Author: Denis Avetisyan
Researchers have unveiled MarketGen, a scalable simulation environment designed to train and evaluate robots in realistic, automatically generated supermarket scenarios.
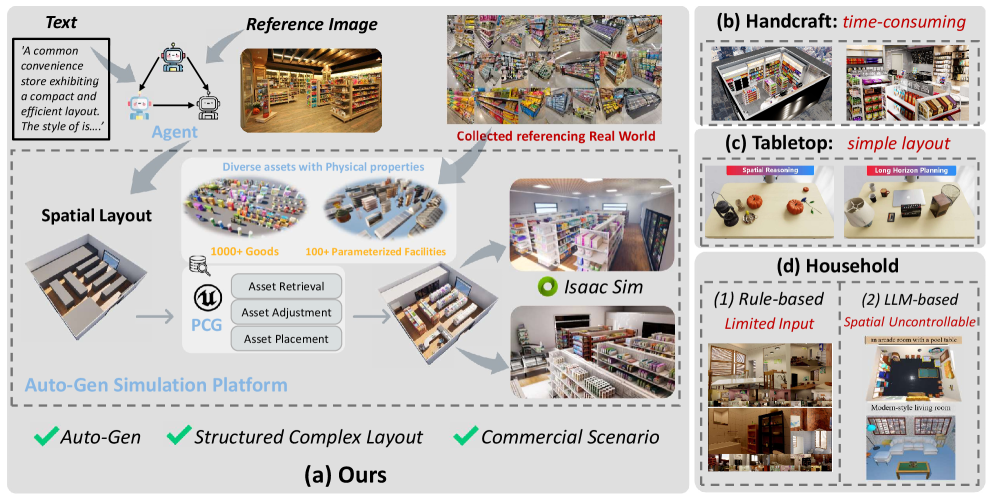
MarketGen combines procedural content generation and agent-based systems to create diverse and challenging environments for sim-to-real transfer in robotic manipulation and embodied AI.
Despite advances in embodied AI, a critical lack of realistic and scalable environments hinders the development of agents for complex commercial settings. To address this gap, we introduce MarketGen: A Scalable Simulation Platform with Auto-Generated Embodied Supermarket Environments, a novel platform leveraging agent-based procedural content generation to automatically create diverse and detailed supermarket scenes. This enables the training and evaluation of robotic agents-from cashier systems completing long-horizon unloading tasks to mobile salespeople navigating aisles-with an accompanying benchmark for assessing performance. Will MarketGen accelerate progress towards deploying robust, commercially-viable embodied AI systems in real-world retail environments?
The Challenge of Realism: Bridging the Simulation Gap
Contemporary artificial intelligence frequently encounters difficulties when operating within the chaotic reality of complex, unstructured environments-a typical supermarket serves as a prime example. Unlike the controlled conditions of many training scenarios, these spaces present a constantly shifting array of obstacles, unpredictable human behavior, and a vast number of potential interactions. This necessitates a significant advancement in simulation fidelity; current models often simplify these environments to a degree that hinders an agent’s ability to generalize to the real world. To truly navigate such spaces, AI must move beyond recognizing static objects and begin to understand dynamic relationships, anticipate occlusions, and adapt to unforeseen circumstances-a level of complexity demanding substantial computational resources and innovative algorithmic approaches.
The creation of convincingly realistic virtual environments for artificial intelligence training presents a significant computational bottleneck. Detailed simulations, encompassing accurate physics, diverse object interactions, and nuanced lighting, demand substantial processing power and lengthy rendering times. Each iteration of environment design and modification requires considerable resources, slowing down the development cycle and limiting the number of scenarios an AI agent can experience before real-world deployment. This expense isn’t merely about graphical fidelity; it extends to modeling the unpredictable behaviors of crowds, the variations in product placement within a store, or even the subtle imperfections of everyday objects – all of which contribute to a truly robust and generalizable AI, but at a considerable cost in time and computational resources.
