgent development of robust detection and verification technologies to safeguard against these emerging threats.

Pruning the Noise: A Two-Step Approach to Reality Checks
The detection framework utilizes a two-stage process to identify synthetic videos. Initially, a fidelity assessment determines if a video generally conforms to the characteristics of real-world footage. Samples failing this initial assessment are flagged as off-manifold. Subsequently, videos passing the fidelity check undergo a micro-temporal fluctuation analysis, scrutinizing subtle inconsistencies in frame-to-frame changes that may indicate manipulation. This sequential approach prioritizes efficient pruning of clearly synthetic content before applying computationally intensive analysis to potentially more realistic, yet still fabricated, videos.
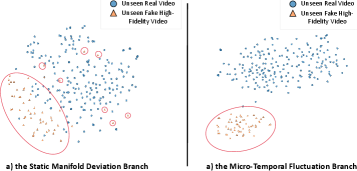
The Static Manifold Deviation Branch utilizes Large-Scale Vision Foundation Models (VFMs), specifically PE Core and MetaCLIP-v2, to determine if a video deviates from the expected distribution of authentic footage. These VFMs are trained on extensive datasets of real-world videos, enabling them to assess the fidelity of input content and identify synthetic or manipulated samples. Performance metrics indicate a 97% accuracy rate in correctly identifying and filtering (“pruning”) videos that fall outside this established manifold of realistic content, thereby significantly reducing the need for more computationally intensive analysis on likely synthetic samples.
The Static Manifold Deviation Branch functions as a primary filter, significantly decreasing the number of videos requiring detailed analysis. By leveraging Large-Scale Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) to identify out-of-distribution samples with 97% accuracy, this stage proactively removes a substantial portion of synthetic content before it reaches the more computationally intensive micro-temporal fluctuation analysis. This pre-screening process demonstrably lowers the overall processing demands, allowing for more efficient resource allocation and reduced latency in detecting manipulated videos.

Unmasking the Machine: Pinpointing Micro-Temporal Artifacts
The Micro-Temporal Fluctuation (MTF) branch centers on the analysis of Manifold Projection Fluctuations (MPF) present in AI-generated video content. These fluctuations represent inherent inconsistencies within the temporal structure of the video, arising from the generative process. Unlike traditional video artifacts that manifest as spatial distortions or noise, MPF relate specifically to discontinuities and inconsistencies in how frames transition over time. The underlying principle is that AI generation, while increasingly sophisticated, does not perfectly replicate the continuous, coherent temporal dynamics of naturally captured video, leading to detectable fluctuations in the projected manifold of video frames. Analysis of these MPF forms the basis for identifying AI-generated content by exploiting these subtle, but measurable, temporal inconsistencies.
The Micro-Temporal Fluctuation branch employs a multi-faceted approach to artifact extraction, beginning with Optical Flow analysis to quantify motion vectors between consecutive frames. This data is then subjected to Frequency Domain Analysis, specifically Discrete Fourier Transforms, to identify inconsistencies in the video’s spectral components that deviate from natural video patterns. To model the temporal dependencies within the extracted features, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are utilized; these recurrent neural networks are trained to recognize subtle, frame-to-frame inconsistencies that indicate AI-generated content. Quantification involves calculating metrics derived from these analyses, allowing for a numerical representation of the artifact presence and severity, facilitating automated detection and classification.
The framework analyzes AI-generated videos by calculating Frame Residuals and Normalized Residuals to detect inconsistencies indicative of artificial creation. Frame Residuals are determined by subtracting consecutive frames, highlighting motion differences, while Normalized Residuals account for varying illumination and contrast, emphasizing textural anomalies. These residuals are then quantified; significant deviations from expected values-characteristic of natural video-reveal inconsistencies in the generated content. The resulting data provides a measurable ‘fingerprint’ of AI generation, as natural videos exhibit more consistent frame-to-frame coherence in both motion and texture compared to synthetically generated content.
Temporal Transformer models enhance the accuracy of micro-temporal artifact detection by effectively modeling long-range dependencies within video sequences. This approach addresses limitations of methods sensitive to only local frame information. The framework achieves high detection rates, demonstrably correlating with perceived video quality; specifically, higher scores align with fewer visible artifacts and improved visual fidelity. Analysis indicates the framework is particularly effective at identifying inconsistencies during the initial stages of AI video generation, a period often characterized by increased instability and more prominent temporal artifacts, thereby strengthening its overall reliability.
Beyond the Benchmarks: Implications for a World of Synthetic Realities
A highly effective strategy for discerning AI-generated videos from authentic content centers on a two-pronged approach: fidelity screening and manipulation pattern fingerprinting (MPF) analysis. Initial fidelity screening quickly identifies videos exhibiting the telltale signs of artificial creation – inconsistencies in lighting, unnatural textures, or subtle artifacts often introduced during the generation process. However, increasingly sophisticated AI can produce remarkably realistic outputs that bypass these initial checks. This is where MPF analysis proves critical, moving beyond surface-level realism to examine the underlying structural inconsistencies – the unique ‘fingerprint’ of the AI generator itself. By combining these techniques, the system not only achieves higher detection rates but also significantly reduces false positives, ensuring that genuine videos are not incorrectly flagged as synthetic, and establishing a more reliable foundation for digital forensics.
Authenticity assessment in video forensics often relies on identifying subtle inconsistencies introduced during AI generation, but a comprehensive evaluation necessitates considering the inherent qualities of the video itself. Researchers developed a Composite Quality Score that moves beyond isolated artifact detection by integrating metrics such as frames per second (FPS), bitrate, and spatial resolution. This holistic approach acknowledges that realistic AI-generated content will increasingly mask traditional forgery indicators, demanding a nuanced understanding of the video’s technical characteristics. By analyzing these fundamental properties, the framework establishes a baseline for expected quality, allowing for more accurate identification of anomalies and a reduction in false positives – ultimately providing a robust measure of whether a video aligns with the characteristics of genuine content.
The developed framework demonstrates a significant advancement in AI-generated video detection, achieving state-of-the-art results on the challenging GenVideo benchmark. Crucially, the system excels at identifying high-fidelity on-manifold forgeries – those AI-generated videos that closely mimic real footage, making them particularly difficult to discern. This superior performance stems from the combined approach of fidelity screening and manipulation pattern analysis, enabling more accurate identification of subtle inconsistencies. Comparative evaluations consistently show the system outperforming existing methods, indicating a substantial leap forward in the field and offering a robust defense against increasingly sophisticated AI-powered disinformation campaigns. This capability is vital as generative models continue to produce increasingly realistic content, blurring the lines between authentic and synthetic media.
Continued development of this forensic framework prioritizes proactive adaptation to the evolving landscape of AI-generated content. Researchers aim to refine the system’s ability to detect increasingly subtle and sophisticated forgeries produced by future AI generators, anticipating advancements in generative models. Beyond video analysis, efforts are underway to expand the framework’s capabilities to encompass other crucial modalities, notably audio. This multi-modal approach seeks to establish a more comprehensive assessment of digital authenticity by integrating cues from both visual and auditory data, ultimately bolstering the system’s resilience against increasingly complex and deceptive AI-driven manipulations.
The advancements in automated forgery detection presented by this research extend far beyond technical benchmarks, carrying substantial weight in the broader societal context of digital information. As AI-generated content becomes increasingly realistic and pervasive, the ability to reliably distinguish authentic media from manipulated content is paramount to safeguarding public trust and countering the spread of misinformation. This work directly addresses the growing threat of deceptive media, offering tools to verify the integrity of videos and potentially mitigate the damage caused by malicious actors. Furthermore, by enabling more accurate detection of AI-generated forgeries, this framework supports the responsible development and deployment of artificial intelligence technologies, fostering a digital landscape where innovation and trustworthiness can coexist and promoting a future where the authenticity of information is more readily assured.