The creation of truly adaptable artificial intelligence hinges on exposure to a breadth of experiences, yet current training resources often fall short. Existing datasets and simulated environments, while valuable, frequently lack the sheer scale and diversity necessary for developing agents capable of generalizing to unpredictable real-world scenarios. An agent trained solely on a limited set of virtual supermarkets, for instance, may struggle when confronted with the nuanced layouts, product arrangements, and human behaviors present in an actual store. This gap between simulation and reality necessitates the development of significantly larger and more varied datasets, encompassing a wide range of environments, object variations, and interaction dynamics, to foster the robustness and adaptability required for successful deployment of embodied AI in complex, unstructured settings. Without this expanded training ground, agents risk becoming brittle and unreliable when faced with the infinite variability of the real world.
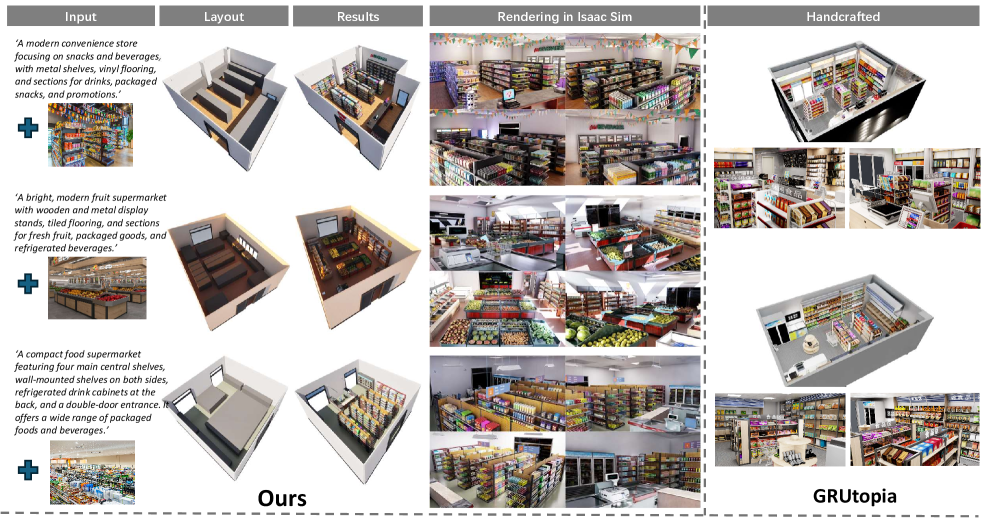

MarketGen: Automated Scene Generation for Scalable Training
MarketGen employs an Agent-Based Procedural Content Generation (PCG) framework to automatically create diverse supermarket layouts. This system operates by defining multiple autonomous agents, each responsible for specific aspects of the layout, such as aisle creation, shelving arrangement, and product categorization. The interactions between these agents, governed by predefined rules and constraints, result in a dynamically generated environment. This approach contrasts with static or manually designed layouts by enabling the creation of a virtually limitless number of unique supermarket configurations, each exhibiting variation in size, shape, and product distribution. The agent-based method ensures realism by simulating the practical considerations of supermarket design, such as accessibility, flow of traffic, and efficient space utilization.
MarketGen employs a dual-agent system to construct realistic supermarket environments. Semantic Agents are responsible for product categorization and placement based on real-world retail strategies – for example, grouping complementary items or positioning high-margin goods for maximum visibility. Simultaneously, Spatial Agents define the functional zones within the supermarket – including produce, dairy, bakery, and dry goods sections – and manage aisle layouts to ensure navigability and accessibility. These agents operate in concert, with the semantic decisions influencing spatial arrangements and vice versa, resulting in coherent and logically organized supermarket layouts that simulate authentic retail spaces.
The Reflection & Refiner Module within MarketGen employs an iterative process to enhance the quality of generated supermarket layouts. This module assesses layouts based on two primary criteria: realism and agent accessibility. Realism is evaluated through metrics such as shelf arrangement plausibility and adherence to typical supermarket zoning. Agent accessibility refers to the ability of simulated agents – used for AI training – to navigate the layout efficiently and reach designated product locations. The module utilizes a feedback loop, adjusting parameters within the procedural generation framework based on these evaluations to progressively refine the layout until pre-defined performance thresholds for both realism and accessibility are met. This iterative refinement process ensures the generated environments are not only visually plausible but also functionally suitable for training AI models.
MarketGen incorporates a 3D asset library comprising over three thousand unique models, including individual grocery items, packaging variations, and complete store fixtures. These assets are parameterized, allowing for adjustments to properties such as color, size, and material to increase visual diversity within generated scenes. The library also includes parameterized facilities – complete sections like produce displays, bakery counters, and refrigerated units – enabling the system to rapidly construct complete supermarket environments. This approach significantly reduces the reliance on manually created content and enables the generation of visually rich and varied training data for AI models.

Empowering Mobile Manipulation: Validating Performance on a Benchmark
MarketGen was evaluated through agent training on the Supermarket Benchmark, specifically addressing the tasks of Checkout Unloading and In-Aisle Item Collection. This benchmark presents a complex environment requiring agents to navigate a simulated supermarket, identify target items, and manipulate them to designated locations. Training focused on enabling agents to successfully perform these tasks within the simulation, providing a platform to assess the efficacy of the system’s components – including perception, planning, and manipulation – in a realistic, yet controlled, setting. Performance on these tasks served as a primary indicator of the system’s ability to handle the challenges inherent in real-world mobile manipulation scenarios.
The mobile manipulation system leverages Gemini-2.5-Pro as its core reasoning engine, integrated with AnyGrasp for grasp pose generation and Set-of-Mark (SoM) for task specification. This architecture facilitates execution of complex manipulation tasks; however, initial evaluations demonstrate a limited success rate. Specifically, across tested scenarios, the system achieved a less than 15% success rate when solely driven by Gemini-2.5-Pro, indicating substantial room for improvement in robustness and task completion despite the advanced capabilities of the underlying components.
The system integrates the Segment Anything Model (SAM) for robust scene understanding, enabling the identification and segmentation of objects within the environment. This segmentation data is then utilized by cuRobo, a framework designed for efficient motion planning and control of robotic manipulators. Specifically, cuRobo leverages the identified object segments to generate collision-free trajectories and execute grasping actions. The combination of SAM and cuRobo facilitates the perception and manipulation capabilities necessary for complex tasks, reducing the computational burden associated with both scene analysis and path planning.
Affordance prediction model performance demonstrated a strong correlation between simulated and real-world environments, suggesting successful sim-to-real transfer capabilities. This correlation was evaluated through 20 grasp experiments conducted for each of four distinct object shapes in both simulation and the physical world. Data collected from these experiments indicates a statistically significant relationship between the model’s predictive accuracy in simulation and its success rate when applied to real-world grasping tasks, validating the effectiveness of the simulation environment for training and evaluating manipulation algorithms.

Scaling and Generalizing Intelligence: A Future Unbound
The rapid advancement of embodied artificial intelligence hinges on access to extensive and varied training data, and MarketGen addresses this critical need through its inherent scalability. This platform isn’t limited by the constraints of real-world data collection; instead, it procedurally generates countless unique scenarios, effectively creating a virtually limitless dataset for AI agents to learn from. This ability to produce data at scale dramatically accelerates the training process, allowing developers to move beyond painstakingly curated datasets and towards continuously learning agents. The resulting AI benefits from exposure to a far wider range of situations, leading to increased robustness, improved generalization to novel environments, and ultimately, more capable robotic systems. By overcoming the data bottleneck, MarketGen paves the way for AI agents that can reliably operate and adapt in the complexities of the real world.
The ability of an artificial intelligence agent to perform well in novel situations hinges on its exposure to a sufficiently varied training ground. MarketGen addresses this challenge through procedural generation, a technique that automatically creates a virtually limitless range of environments and object arrangements. Rather than relying on a fixed set of pre-designed scenarios, the platform dynamically constructs new challenges, varying factors like room layouts, object positions, and lighting conditions. This constant diversification prevents the AI from overfitting to specific training examples and fosters a more robust understanding of the physical world. Consequently, agents trained within MarketGen demonstrate improved generalization capabilities, allowing them to adapt and succeed in previously unseen environments – a critical step towards deploying AI in real-world applications where predictability is limited.