The pursuit of ever-more-realistic AI-generated video, as this paper details with its focus on ‘Manifold Projection Fluctuations’, feels predictably Sisyphean. It’s a constant escalation; refine the forgery, refine the detection, repeat ad nauseam. As Geoffrey Hinton once observed, “The problem with deep learning is that it’s a black box.” This feels particularly apt here. Researchers chase artifacts – these subtle MPF deviations – in a system they barely understand, hoping to catch the ghosts in the machine before someone figures out how to exorcise them. One anticipates a future where these ‘reliable’ detection methods are, inevitably, circumvented, and the cycle begins anew. Production, as always, will validate-or invalidate-the theory.
What’s Next?
The pursuit of reliably identifying AI-generated video will inevitably resemble an escalating arms race. This work, focusing on manifold projection fluctuations and temporal inconsistencies, offers a momentary advantage – a slightly more robust set of features to exploit. However, it’s a safe prediction that future generative models will learn to mimic, and ultimately suppress, these very same artifacts. The current focus on low-level vision, while logical, feels reminiscent of earlier image forensics, where each ‘unforgeable’ watermark eventually succumbed to clever adversarial attacks.
A critical, and often overlooked, challenge lies in deployment. A theoretically perfect detector, capable of flawlessly distinguishing synthetic from real, is useless if it introduces unacceptable latency or fails when faced with the inevitable compression and post-processing applied in the wild. The real-world signal-to-noise ratio will always be far lower than anything achievable in a controlled laboratory setting. If code looks perfect, no one has deployed it yet.
The field should perhaps shift focus. Instead of endlessly refining detection algorithms, a more sustainable approach might involve developing methods to watermark or cryptographically sign generated content at its source. That is, accepting that synthetic media is inevitable, and concentrating on attribution rather than simple binary classification. It’s a less glamorous problem, but likely a more practical one.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.21408.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- 2025 Crypto Wallets: Secure, Smart, and Surprisingly Simple!
- TON PREDICTION. TON cryptocurrency
- 10 Hulu Originals You’re Missing Out On
- The 11 Elden Ring: Nightreign DLC features that would surprise and delight the biggest FromSoftware fans
- 17 Black Voice Actors Who Saved Games With One Line Delivery
- The Gambler’s Dilemma: A Trillion-Dollar Riddle of Fate and Fortune
- American Bitcoin’s Bold Dip Dive: Riches or Ruin? You Decide!
- Gold Rate Forecast
- 📅 BrownDust2 | August Birthday Calendar
- MP Materials Stock: A Gonzo Trader’s Take on the Monday Mayhem
2026-01-31 17:04