The utility of MarketGen is significantly enhanced through Parameterized Shelving, a system that expands the platform’s 3D asset library with customizable shelving units. This allows for the automated generation of a virtually limitless range of environments, differing in shelf height, depth, material, and object arrangement. Critically, this dynamic configuration isn’t merely aesthetic; it directly impacts task variation for AI agents. An agent trained to retrieve an item from a shelf in one configuration will be compelled to adapt its manipulation strategies when faced with a differently arranged shelf, fostering robust generalization capabilities. By programmatically altering the environment’s complexity and the spatial relationships between objects, Parameterized Shelving provides a powerful mechanism for creating challenging and diverse training scenarios, pushing the boundaries of what embodied AI agents can learn and achieve.
The convergence of high-fidelity simulation, sophisticated manipulation algorithms, and readily available, large-scale datasets is poised to unlock substantial advancements in the fields of embodied artificial intelligence and robotics. By providing a virtual proving ground for complex tasks, realistic simulation allows agents to learn and refine their skills without the constraints – and costs – of real-world experimentation. This, coupled with algorithms designed for precise object handling and interaction, enables robots to perform increasingly intricate maneuvers. Crucially, the ability to train these systems on datasets of immense size – generated through procedural methods like those offered by MarketGen – fosters robust generalization, allowing agents to adapt and excel in novel and unpredictable environments, ultimately bridging the gap between virtual training and real-world performance.

The development of MarketGen exemplifies a pursuit of essentiality. The platform distills the complexities of a real-world supermarket into a manageable, yet robust, simulation. This mirrors a dedication to removing superfluous elements to reveal core functionality. As John McCarthy aptly stated, “The best way to predict the future is to invent it.” MarketGen isn’t merely replicating an environment; it’s actively constructing a future for embodied AI research, focusing on what truly matters for training and sim-to-real transfer – scalable realism born from procedural generation and agent interaction. The platform’s power lies not in exhaustive detail, but in the purposeful selection of elements crucial for effective agent learning.
Beyond the Aisles
The proliferation of simulation platforms invariably invites a reckoning with what constitutes ‘reality’ for an artificial intelligence. MarketGen, by prioritizing scalable procedural generation, sidesteps some of the intractable complexities of hand-authored environments. Yet, the true test lies not in the volume of virtual shelves, but in the subtle failures exposed when these agents encounter the irreducible messiness of the physical world. The platform’s utility rests on its capacity to expose, rather than conceal, these gaps.
Future iterations should focus less on replicating visual fidelity and more on modeling the inherent uncertainty of real-world interactions. Consider the physics engine not as a source of truth, but as a probabilistic estimate. Robustness will not emerge from perfectly simulated collisions, but from agents capable of adapting to their inevitable imperfections. The pursuit of perfect simulation is a distraction; the useful work lies in building systems that gracefully degrade.
Ultimately, the value of a platform like MarketGen resides in its disposability. The ideal simulation is one that quickly becomes obsolete, superseded by increasingly capable agents that demand ever more nuanced and challenging environments. The platform is not an end in itself, but a temporary scaffolding, destined to be dismantled as its purpose is fulfilled.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2511.21161.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- TON PREDICTION. TON cryptocurrency
- 2025 Crypto Wallets: Secure, Smart, and Surprisingly Simple!
- The 11 Elden Ring: Nightreign DLC features that would surprise and delight the biggest FromSoftware fans
- 10 Hulu Originals You’re Missing Out On
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Walmart: The Galactic Grocery Giant and Its Dividend Delights
- 17 Black Voice Actors Who Saved Games With One Line Delivery
- Is T-Mobile’s Dividend Dream Too Good to Be True?
- Top Actors Of Color Who Were Snubbed At The Oscars
- Is Kalshi the New Polymarket? 🤔💡
2025-11-29 08:56